Introducing Isotopes
advertisement

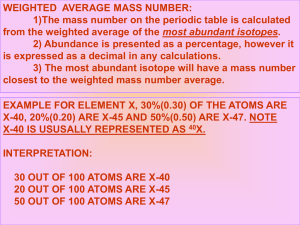
Introducing Isotopes Pre-thinking questions 1. How are atoms of the same element the same? 2. What do the symbols A and Z represent? 3. How is an average calculated? 4. How would an average be calculated for a course in which the tests count more than the homework? How are atoms the same? Atoms An of the same element are the same element is identified by its atomic number, Z, which also represents the number of protons in the nucleus How can atoms of the same element be different? Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. If the neutrons are different, what else will change for the given atoms? Mass number (A) Example of Isotopes Example Protons Neutrons Carbon-12 6 6 Carbon-13 6 7 Carbon-14 6 8 Example of Isotopes Example Iron-55 Iron-56 Iron-57 Protons Neutrons Isotope Notation Isotopes are written with the name followed by the isotope mass Carbon-12 or carbon-13 or C-14 Average Atomic Mass Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of the known isotopes Weighted average takes into account the mass and the relative abundance Carbon-12 98.90 % Carbon-13 1.10 % Carbon-14 trace Average: 12.0111 Calculating a weighted average: a classroom example Sammy is in a college biology class that has a weighted average. His exams count for 50% of his grades, labs are 30%, and his final counts for 20%. By the end of the semester these are his grades: Exams: 87% Labs: 75% Final: 74% What is his overall average for the course? Calculating Weighted Average Avg x abundance + avg x abundance + …. 100 (50 x 87) + (30 x 75) + (20 x 74) 100 = 80.8 % (If you calculated his grade just using the grades he would have a 79% (87+75+74)/3 Post-thinking questions 1. 2. 3. 4. What does the number represent in the isotope platinum-194? Write the symbol for this atom using the A and Z notation (superscripts and subscripts). What is the difference between the mass number and the atomic number of an atom? How is an average mass different from a weighted average mass? The four isotopes of lead are shown below, each with its percent by mass abundance and the composition of its nucleus. Using these data, calculate the approximate atomic mass of lead. 82 p 122 n 1.4% 82 p 124 n 24.1% 82 p 125 n 22.1% 82 p 126 n 52.4%