Teachers and School Boards
advertisement

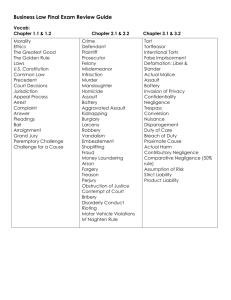
Teachers and School Boards Rights as a citizen Statutory rules that govern boards Contractual conditions http://www.foxnews.com/video/in dex.html?playerId=videolanding page&streamingFormat=FLASH &referralObject=3138015&referr alPlaylistId=playlist http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0mvP0ArKIGY First Amendment Rights Speech Expression Association Religion Freedom of Speech Connick v. Myers and Pickering v. Board Speaking out as a citizen on matters of public concern is free speech Balance of interest test Private communications without disturbance is protected Dress is not a first amendment right; school board dress code is constitutional Privacy- not mentioned in Constitution but inferred Personnel may be required to seek help if there is a reason to doubt the ability to contend Drug test if a problem is suspected but not random testing Search teacher workplace- any area related to work Religion- first amendmentTitle VII Subject to certain limits 1972- amended Civil Rights Act to include religion- employer accommodation as long as no undue hardship Neither inhibit nor promote religion Religious garb- if a state prohibits such attire, the courts sustain Self-incrimination Fifth amendment A superintendent has a right to inquire Due process- 4th and 14th amendment Procedural Substantive- liberty, tenure is a property right Vagueness- may require states to uphold state and federal constitutions Irrationality- a rule cannot be arbitrary or irrebuttable Take home test Torts- A civil wrong for which the courts can provide a remedycaused by unreasonable conduct of others Intentional interference Strict liability Negligence Intentional interference Not necessary for the wrongdoer to be hostile- could be a practical joke Assault- mental rather than physical violence; mental distress Battery- physical contact False imprisonment Read Spears v. Jefferson p.553 Strict Liability Liability without fault Danger is inherent in the activity Not negligent or intentional behavior Read Fallon v. Indiana Trail School p. 555 Negligence- neither expected nor intended Could be prevented by reasonable care Must sustain an injury resulting from an unreasonable risk Who is a reasonable person? Person of ordinary sense using ordinary care Elements of Negligence A duty to protect others Failure to exercise that duty with a standard of care A causal connection between act and injury (proximate cause or legal cause) An injury- damage or loss All elements must be proven or case fails Duty of care Educators are negligent when they do something or omit something- that a reasonable person might deem harmful No general- or at large duty But if you make it your duty- you must act as a prudent person Standard of care As the risk increases, the standard of care increases- ex. Chemistry lab vs. study hall or reading class Children between 1 and 7 cannot be liable for negligence Between 7 and 14- prima facie case for incapacity but it can be rebutted Reasonably prudent person Proximate or legal cause ACT_____________Injury Proper supervision Defenses for negligence 1. 2. 3. 4. Contributory negligence Comparative negligence- assign degrees- FL is a comparative state Assumption of risk ImmunityGovernmental Charitable Infants Mentally disabled Negligence cases Brown v. Tesack Johnson v. School District of Millard Stevens v. Chasteen Simonetti v. School District of Philly Hutchison v. Toews Wagenblast v. Odessa Defamation Using spoken or written word to accuse another person of immorality, dishonesty, or dishonorable conduct Libel- for visual perception Slander- spoken words School personnel- privilege Cannot say anything you want to about others In good faith- without malice Truth is defense against defamation Read Hett v. Ploetz 5 and 11 in case notes Florida- hold harmless Waived sovereign immunity for $100,000 to 200,000. You must know of the standard of care that is required What if a person is invited to be on campus? Only compensatory charges can be levies; not punitive charges