Intro to Nuclear Chemistry Notesheet
advertisement

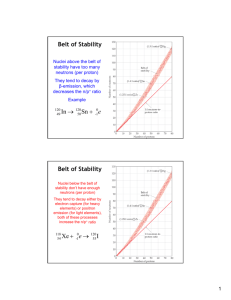
Ch. 21 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY INTRO Name_________________________ Hr____ 1) In the space below, list anything that comes to mind when you think of "nuclear chemistry", "radioactivity", and/or "nuclear power". These ideas can be things you are sure of, things you have heard of, or something you have a question about. 2) ISOTOPE NOTATION REVIEW Before we explore the specifics of radioactivity, we must be comfortable analyzing different isotopes of elements and using isotope notation. Recall that for the following isotope, known as radium-226, we know that its nuclei contain 88 protons and 138 neutrons (mass number minus atomic number = number of neutrons). Since no ionic charge is present, there are also 88 electrons in these atoms. 226 88Ra NAME NOTATION # of p+ # of no # of e- 88 134 86 MASS # Carbon-12 32 315P Iodine-131 54 6 14 238 92U Lead-____ 128 ___ ___Tc 78 99 84 134 21.2 RADIOACTIVE DECAY Name_______________________ Hr___ Radiation -- ___________________ or ______________________ emitted from a source. Radioactive elements are usually _________________ of an atom with an unstable _________________. What do we mean by an unstable nucleus? Too many or too few ___________________ All radioactive elements decay naturally into OTHER _______________________. --the rate varies from _________________ to billions of ___________. --this rate of decay cannot be ___________________. Types of Radioactive Decay Alpha particle Symbol = ________ Nuclear Equation for Alpha Decay: Beta particle Symbol = ________ Nuclear Equation for Beta Decay: Gamma ray Symbol = ________ Nuclear Equation involving gamma rays: Positron Symbol = ________ Nuclear Equation for Positron Production: Electron Capture Symbol = ________ Nuclear Equation for Electron Capture: