Chapter 9
advertisement
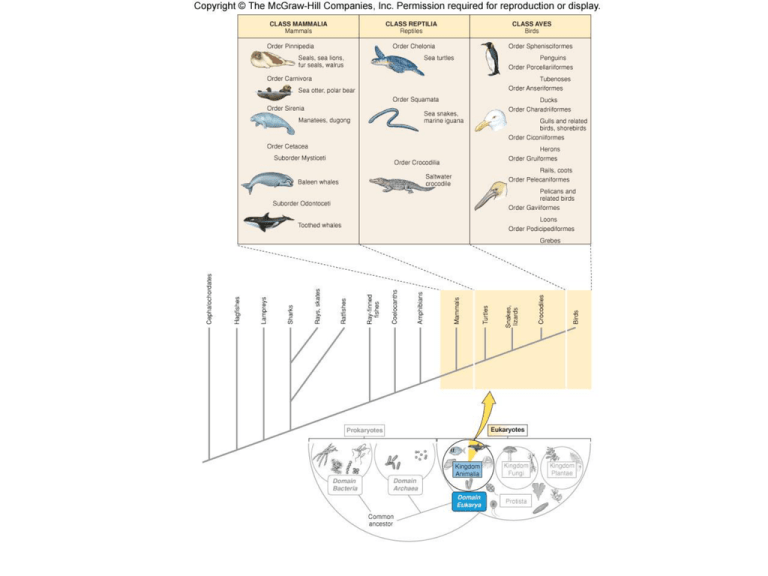
Sea turtles • Air breathing • Ectothermic (coldblooded) poikilotherms – Metabolism fluctuates with the environment temp. • Return to land for reproduction • Scaled carapace fused to backbone • Not very diverse – 7 species • Green – herbivores • Hawksbill – feed on encrusting organisms • Leatherbacks – Largest (upto 2 m) – Feed on jellies – Warm, tropical waters • Long migrations (e.g. 2200 km) • Vulnerable (see pg. 180) – E.g. products, food, by-catch Sea snakes • Tropical Indian & Pacific oceans • Laterally compressed – E.g. Yellow-bellied sea snake (Puerto Vallarta, Mex; Costa Rica) • Protective scales like terrestrial snakes • Very venomous Marine lizards • Marine iguana – – – – Galapagos Islands Laterally compressed tail Herbivore Salt excreting glands around eyes (like many marine reptiles) • Saltwater crocodile – – – – Coastal & estuaries Narrow snout Aggressive carnivores Farmed for skins Birds: seabirds & shorebirds • Homeothermic endotherms • Adaptations for flight & sea life – Pneumatized bone (dense skull) – Waterproof feathers – Webbed feet • High metabolisms – Lots of food (fish & inverts) • Diverse morphologies and environments • Breed on land, typically monogamous pairs • Pelicans – Plunge, fill pouch with fish • Cormorants – Great divers, swimmers – oily feathers; yet not entirely waterproof • Frigate birds – Long distance fliers • Not very oily feathers – Surface feeders Gulls, terns, & shorebirds • Gulls – Predators, scavengers • Terns – Surface fliers/plungers – Favor nesting sites • Shorebirds – – – – Lack web feet diverse bills Estuaries & coastal E.g: plover, curlew, oyster catcher Penguins • Flightless; advanced swimming • Denser bones • Subcutaneous fat • Antarctica mostly • Eat krill, fish, squid • Monogamous pairs – Emperors: Lay a single egg in winter • Male incubates on top of feet (64 days) • Female collects food Class Mammalia Marine mammals • Brain sizes are larger per pound of body weight than most other animals' • Mammals have more efficient control over their body temperatures than do birds • Hair provides insulation • Mammary glands provide milk to nourish the young • Teeth are specialized for cutting, shearing or grinding; thick enamel helps prevent teeth from wearing out • Well developed in comparison to other vertebrates – Branched from 5 ancestral land mammals • Oils, fat layers, blubber • Viviparous; placental • Very diverse feeding strategies and adaptations – – – – Piscivores Indiscriminate carnivores Herbivores Filter feeders • baleen Order Pinnipedia • Shared terrestrial Carnivora ancestor • Blubber – Insulates, buoyancy, stored energy • Breed on land • Seals – Streamlined body, rear flippers good for swimming • Sea lions – Flippers support body on land and for swimming – External ears • Walrus – Feed on bottom inverts – Deep divers – Tusks for defense and anchoring (arctic ice) Sea Otter Class Mammalia, Order Carnivora, Family Musetlidae (river otters, skunks, weasels) • Smallest marine mammal • Shallow coastal water • No blubber; two layers of fur • Front limbs for prey capture and manipulation • Feed on benthic inverts – Typically bring to surface Polar Bears Order Carnivora, Suborder Caniformia, Family Ursidae (bears) • Semiaquatic – Good swimmers, travel miles on arctic ice, ice dens • • • • • • • huge feet with heavy fur Tremendous claws White fur for camouflage. Black skin for absorbing heat. Hollow hair for reradiating and collecting heat. Blubber for energy storage and protection from the cold. Incredible sense of smell – locating food – locating each other for mating (pheromones) • need to be able to come together in the vastness of the Arctic. Manatees & Dugongs Order Sirenia Family Dugongidae (dugong and sea cow) Dugong dugon (dugong) Hydrodamalis gigas (Stellar's sea cow) Family Trichechidae (manatees) • Elephant-like ancestor – – – – – Herbivorous; teeth Bone structure Thick skin Nasal morphology Pectoral mammaries Whales • Order Cetacea – Whales, dolphins, porpoises – Horizontal flukes – Top blowhole – Spend entire life in water – Toothed whales • Carnivorous • Includes dolphins & porpoises – Toothless whales Baleen whales • Filter feed with baleen plates (keratin) • Two blowhole openings • Surface feeders – Right and Bowhead • Rorquals – Expandable throat to gulp large amounts of fish and krill Toothed whales • Sperm whales • Orcas • Dolphins – Beaked typically • Porpoises – No or less beak