STD/STI Powerpoint
advertisement

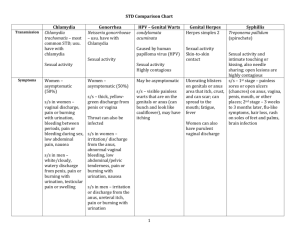
Sexually Transmitted Diseases All statistics and facts were provided by the Centers for Disease Control 2011 facts. STDs are a significant health challenge facing the United States. CDC estimates that nearly 20 million new sexually transmitted infections occur every year in this country, half among young people ages 15–24. Each of these infections is a potential threat to an individual’s immediate and long-term health and well-being. In addition to increasing a person’s risk for HIV infection, STDs can lead to severe reproductive health complications, such as infertility. According to CDC's 2009 National Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) many adolescents begin having sexual intercourse at early ages: • 46.0% of high school students have had sexual intercourse • 5.9% reported first sexual intercourse before the age of 13. • • 24.2% of high school students had had five or more drinks of alcohol in a row on at least 1 day during week • 20.8% had used marijuana • Both casual and chronic substance users are more likely to engage in high-risk behaviors, such as unprotected sex, when they are under the influence of drugs or alcohol Exams for STD/STI’s Women -Pap Smear & Blood Tests -Urine Sample Men -Urethral Culture (Wire Loop) -Blood Test -Urine Sample Washing the genitals, urinating, or douching after sex will not prevent any STD. When should I get tested? • In between each of your sexual partners • As a couple before sexual activity begins • Within 6 months of intercourse with the same partner The only way to prevent STD/STI’s is getting tested or abstaining from sexual activity. Why such an increase in STD’s??? In Adolescents • Physicians frequently fail to inquire about sexual behavior during an exam • Frequently have unprotected sex • Are biologically more susceptible to infection • Engaged in partnerships that are often limited in duration • Multiple sex partners in their youth Bacterial vaginosis (back TEER ee el / va gin NO sus) (BV) is a condition in which there is an overgrowth of some kinds of bacteria in the vagina. BV can cause symptoms such as vaginal discharge. Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) is the most common vaginal infection in women of childbearing age. ProtectYourself+ProtectYourPartner How can I lower my risk of a Yeast Infection ? Scientists do not fully understand BV and do not know the best ways to prevent it. However, it is known that having a new sex partner or having more than one sex partner increases your risk of getting BV. To lower your risk of getting BV: • Do not have sex. • If you decide to be sexually active, limit the number of partners you have. • Do not douche. • Use all the medicine prescribed to treat BV, even if the symptoms go away. Women with BV may have an abnormal vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. Discharge, if present, is usually white or gray; it can be thin. Women with BV may also have burning during urination or itching around the outside of the vagina, or both. However, most women with BV report no signs or symptoms at all. Women do not get BV from toilet seats, bedding, or swimming pools or from touching objects around them. Women who have never had sex rarely get BV. When should I be tested? You should be tested for BV if you have any symptoms (like a vaginal discharge) or if your female sex partner has BV or symptoms that could be BV. Can I get BV again after I’ve been treated? Yes, you can get BV again. What happens if I don’t get treated? You may have a higher risk of getting another STD, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. You may have a higher risk of getting HIV infection if you have unprotected sex with an HIV-infected partner Facts Chlamydia (cla MI dee a) is a sexually transmitted disease (STI). Anyone can get chlamydia. It is very common among teens and young adults. Young, sexually active females need testing every year. Most people who have chlamydia don’t know it. Often the disease has no symptoms. You can pass chlamydia to others without knowing it. Chlamydia is easy to treat and cure. If you do not treat chlamydia, it can lead to serious health problems. HOW CAN I LOWER MY RISK FOR CHLAMYDIA? The surest way to prevent chlamydia is not to have sex or to have sex only with someone who’s not infected and who has sex only with you. Washing the genitals, urinating, or douching after sex will not prevent any STD. •Condoms can reduce your risk of getting chlamydia if used the right way every single time you have sex. How does someone get chlamydia? You can get chlamydia by having sex with someone who has it. “Having sex” means having anal, oral, or vaginal sex. If you are a pregnant woman who has chlamydia, you can pass the infection to your baby. Most people who have chlamydia don’t know it since the disease often has no symptoms. Chlamydia is the most commonly reported STD in the United