UNIT 2 NUCLEAR REACTIONS 2.1 What are the types of radiation?
advertisement

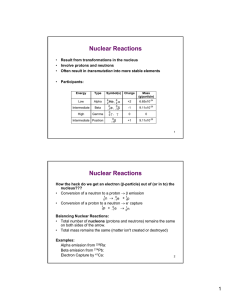
UNIT 2 NUCLEAR REACTIONS 2.2 What nuclear stability and radioactive decay? May 16, 2011 DO NOW: What are the types of radiation? Alpha Beta Gamma Positron What is the decay mode for krypton-85? TABLE N Beta -β NUCLEAR REACTIONS • A nuclear reaction is a reaction that involves a CHANGE in an atom’s IDENTITY. • Nuclear reactions occur because the nucleus is UNSTABLE NUCLEAR STABILITY Depends on Proton to Neutron Ratio Proton to Neutron Ratio ≠ 1:1 Proton to Neutron Ratio = 1:1 Spontaneous Decay STABLE NUCLEUS Isotope (or RADIOISOTOPE) will undergo decay Neutron to proton ratio Makes it stable NOTE • Elements with an atomic number greater than 82 are always radioactive. Going back to our key questions: • What makes something radioactive? When the Neutron to Proton Ratio is not 1:1 When the Nucleus is UNSTABLE • What happens when something is radioactive? It emits energy as it decays into a more stable isotope STABILITY BAND TYPES OF RADIOACTIVE DECAY Term Law of Conservatio n of Mass Definition Energy may change from one form to another, but it is neither created nor destroyed. CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 210 4 206 Po 84 14 c 6 He + 82 Pb 0 14 e + N -1 7 11 0 C 6 2 e +1 + 11 B 5 TRY THIS! Write the alpha decay nuclear equation for Bi-214 (atomic number 83). 214 Bi 83 4 210 He + Ti 2 81 TRY THIS! Write the decay reaction for gold-198. 198 Au 79 0 e -1 + 198 Hg 80 TRY THIS! Write the decay reaction for iron-53. 53 Fe 26 0 e +1 + 53 Mn 25 TRANSMUTATIONS These reactions are called TRANSMUTATIONS because we start out with one element and change it to another element. INDEPENDENT PRACTICE • Complete the worksheet • HOMEWORK: READ THE ARTICLE AND WRITE A SUMMARY (answer all the questions listed)