Congress Vocabulary
advertisement

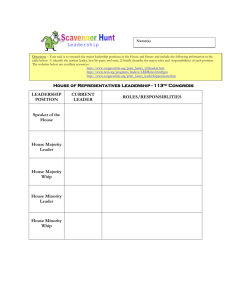
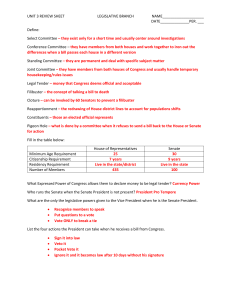
AP Government - Congress The Organization of Congress Bi-cameral Deliberative Caucus/conference Speaker of the House Majority leader Minority leader Whip Committee Chair Seniority Appropriations Committee Rules Committee Ways and Means Committee Standing committee Select committee Joint committee specialization How a Bill Becomes a Law (maybe) Authorization Bill Appropriation Bill Public bill Private bill Multiple referral, sequential referral Hearings Mark up Rules - open, restrictive, closed Conference committee Congressional Budget Office (CBO) Omnibus bill Pork/Pork Barrel/Earmark Christmas tree Discharge petition The Voting Choice Delegate Trustee Partisan Whip Logrolling Legislative Liaison Lobbying Iron Triangle PAC Gridlock Powers of Congress Necessary and proper/elastic clause Commerce clause Levy taxes and borrow money Declare War Implied Representation Constituent Casework Descriptive representation Substantive representation Oversight, Separation of Powers & Checks and Balances Government Accountability Office (GAO) Congressional Budget Office Power of the purse Bureaucracy Veto Override Pocket veto Legislative veto INS v. Chadha Budget Control and Impoundment Act War Powers Act Impeach Elections and Incumbent Advantage Apportionment/Reapportionment/malapportionment redistricting Census Baker v. Carr Wesberry v. Sanders Reynolds v. Sims Gerrymander Majority minority/racial gerrymander Incumbent Safe seat/district PAC Franking The Senate Advice and consent Senatorial courtesy 17th Amendment filibuster cloture holds president pro tempore Policy fiscal policy distributive policy redistributive policy progressive tax regressive tax revenue entitlement program/spending discretionary spending Medicare Social Security means tested Medicaid AFDC/TANF monetary policy Federal Reserve policy cycle Wagner Act/Taft Hartley Act List the qualifications to serve in the House and Senate. Explain the leadership system used in the House and Senate and the role of majority/minority status. Describe the committee system used by Congress and identify those committees which exercise significant power. Explain each step in how a bill becomes a law. Identify the various groups/individuals that play a role in the legislative process and in the legislators voting decision. Identify the ways in which the House and Senate differ. Explain the importance of the "necessary and proper clause." Describe the demographic makeup of Congress and the electoral advantages of incumbency. Describe the various type of policies and programs established by the federal government.