8. Mitosis Test Review
advertisement

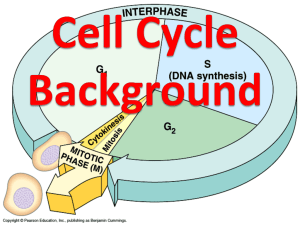
Our Lady of Mercy Biology 9 Mitosis Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. What is the cell cycle? What are the two main parts of the cell cycle? What is interphase? Which phases make up interphase? What phases make up cell division? What is mitosis? What are the names of the phases of mitosis? How long is interphase compared to cell division? What molecules control the cell cycle? Do plants undergo mitosis? What is cancer? What causes cancer? How does DNA become condensed? What things prevent cancer? What is a gene? What happens in prophase? What happens in metaphase? What happens in anaphase? What happens in telophase? How does cytokinesis occur in plant cells? What is a centriole? What is a somatic cell? What are the two types of gametes? What are spindle fibers? What is the difference between centromere, centriole, chromatid, chromosome, and chromatin? Make sure to study: 1. Your notes 2. Your mitosis drawing 3. Your vocab quiz *Vocab is REALLY important in this unit. On the test, you might see more than one question on the same word! Our Lady of Mercy Biology 9 Mitosis Review Key 1. What is the cell cycle? What are the two main parts of the cell cycle? Cell cycle: series of events that takes place within a cell leading toits division and duplication Two parts: Interphase & cell division 2. What is interphase? Which phases make up interphase? Interphase: when the cell prepares for division Gap 1, Synthesis, and Gap 2 phases make up interphase 3. What phases make up cell division? Mitosis phase 4. What is mitosis? What are the names of the phases of mitosis? Mitosis: the process of nuclear division in somatic cells Phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PMAT) 5. How long is interphase compared to cell division? Interphase is much longer than cell division; the cell spends the majority of its life in interphase 6. What molecules control the cell cycle? Enzymes and cyclins (both are proteins) 7. Do plants undergo mitosis? Yes- only, they have to build new cell walls in between the two new daughter cells 8. What is cancer? A malignant growth resulting from uncontrolled cell division 9. What causes cancer? When the cell cycle is not controlled correctly, leading to uncontrolled mitotic division 10. How does DNA become condensed? The long strand of DNA is wrapped around proteins 11. What things prevent cancer? Balanced diet, exercise, staying off drugs 12. What is a gene? A piece of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein 13. What happens in prophase? Nuclear membranes disappear, chromatin condense into chromosomes 14. What happens in metaphase? Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, spindle fibers sprout from centrioles and connect to centromeres 15. What happens in anaphase? Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite sides of the cell 16. What happens in telophase? Nuclear membranes reform and chromosomes expand back into chromatin 17. How does cytokinesis occur in plant cells? A new cell wall forms in between the daughter cells 18. What is a centriole? The organelle from which spindle fibers sprout 19. What is a somatic cell? What are the two types of gametes? Somatic cell: any type of cell in the body that is not a gamete Gamete: sex cells (sperm in males and eggs in females) 20. What are spindle fibers? Rope like structures consisting of thin fibers 21. What is the difference between centromere, centriole, chromatid, chromosome, and chromatin? Centromere: the structure that holds sister chromatids together Centriole: the organelle from which spindle fibers sprout Chromatid: ½ of a chromosome Chromosome: DNA after it has been condensed and duplicated Chromatin: DNA in its expanded form