Circulatory System: Heart, Blood, Vessels - Middle School

The Circulatory System
Lesson 2: Standard 9a. Students know how the complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide
What have we learned so far?
• The definitions of specialized cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems
• The body is kept in homeostasis (balance) by the actions of different organ systems working together
• Feedback inhibition is the mechanism for maintaining homeostasis in the body
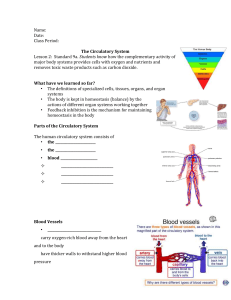
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the ___________
• the ___________
• blood _________
_________
_________
_________
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the heart
• the ___________
• blood _________
_________
_________
_________
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the heart
• the blood
• blood _________
_________
_________
_________
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the heart
• the blood
• blood vessels
_________
_________
_________
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the heart
• the blood
• blood vessels
veins
_________
_________
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the heart
• the blood
• blood vessels
veins
arteries
_________
Parts of the Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of
• the heart
• the blood
• blood vessels
veins
arteries
capillaries
Check for Understanding
Using your iPads, go to www.awwapp.com
to get to the online whiteboard
Write in the answer to question 1 and hold your iPads so I can see them.
1.
What are the three main parts of the circulatory system?
Now tap the menu button and tap clear to clear your whiteboard and answer question 2. Hold up your iPads when you are finished so I can see them.
2. What are the three types of blood vessels in the human circulatory system?
Blood Vessels
• ______________
– carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the body
– have thicker walls to withstand higher blood pressure
• ______________
– carry oxygen-poor blood to the heart
– have valves to prevent blood from flowing back in the wrong direction
• ______________
– are the smallest blood vessels
– so narrow that blood cells pass through in a single file
– deliver oxygen and nutrients to all cells of the body
Blood Vessels
• arteries
– carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the body
– have thicker walls to withstand higher blood pressure
• ______________
– carry oxygen-poor blood to the heart
– have valves to prevent blood from flowing back in the wrong direction
• ______________
– are the smallest blood vessels
– so narrow that blood cells pass through in a single file
– deliver oxygen and nutrients to all cells of the body
Blood Vessels
• arteries
– carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the body
– have thicker walls to withstand higher blood pressure
• veins
– carry oxygen-poor blood to the heart
– have valves to prevent blood from flowing back in the wrong direction
• ______________
– are the smallest blood vessels
– so narrow that blood cells pass through in a single file
– deliver oxygen and nutrients to all cells of the body
Blood Vessels
• arteries
– carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the body
– have thicker walls to withstand higher blood pressure
• veins
– carry oxygen-poor blood to the heart
– have valves to prevent blood from flowing back in the wrong direction
• capillaries
– are the smallest blood vessels
– so narrow that blood cells pass through in a single file
– deliver oxygen and nutrients to all cells of the body
Check for Understanding
Using awwapp again, answer these questions one at a time.
1. Why do arteries need to be thicker than veins?
2. Why do veins need to have valves?
3. Which blood vessels carry blood to the heart?
4. Which blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Blood is made of:
• A liquid called
____________
• Red blood cells, also called
____________
• White blood cells, also called
____________
• ____________, also called thrombocytes
Blood
Blood is made of:
• A liquid called plasma
• Red blood cells, also called
____________
• White blood cells, also called
____________
• ____________, also called thrombocytes
Blood
Blood is made of:
• A liquid called plasma
• Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes
• White blood cells, also called
____________
• ____________, also called thrombocytes
Blood
Blood is made of:
• A liquid called plasma
• Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes
• White blood cells, also called leukocytes
• ___________, also called thrombocytes
Blood
Blood is made of:
• A liquid called plasma
• Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes
• White blood cells, also called leukocytes
• Platelets, also called thrombocytes
Blood
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
__________. They contain a protein called ____________ that carries ____ to cells and
____ away from cells.
• White blood cells help the body fight off ___________.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell __________ that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called ____________ that carries ____ to cells and
____ away from cells.
• White blood cells help the body fight off ___________.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell __________ that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries ____ to cells and
____ away from cells.
• White blood cells help the body fight off ___________.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell __________ that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries O
2 to cells and
____ away from cells.
• White blood cells help the body fight off ___________.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell __________ that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries O
2 to cells and CO away from cells.
2
• White blood cells help the body fight off ___________.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell __________ that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries O
2 to cells and CO away from cells.
2
• White blood cells help the body fight off infections.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell __________ that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries O
2 to cells and CO away from cells.
2
• White blood cells help the body fight off infections.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell fragments that help with blood _______
Blood Cells
• Red blood cells have no
nucleus. They contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries O
2 to cells and CO away from cells.
2
• White blood cells help the body fight off infections.
There are many different types of white blood cells
• Platelets are cell fragments that help with blood clotting
Check for Understanding
Using awwapp, answer these questions one at a time
1. What would happen to you if some or all of your hemoglobin was damaged?
2. What would happen to you if your white blood cells died or stopped working?
3. What would happen to you if your platelets were missing or damaged?
The Heart
Label the chambers, valves, veins, and arteries
Blood Flow Through the Heart
Draw arrows to trace the flow of blood through the heart
Check for Understanding
Using awwapp, answer these questions one at a time
1. Where does oxygen-poor blood enter the heart?
2. Where does oxygen-rich blood exit the heart?
3. How many chambers are in the heart?
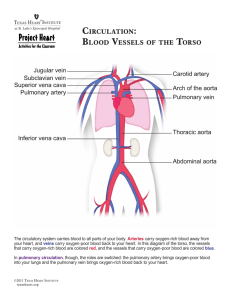
Blood Circulation Through the Body
• The right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs. This is called ________________ circulation.
• In the lungs, CO
2 in the blood is _______________ for O
2
• Oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs, into the left side of the heart, and to the rest of the body. This is called _______________ circulation.
Blood Circulation Through the Body
• The right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs. This is called pulmonary circulation.
• In the lungs, CO
2 in the blood is _______________ for O
2
• Oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs, into the left side of the heart, and to the rest of the body. This is called _______________ circulation.
Blood Circulation Through the Body
• The right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs. This is called pulmonary circulation.
• In the lungs, CO
2 in the blood is exchanged for O
2
• Oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs, into the left side of the heart, and to the rest of the body. This is called _______________ circulation.
Blood Circulation Through the Body
• The right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs. This is called pulmonary circulation.
• In the lungs, CO
2 in the blood is exchanged for O
2
• Oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs, into the left side of the heart, and to the rest of the body. This is called systemic circulation.
Check for Understanding
Using awwapp, answer these questions one at a time
• Which system carries oxygen rich blood – systemic or pulmonary?
• Which system carries oxygen poor blood back to the heart?
Making a Set on Quizlet
• Log in to quizlet.com
• If you have not signed up for quizlet, go to my page on the
Stern MASS website. Scroll down until you find the directions for joining quizlet. Make sure you join the right class.
• At the top of the page, tap on “Create a set”
• Enter in the set title and description (YOU get to choose what to name these)
• Find the definitions or descriptions of the following words in the textbook or using the internet and include them in your set: atrium, ventricle, pulmonary circulation, systemic circulation, valve, aorta, vena cava, artery, capillary, vein,
• Study your set for the rest of the class period. Make sure you use all of the functions (except spell) – flashcards, learn, scatter, race, and test