23.2 Roots - OG
advertisement

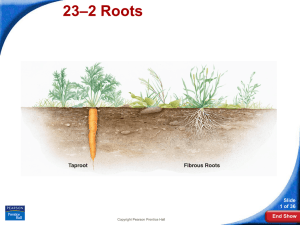
ROOTS: STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Workbook 23.2 1. Comparing types of root systems TYPE OF ROOT DESCRIPTION DICOTS OR MONOCOTS? EXAMPLES TAPROOT Long, thick primary roots; grow deep in soil DICOTS CARROTS, BEETS, DANDELIONS FIBROUS ROOTS Equally sized branch roots; grow separately from base of stem MONOCOTS GRASSES Fill in the blank 2. A mature root has a large area of _____________ tissue between its GROUND dermal and vascular tissues. 3. A root’s surface area for absorption of water is increased by _____________ ROOT HAIRS 4. One function of the is the storage of starch. VASCULAR 5. The _____________cylinder, made up of xylem and phloem, is found at the center of a root. 6. A root’s apical meristem can be found just behind the ______________ ROOT CAP ROOT CROSS SECTION EPIDERMIS ENDODERMIS CORTEX ROOT HAIRS ZONE OF MATURATION ZONE OF ELONGATION PHLOEM XYLEM VASCULAR CYLINDER APICAL MERISTEM ROOT CAP Root Functions #8 -14 8. Name at least 2 functions, besides uptake of water/nutrients SUPPORT, ANCHOR IT IN GROUND, FOOD STORAGE 9. What is the role of active transport in the uptake of water by plant roots? ACTIVE TRANSPORT BRINGS NUTRIENTS FROM SOIL INTO PLANT, INCREASING THE SOLUTE CONCENTRATION. THIS ALLOWS WATER TO MOVE IN VIA OSMOSIS 10. Where in roots are active transport proteins located? CELL MEMBRANES OF ROOT HAIRS, ROOT EPIDERMIS 11. What happens to water and dissolved minerals after they move across the epidermis of a root? THRU THE CORTEX, ACROSS ENDODERMIS, INTO VASCULAR CYLINDER (XYLEM/PHLOEM) 12. Why is there a one-way passage of materials into the vascular cylinder in plant roots? WATER/MINERALS PASS THRU CASPARIAN STRIP AND BECOME TRAPPED IN VASCULAR CYLINDER. GIVES PRESSURE WHICH ALLOWS MATERIALS TO TRAVEL UPWARD 13. How do water and nutrients cross the endodermis that surrounds the vascular cylinder? OSMOSIS AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT BRING WATER/NUTRIENTS THROUGH THE CELLS (NOT AROUND THE CELLS) Root Functions & Big Idea 14. What is root pressure? FORCE THAT CAUSES WATER/NUTRIENTS TO MOVE UPWARD TOWARDS THE STEM 15. People often give potted houseplants more fertilizer than needed. As a result, plants begin to wilt and eventually die instead of getting healthier and larger. What could be the reason? Roots will take in too much, bursting the cell membranes.