introandchem
advertisement

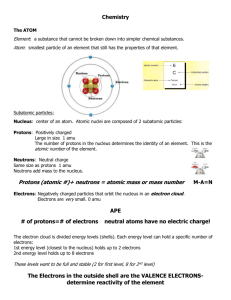
CH 1 INTRODUCTION What is science? SCIENCE = is the knowledge based on observation and experimentation. What are the 4 branches of science? 1. BIOLOGY = study of life. 2. CHEMISTRY = composition & properties of matter 3. PHYSICS = forces & motion of matter 4. EARTH SCIENCE = study of earth and it’s surroundings Four Branches of Earth Science 1. GEOLOGY = study of solid earth. 2. OCEANOGRAPHY = study of oceans. 3. METEOROLOGY = study of the atmosphere & weather 4. ASTRONOMY = study of the universe. 4 Earth’s Spheres 1. Hydrosphere water 2. Atmosphere air 3. Geosphere solid earth 4. Biosphere living things Interaction of the 4 Spheres 5 Steps of Scientific Method 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify problem Make observations Form a hypothesis Test the hypothesis Accept, reject, or modify hypothesis. Chemistry Introduction Matter – anything w/ volume and mass 4 states of matter Solid – definite shape and definite volume atoms close together Liquid – no def. shape but definite volume atoms further apart Gas – no definite shape or volume atoms real far apart move easily Plasma—charged particles(lightning, etc.) ELEMENTS Elements = building blocks of minerals. Can’t be broken down into simpler substances by chemical/physical means Periodic Table Each element represented by 1-3 letters 8 elements make up most of earth’s crust. Know top 2! (page 35) Oxygen=47% Silicon=28% Metals – malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat/electricity left side of periodic table Non-metals – brittle and poor conductors right side of the periodic table Atom Parts Protons – positively charged 1 amu = mass Found in nucleus Neutrons – no charge (neutral) 1 amu = mass Found in nucleus Electrons – negatively charged Very little mass Outside of nucleus in energy levels Atoms=smallest particle of matter that contains all of the characteristics of the element Atoms are neutral (no charge) Equal #’s protons + and electrons - Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus Mass number - number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus Isotope – atom with same number of protons but different number of neutrons Used for dating rocks/fossils 12C and 14C EX: Ion – atoms that gained or lost electrons giving them a charge (+ or -) Mixtures & Compounds Mixture – combination of substances… Don’t lose identities (of components) Easy to separate components Not in a set ratio Solutions – special type of mixture (Solute vs. Solvent) (Alloys=mixture) Compounds – 2 or more elements chemically combined Components lose their identity Components can’t be separate out easily Components in a specific, set ratio Atomic Bonds (James) 1. Atoms without a full outer energy level are likely to bond chemically. 3 types: Ionic – formed when electrons are transferred from a + ion to a – ion - between metals and non-metals 2. 3. Covalent – when electrons are shared between the atoms of non-metals Metallic – when electrons are shared by metal ions. Determining Location Latitude – distance N or S of equator, measured in degrees (are parallel) Lines run East and West Oº = equator 90º = poles Longitude – distance E or W of prime meridian, measured in degrees (not parallel) Lines run North and South Oº = Prime Meridian 180º = International Date Line Topographic Maps Represents the 3-D earth in 2-D. Contour lines - lines of equal elevation; shows elevation on a flat map Contour interval – elevation difference between adjacent lines Hachure marks – represent depressions Scale – a distance on the map = a distance on the surface (ratio, bar, verbal) Legend/key – explains map symbols Benchmark -- triangle represents special elevation THE END !