Kidney - TeacherWeb
advertisement
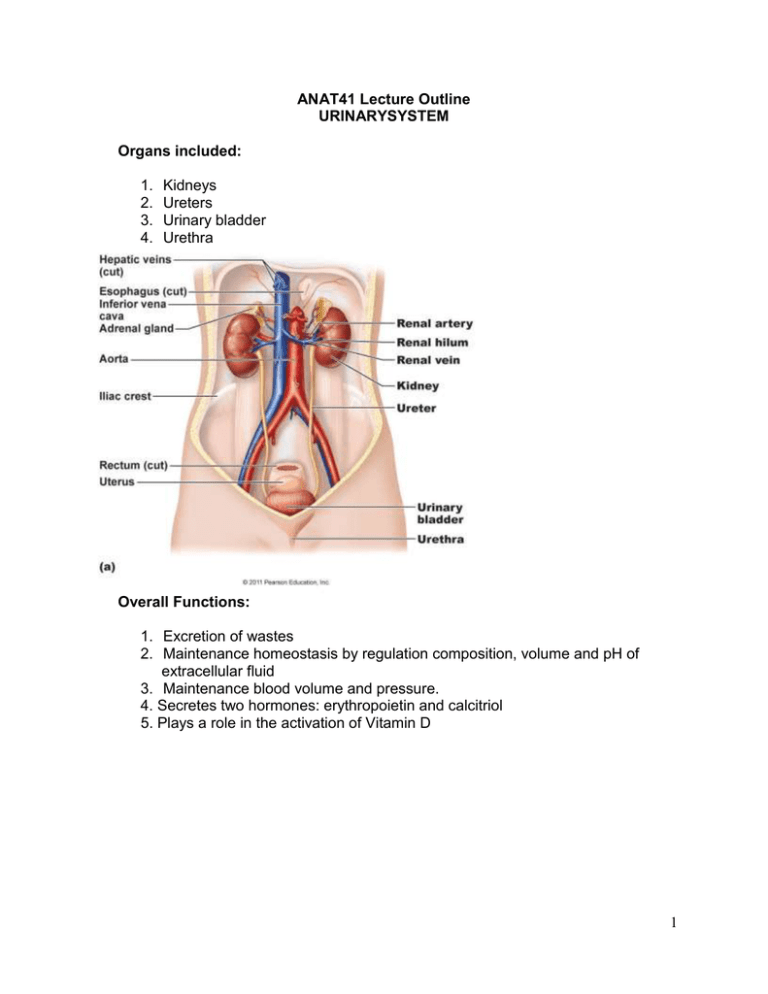
ANAT41 Lecture Outline URINARYSYSTEM Organs included: 1. 2. 3. 4. Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Overall Functions: 1. Excretion of wastes 2. Maintenance homeostasis by regulation composition, volume and pH of extracellular fluid 3. Maintenance blood volume and pressure. 4. Secretes two hormones: erythropoietin and calcitriol 5. Plays a role in the activation of Vitamin D 1 Kidney: The paired kidneys lie retroperitoneal in the abdominal cavity. They lie at the level between T12 and L5 vertebrae. Which kidney lies slightly higher than the other one? Why is this one slightly higher? Coverings that protect the kidney 1. Adipose capsule (perirenal fat) 2. Renal capsule - tough fibrous connective tissue Macroscopic structure: Renal cortex Renal medulla a. renal pyramids b. renal papillae - series of small elevations Calyces a. major calyx - pelvis divides Into 2 or 3 tubes b. minor calyx - each major calyx divides into several more branches, each draining a papilla Renal pelvis - Superior end of the ureter that expands to form a funnel shaped sac (pelvis) inside the renal pelvis Renal sinus - medial depression that leads into a hollow chamber Hilum - the medial Indentation where blood vessels, nerves and the ureter leave/enter the kidney 2 Relationship of blood vessels to kidney macroscopic structure: abdominal aorta renal artery interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries (cortical radiate) afferent arteriole glomerulus efferent arteriole peritubular capillaries interlobular veins (cortical radiate) arcuate veins Interlobar veins renal vein Microscopic structure Overview of nephron - the single functional unit of the kidney; approx 1 million in each kidney Parts of the nephron: Renal corpuscle glomerulus a) afferent arteriole b) efferent arteriole Bowman's capsule (glomerular capsule) Renal tubule 1) proximal convoluted tubule 2) loop of Henle 3) distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct 3 Relationship of nephron and collecting duct to macroscopic structure of the kidney: Which structures of the nephron lie in the medulla and cortex of the kidney? Processes involved in urine formation: 1. Glomerular filtration - forcing of fluids and dissolved substances smaller than a certain size through a membrane by pressure What determines filtration pressure? What are the factors that affect filtration rate? Glomerular hydrostatic pressure Colloid osmotic pressure Capsular hydrostatic pressure 2. Tubular reabsorption - movement of substances from the tubular fluid back into the blood within the peritubular capillaries 4 What factors enhance tubular reabsorption: 1. Active reabsorption of sodium 2. Passive reabsorption of chloride 3. Passive reabsorption of water Proximal convoluted tubule - mainly takes place here Which ion is reabsorbed into the PCT at a rate of 70%? Sodium b. Loop of Henle c. Distal convoluted tubule d. Collecting duct 3. Tubular secretion - movement of substances from the blood within the peritubular capillaries into the renal tubule 5 Hormonal control of Urine Concentration and Volume: Control of salt and water balance 1. Aldosterone - secreted by the adrenal gland in response to changes in blood concentration of sodium and potassium What part of the nephron does aldosterone act upon? What ions does this part of the nephron reabsorb and secrete? Control of salt and water balance 2. ADH - anti-diuretic hormone - stimulates reabsorption of water Final product Is Urine: Amt excreted in urine = Amt filtered @ glomerulus - amt reabsorbed by the tubule + amt secreted by tubule 6 Normal constituents of urine: water urea & ammonia = uric acid = phosphates, sulfates, salts(NaCl, KCl) urobilin = Abnormal constituents of urine: glucose, ketones, protein, blood cells Ureters: Function -transports urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder What tissue makes up the ureters? Urinary bladder: has 4 layers Function - store urine before release from the body What body cavity does the urinary bladder lie in ? What type of tissue make up each of the 4 layers. 1. Mucous coat 2. Submucosa 3. Muscular coat 4. Serous coat 7 Urethra: begins In the floor of the urinary bladder to the exterior of the body Function? Female urethra vs. Male urethra 8







