Executive Power
advertisement

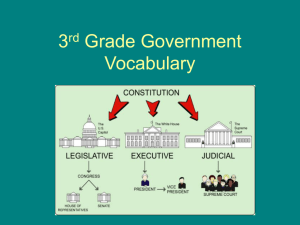
Aim: How powerful is the President? I. Terms A. The president is elected to a four year term 1. He or she may run for reelection B. The president is allowed to serve a maximum of two full terms C. George Washington 1. The Constitution as originally written did not set a term limit 2. George Washington voluntarily stepped down after two full terms and set a precedent for others to follow 3. He did not want to be seen as a power hungry monarch and believed serving longer would violate the principles of democracy 4. Every president until FDR followed this tradition D. Franklin Delano Roosevelt 1. Elected to four separate terms a. 1932, 1936, 1940, 1944 i. The Great Depression and World War II II. Term Limits A. After FDR, the nation became fearful that the office of the president could become too powerful if strict term limits were not instituted B. In 1951, the 22nd Amendment was passed 1. the 22nd Amendment limit the president to two full terms 2. A vice president who served two years of another president’s term may serve two full terms of there own 3. Thus, today it is possible for a president to serve a maximum of 10 years Presidential Term Trivia • 12 Presidents have served a single elected term - John Adams, John Quincy Adams, Martin Van Buren, James K Polk, Franklin Pierce, James Buchanan, Rutherford B Hayes, Benjamin Harrison, William Howard Taft, Herbert Hoover, Jimmy Carter and George HW Bush. • 4 Presidents - Theodore Roosevelt, Calvin Coolidge, Harry S Truman and Lyndon B Johnson - have succeeded to the Presidency through death, and then gone on to serve a single elected term of their own. • 3 Presidents were elected to second terms but failed to complete them. - Abraham Lincoln and William McKinley served only a few weeks or months of their second terms before being assassinated, and Richard M Nixon, resigned 19 months into his second term. • 5 Presidents - William H Harrison, Zachary Taylor, James A. Garfield, Warren G Harding, and John F. Kennedy - died during their first terms and so had no opportunity to seek a second. • 5 Presidents - John Tyler, Millard Fillmore, Andrew Johnson, Chester A. Arthur, and Gerald Ford - succeeded from the VicePresidency but did not win elected terms of their own. • Grover Cleveland is the only president to serve two nonconsecutive terms: he is the 22nd and 24th president III. Executive Order A. B. A legally binding order given by the president as head of the Executive Branch They are used to guide departments or officials in the carrying out of Congressional laws – often they relate to national defense, war, or homeland security 1. Examples: Lincoln suspends writ of habeas corpus and issues Emancipation Proclamation, FDR orders internment of Japanese-Americans 2. Youngstown v. Sawyer – invalidated an executive order made by Truman placing all steel mills under federal control 3. Legislative Veto – the authority of Congress to block a presidential action after it has taken place. This power of Congress was declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court IV. Executive Agreements A. An agreement made between the president and the leader of a foreign nation 1. Similar to a treaty, but does not need to be approved by the Senate V. Executive Privilege A. The right of the president to withhold information from Congress, the courts, or anyone else, even when faced with a subpoena 1. It is not mentioned in the Constitution 2. United States v. Nixon – Executive privilege does exist, but it is not absolute VI. Line-Item Veto A. In 1996, the Line-Item Veto Act was passed. 1. Gave the president power to veto specific parts (line items) of appropriations bills the way state governors do. 2. In the case of Clinton v. City of New York (1998), the act was considered unconstitutional because it gave the President legislative powers. An Amendment would be needed to give the president such power. 3. In 2012, the House voted to give President Obama limited Line Item veto power in a method that would not violate the Constitution, but the bill did not pass the Senate. 3. The president DOES NOT have the power of line item veto. 4. Similarly, Congress cannot use Legislative Vetoes: The power of Congress to block a presidential action after it has taken place. VII. The Imperial Presidency A. The idea that the power of the president has grown without regard to Constitutional boundaries or limits 1. 2. 3. 4. Executive Privilege Power to make war Executive Orders White House staff, Chief of Staff, Executive Offices VII. Impeachment A. Congress has the power of impeachment 1. an impeachment is a formal accusation a. An impeachment is brought for “high crimes and misdemeanors” 2. Charges are drawn up in the House of Representatives a. If a majority of the House votes to pursue the charges, the accused official is officially impeached, or formally accused B. The Impeachment Trial 1. The impeachment trial is carried out in the Senate 2. The Vice President acts as judge a. If the President or Vice President is being impeached, the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court presides instead 3. The members of the Senate act as the jury a. If two-thirds of the Senate find the official guilty, he or she can be dismissed from office