I. Negligence
advertisement

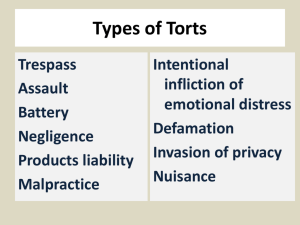
I. Negligence A. Characteristics 1. definition 2. elements 3. defenses I. Negligence (cont.) B. Duty 1. standard is flexible 2. duty is determined by the court a. relationship of the parties b. statute c. negligent per se 3. owner/occupier of land I. Negligence (cont.) C. Breach of Duty 1. definition 2. test 3. reasonableness factors 4. particular standards of care I. Negligence (cont.) D. Causation 1. direct result of negligent act 2. proximate cause 3. Courts may hold defendant's liable only for a. reasonably foreseeable results b. within scope of foreseeable risk 4. intervening force a. foreseeable intervening forces b. superseding intervening forces I. Negligence (cont.) E. General rules of Causation 1. thin skull rule 2. negligent medical care F. Res ipsa loquitur 1. definition 2. elements 3. burden 4. examples I. Negligence (cont.) F. Negligent Infliction of Emotional Distress 1. more recent development 2. prove some physical injury 3. erroneous report of relative's death or mishandling of corpse 4. zone of danger 5. Third Party recovery G. Defenses to Negligence 1. contributory negligence 2. last clear chance 5. COMPARATIVE NEGLIGENCE 6. Assumption of the risk II. Strict Liability A. Characteristics 1. definition 2. elements B. Rationale C. Application to ultrahazardous D. Application to unreasonably dangerous products III. Product liability A. Three legal bases for liability 1. breach of warranty 2. negligence 3. strict liability B. Negligence theory rationale: liable if mfr was negligent C. Privity & disclaimers III. Product liability (cont.) D. Strict liability 1. response to limitations in negligence & breach 2. rationale 3. elements 4. state of the art 5. defenses E. Industry-wide or market share liability 1. definition 2. rationale 3. example 4. court apportions liability 5. defenses III. Product liability (cont.) F. Limitations on strict liability G. Statutes of repose 1. definition 2. purpose 3. must be unconstitutional H. Current issues 1. tort reform from a federal perspective 2. design defects 3. punitive damages Negligence Policy • POLICY: who should bear loss of injury from products placed in marketplace, the party who created the condition or the party who suffered from it? • What about instances where manufacturer used due care, but injury still occurs? • Are we concerned that consumer no longer has means or skill enough to investigate the soundness of a product