Sexually Transmitted Infections
advertisement

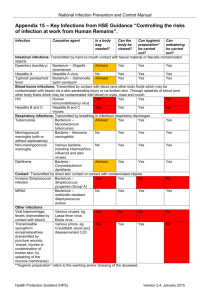
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Target: I will be able to distinguish the various STI’s from one another, describe the ways in which they enter the body, and explain which are curable and which are not Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Infections transmitted through intimate, usually sexual, contact Pg. 43 Chlamydia: A bacterial infection of the urogenital tract that can be easily cured with antibiotics • Transmitted through contact with a penis, vagina, mouth, anus, and during childbirth • “Silent Infection”- most infected people are asymptomatic for several weeks after exposure • Causes painful urination, white discharge, inflammation of the cervix, urethra, prostate, and sterility • 2/3 of new infections occur among youth 15-24 years old Gonorrhea: A bacterial infection that causes infertility if not treated with antibiotics • Transmitted through contact with a penis, vagina, mouth, anus, and during childbirth • Can infect the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and urethra; as well as the mouth, throat, eyes, and rectum • 2nd most common STI in the United States Trichomoniasis: A vaginal STI caused by a parasite that causes foamy, yellow discharge and an unpleasant odor • Transmitted through contact with a penis, vagina, mouth, anus, or hands • Cured with a single dose of antibiotics Human Papilloma Virus (HPV): A group of viruses that the body harbors for a lifetime (not cureable), which are characterized by warts on various parts of the body. • Most common STI in the US- 20 million Americans currently infected and 6 million new cases each year • Some health effects caused by HPV can be prevented with the vaccination Genital Herpes: STI caused by the herpes simplex virus which causes blisters/open sores on the genitals • Highly contagious and incurable (no cure, but there is medicine to reduce symptoms) • Many people infected are unaware that they have it because of such mild symptoms; therefore passing it onto partners unknowingly Syphilis: A contagious bacterial infection that is characterized by distinct phases • Starts as a painless sore (chancre) on the penis, scrotum, vaginal wall, or cervix • If left untreated, a rash and white patches appear on the skin in the mouth, throat, and genitals. • A curable disease with prompt treatment. • If treated too late, there may be permanent damage to the heart and brain Candidiasis: Yeastlike fungal infection from a normal fungus inhabiting the vaginal tract • When the normal chemical balance of the vagina is disturbed, the organisms multiply and cause the infection which can be cured with over the counter medication Pubic Lice: Parasitic insects that inhabit the genitals and are killed with lice shampoo- aka “Crabs” HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus): An incureable virus that causes AIDS by infecting helper T cells and making the individual more vulnerable to infections, cancers, and neurological disorders • AIDS: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome- a disease that attacks the immune system • Transmitted when infected bodily fluids (semen, vaginal secretions; blood) enter the body through an open cut, or wound. Summary CONNECTING THE INFECTIONS Create a concept map to show the similarities/differences between the 9 STIs that you learned today. •Be sure to make include which are cureable and which are not. *Use a minimum of 4 colors Pg. 42