Ch3 and Ch21 Objectives
advertisement

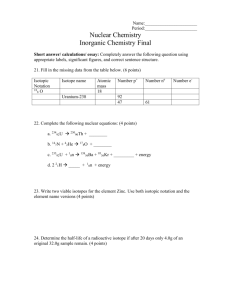
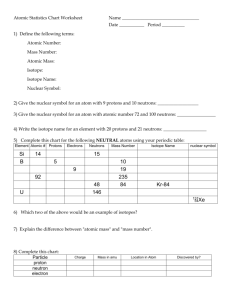
Ch3 and Ch21 Objectives Ch3 Recall a very brief history of Atomic Theory ( Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford) Know and understand the five main aspects of Dalton's Atomic Theory Know how Modern Atomic Theory is the same and different from Dalton’s Atomic Theory Recall some of the experiments that led to the identification of sub-atomic particles (Cathode Ray Tube, Oil Drop, Gold Foil) Know the three particles that make up the atom and their relative charges, masses and positions in the atom Be able to use the Atomic # and Mass # of an isotope to calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons Know what the term isotope means Be able to perform calculations of weighted average atomic mass from isotope data Ch21 Be able to use neutron:proton ratio to make predictions about stability(belt of stability) Understand the phenomenon of radioactivity and the properties of radioactive particles Know the three most common forms of radioactive decay (alpha, beta, and gamma) and know how the nucleus changes in each type of decay. Know protons and neutrons have substructures and consist of particles called quarks. Be able to write nuclear equations Understand the term mass deficit Know protons and neutrons in the nucleus are held together by nuclear forces that overcome the electromagnetic repulsion between the protons. Understand the concept of half-life and be able to perform calculations related to it Know how to calculate the amount of a radioactive substance remaining after an integral number of half lives have passed. Recall some uses of radioactivity Know alpha, beta, and gamma radiation produce different amounts and kinds of damage in matter and have different penetrations. Know the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E=mc2) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Understand the terms nuclear fission and fusion Understand, that in very general terms, radioactivity involves the rearrangement of the nucleus and chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of electrons Know some naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioactive, as are isotopes formed in nuclear reactions. Know that how man-made elements are created.