Vitamins
advertisement

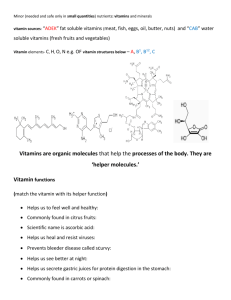
Vitamins are compounds found in food that help regulate body processes. There are two types of vitamins, water soluble and fat-soluble. Water soluble means they can dissolve in water and pass easily into the bloodstream during digestion. The body doesn’t store these vitamins; any unused amounts are removed by the kidneys. Water soluble vitamins include Vitamin C, folic acid and the B vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in body fat for later use. If consumed in large amounts, these vitamins can build up in the body to the point where they become harmful. Fat-soluble vitamins include A, D, E, and K. Water Soluble Vitamins Vitamin B7 (Biotin), also known as Vitamin H is actually a coenzyme rather than a ‘vitamin’ per say. Biotin is a vital vitamin for: • Synthesis of fatty acids • Aids in fat metabolism • Aids in carbohydrate metabolism • Aids in level blood glucose levels • Aids in amino acid metabolism • Necessary for healthy skin and hair cell growth • Helps to transfer carbon dioxide Conditions Related to Biotin Deficiency • Diabetes • Depression • Seborrheic dermatitis (infants) • Alcoholism • Total balding • Brittle Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble Vitamins Fat-Soluble Vitamins • Produces energy • Maintains healthy bones Food Sources dairy products peas meat eggs some cereals breads fish poultry • Magnesium maintains normal muscle and nerve function • Sustains regular heartbeat • Aids in bone growth and energy production • Iron is part of a compound in the red blood cells needed for carrying oxygen. • Aids in energy use • Supports immune system Minerals Water Water is essential for most body functions. All of the body cells contain water. Water’s functions include: • moving food through the digestive system. • digesting carbohydrates and protein, and aiding other chemical reactions in the body. • transporting nutrients and removing wastes. • storing and releasing heat. • cooling the body through perspiration. • cushioning the eyes, brain, and spinal cord. • lubricating the joints.