Types of Forces: Gravity, Friction, and More

2.2 Types of Forces
gravity law of universal gravitation weight friction static friction elastic force tension force compression force normal force sliding friction rolling friction fluid friction
2.2 Types of Forces
Gravity
• Many types of forces act on objects.
• Gravity is an attractive force between all objects that have mass.
Gravity
(cont.)
2.2 Types of Forces
• The ball does not travel in a straight line because of the unbalanced force of gravity acting on it.
2.2 Types of Forces
The Law of Universal Gravitation
• The Law of Universal Gravitation states that all objects with mass are attracted to each other.
• The magnitude of attraction depends on the mass of each object and the distance between them.
2.2 Types of Forces
The Law of Universal Gravitation
(cont.)
• The gravitational force becomes stronger as either or both objects increase in mass or move closer together.
• The gravitational force becomes weaker as either or both objects decrease in mass or move farther apart.
2.2 Types of Forces
Weight and Mass
• Mass is the amount of matter in an object and does not change with location.
• Weight is the gravitational force on a object and changes with location.
• Weight is a force and a vector.
• Weight changes with height above Earth.
2.2 Types of Forces
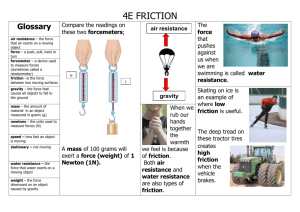
Friction
• Friction is a force that opposes the movement between two surfaces in contact.
• A book pushed across a table slows down because of friction.
• Friction is an unbalanced force acting on the book to slow it down.
2.2 Types of Forces
Static Friction
• Static friction is the force between two surfaces in contact that keeps them from sliding when a force is applied.
• A force is applied to a heavy box, but the box doesn’t move.
• The forces are balanced, the force pushing the box equals the force of static friction pushing in the opposite direction.
2.2 Types of Forces
Sliding Friction
• When the force pushing on the box is larger than the maximum static friction force, the box begins to slide.
• The frictional force that acts on the sliding box is called sliding friction.
2.2 Types of Forces
Sliding Friction
(cont.)
• The book pushed across the table slows down because of sliding friction.
• Without sliding friction, the book would continue moving without a force being applied.
2.2 Types of Forces
Sliding Friction
(cont.)
• Usually friction is present and an unbalancing force must be applied to keep an object moving.
• When friction is greatly reduced, objects move with nearly constant velocity without an applied force.
– Rolling friction
– Smoother surfaces
– Lubricating surfaces
2.2 Types of Forces
Elastic Forces
• An elastic force occurs when a material is stretched or compressed.
• A diving board exerts an upward elastic force on the diver when it is bent downward.
2.2 Types of Forces
Tension
• A tension force is a pulling force exerted by an object when it is stretched, such as a rubber band.
2.2 Types of Forces
Compression
• A compression force is a pushing force exerted by a material when it is squeezed or compressed.
• The size of the compression force exerted by a material is equal to the size of the force that compresses the material.
2.2 Types of Forces
Normal Forces
• A normal force is the force exerted by an object that is perpendicular to the surface of the object.
2.2 Types of Forces
Normal Forces
(cont.)
• The cup is exerting a downward force on the table, caused by gravity.
• The table is exerting an upward normal force on the cup, caused by compression.
Normal Forces
(cont.)
2.2 Types of Forces
Normal Forces
(cont.)
2.2 Types of Forces
2.2 Types of Forces
Forces in the Horizontal Direction
• Friction balances forces applied in a horizontal direction.
• Friction equals the horizontal force on an object that is not changing motion.
2.2 Types of Forces
Forces in the Vertical Direction
• Upward normal force balances the downward force of gravity on an object that is not moving vertically.
2.2 Types of Forces
Forces in the Vertical Direction
(cont.)
2.2 Types of Forces
A(n) ____ force is the force exerted by an object that is perpendicular to the surface of the object.
A compression
B elastic
C normal
D tension
Lesson 2 Review
2.2 Types of Forces
Which force causes a rolling ball to slow down?
A sliding friction
B static friction
C normal force
D gravity
Lesson 2 Review
2.2 Types of Forces
The gravitational force between two objects ____ as ____ increases.
A increases; distance
B decreases; mass
C increases; velocity
D decreases; distance
Lesson 2 Review