Biology
advertisement

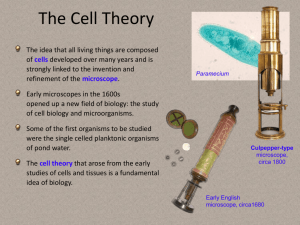
Welcome to Biology- BL. 2 Sit down quietly, get your Syllabus out and turn it into the brown box on the desk by the door. Wait for instructions. Biology CH. 1- The Science of Life and the God of Life 1B- Scientific Method • What is Science? - The collection of observations, inferences, and models produced through a systematic study of nature… OR - Systematic methods that produce the observations, inferences, and models. • Scientific Method - A logical procedure for choosing an answer: 1) Define the problem 2) Do preliminary research 3) Form a hypothesis (a simple, testable statement that predicts the results expected from a research study. Example of the Scientific Method • You are told you can have a new cell phone. Your parent is willing to pay for any phone you want. You just have to choose which one you want…. • Which phone would you choose? • What you would probably do: 1) Realize you have options. 2) Research all the latest phones, check out their reviews online, compare phones that have abilities to do things you want done, try your friend’s phones out, go to the store and check them out, etc. 3) Make up your mind on which one you want the most… Get the phone. Steps of the Scientific Method • Observe the experiment • Collect the information from the experiment and record it (datarecorded information). • Classify the data into a logical order or groups • Analyze the data to determine what they reveal about the problem • Choose the solution that best answers the question • Verify the chosen answer by repeating the experiment - Validity - Reliability • Predict what will happen in a similar situation. Controlled Experiments • Controlled Experiment- Has two groups: 1) control group 2) experimental group • Independent Variable- Difference between two groups • Control Group- group not exposed to independent variable • Experimental group- group exposed to independent variable. • Dependent Variable- the results that are dependent on the Independent Variable Limitations of Science • Phenomenon - Questions dealing with how or why are not measureable, therefore, these questions are beyond the scope of science - Mankind attempts to use science to explain God, his coming of being, how we got here, why people die, etc. Science cannot answer these questions. • Bias - Something someone wants to believe whether they are conscious of their bias or not. • Absolute Answer- Science cannot PROVE anything. It can only suggest based off of previous repetitions and prediction. • Just because an answer is valid does not mean it is correct. Homework Read and Outline CH. 1B and Ch. 1C of Biology text book Work in groups of 2- Create a fictitious experiment. Define: 1. Problem 2. Hypothesis 3. Controlled Group 4. Experimental Group 5. Independent Variable 6. Dependent Variable 7. Possible Limitations Biology - Chapter 1 • Quietly get your “Experiment paper” out from last class’s experiment. Turn them into the brown box on my desk. • Start your quiz. You have 10 minutes. Good Luck! Biology Chapter 1C- Biology and the Study of Life Ch. 1C Biology and the Study of Life Biology • Definition: • Bio- life or Living (Greek term) • Ology- the study of Attributes of Life: 1) Exhibits movements - Including internal movement such as blood in the blood vessels of a fetus 2) Achieves growth • Together= The study of life - Growth is achieved by an organism, it is not done to the organism. - Assimilation- assembling of the component parts that make up their living material. Attributes of life Cont. 3) Reproduces- Making of another organism that has characteristics and limitations similar to the original. 4) Comes from similar preexisting life - Variations: ex. Dogs - Of the same kind 5) Has similar chemical makeup 6) Is composed of cells 7) Exhibits irritability - the ability to respond to a stimuli. 8) Requires energy - Ex: food Microscopes Compound Light Microscope Electron Microscope • Two sets of lenses located in the objective and the ocular (eyepiece). • Many CLM’s consist of several objectives on a revolving nosepiece for different magnifications. • Stage- placement for specimen • Body tube- long tube between eyepiece and objective. ***Replaces small light rays with electrons that travel in a straight line. Electron microscopes have much greater magnification due to this replacement. • 2 types- Transmission and scanning Microscopes Compound Light Microscope Electron Microscope Homework/ Coursework • In class: • Break into groups of 2 and work quietly on the Microscope worksheets • Study together for CH. 1 Test- know material thoroughly • Homework: • Study for CH. 1 Test