half-life
advertisement

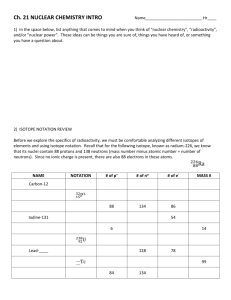
What is radioactivity? What is Radioactivity? Radioactivity -unstable nuclei -emitting particles or releasing energy What is nuclear decay? Nuclear Decay -atom changes into isotope of same element or a new element What is nuclear radiation? Nuclear Radiation -can damage living tissue -released energy or matter What types of nuclear radiation are there? Types of Nuclear Radiation -alpha particles -beta particles -gamma rays -neutron emission Radioactivity occurs when unstable nuclei release energy or particles. Nuclear radiation can damage living tissue. There are 4 types of nuclear radiation: alpha particle, beta particle, gamma rays, and neutron emission. What are alpha particles? What is Radioactivity? Alpha Particles -two protons and two neutrons -positive charge (+2) -most massive -do not travel far through materials -large size and ionizing matter slows A.P. down What are beta particles? Beta Particles -negative charge (-1) -faster than A.P. -travels farther into matter than A.P. -neutron decays into a proton and an electron -electron ejected -lose speed as they ionize matter What are gamma rays? Gamma Rays -penetrates matter more than B.P. -not made of matter -no charge -electromagnetic energy -do not ionize matter -greater danger than A.P. and B.P. What are neutron emissions? Neutron Emission -neutron emitted from unstable nuclei -no charge -does not ionize matter -travels further into matter than A.P or B.P. Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons. They are positively charged (+2). They are the most massive radioactive particle. Beta particles are negatively charged electrons formed from a neutron decaying. Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic energy with no charge. Neutron emission occurs when a neutron is emitted from an unstable nucleus. What is Radioactivity? What is a half-life? Half-life -time it takes ½ of a radioactive substance to decay What determines half-life? -different radioactive isotopes have different half-lives -depends on nucleus stability Radioactive substances decay at a rate known as a half-life. This is the time needed for half of a radioactive substance to decay. The rate of decay depends on the stability of the nucleus.