States. Sexually active females 25 years old and younger need testing every year. Easy to cure, chlamydia can impact a woman’s ability to have children if left untreated. What are the symptoms of chlamydia? IF YOU ARE A WOMAN You can get chlamydia in the vagina or rectum. You may not notice any symptoms. But if you do have symptoms, you might notice: •An unusual discharge from your vagina. •Burning when you urinate. •Pain, bleeding, or discharge from your rectum if you have anal sex. •If the infection spreads, you might get a fever or have pain during sex. IF YOU ARE A MAN You can get chlamydia in the penis or rectum (if you have receptive anal sex). You may not notice any symptoms. But if you do have symptoms, you might notice: •A discharge from your penis. •Burning or itching around the opening of your penis when you urinate •Pain, bleeding, or discharge from your rectum if you have receptive anal sex. Chlamydia—Rates by Age and Sex, United States, 2011 cdc.gov If I have chlamydia, what does that mean for my partner? •Your partner may have chlamydia, too. •Tell your recent sex partners, so they can get tested and treated. •Avoid having sex until you’ve both finished your treatment, so you don't re-infect each other. How is chlamydia treated? •Chlamydia can be treated and cured with antibiotics. •Finish all of the medicine to be sure you are cured. •Do not share your medicine with anyone. You need all of it. •If you still have symptoms after treatment, go back to see the doctor. •You should get tested again three or four months after you finish your treatment. This is especially important if you are not sure if your partner was also treated. Can I get chlamydia again after I've been treated? Yes, you can get chlamydia again. You can get it from an untreated partner or a new partner What happens if I don't get treated? IF YOU ARE A WOMAN •Chlamydia stays in your body if it is not treated. It can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a serious infection of the reproductive organs. •PID may cause serious health problems if you become pregnant. PID can also cause damage that makes you unable to get pregnant. •PID may cause chronic pain in your pelvic area. •If you have untreated chlamydia, you could pass the infection to your baby when giving birth. Chlamydia can cause serious health problems for babies. •If you have untreated chlamydia, you have a higher chance of getting HIV if you have unprotected sex with an HIV-infected partner. IF YOU ARE A MAN •Chlamydia rarely causes long-term health problems in men. You may get an infection in the tube that carries sperm from the testes. This infection can cause pain and fever. In rare cases, this infection may prevent you from fathering children. Gonorrhea Anyone who is sexually active can get gonorrhea. • It is more common among teens and young adults. • Many people who have gonorrhea don’t know it. Especially in women, the disease often has no symptoms. • You can pass gonorrhea to others without knowing it. THE FACTS Gonorrhea is easy to treat and cure, but if you do not treat gonorrhea, it can lead to serious health problems How does someone get gonorrhea? • You can get gonorrhea by having sex with someone who has it. "Having sex" means having anal, oral, or vaginal contact. HOW CAN I LOWER MY RISK FOR GONORRHEA? • The surest way to prevent gonorrhea is not to have sex or to have sex only with someone who’s not infected and who has sex only with you. Condoms • Condoms can reduce your risk of getting gonorrhea if used the right way every single time you have sex. Washing • Washing the genitals, urinating, or douching after sex will not prevent any STD. How do you get it? IF YOU ARE A WOMAN You can get gonorrhea in the anus, eyes, mouth, throat, urinary tract, or uterus. Symptoms will vary depending on what part of your body is infected. If you have gonorrhea in the uterus or urinary tract, you might notice these symptoms: • Vaginal bleeding between your periods. • Pain or burning when you pass urine. • Increased vaginal discharge. If you have gonorrhea in the rectum, you might notice these symptoms: Itching, soreness, bleeding, a discharge from your rectum, or painful bowel movements. If you have gonorrhea in the throat, you might notice that your throat is sore. IF YOU ARE A MAN Symptoms are he same as a woman except for if you have gonorrhea in the penis, you might notice these symptoms: Pain or burning when you pass urine. •A discharge from your penis. •Painful or swollen testicles. Gonorrhea—Rates by Age and Sex, United States, 2011 2011-Fig 21. SR When should I be tested? IF YOU ARE A WOMAN You should be tested for gonorrhea if you have: •Any symptoms, like pain or burning when you pass urine or vaginal discharge. •A partner who has gonorrhea or symptoms that might be gonorrhea. •Another STD, such as chlamydia. •If you're pregnant, ask the doctor if you should be tested for gonorrhea. IF YOU ARE A MAN You should be tested for gonorrhea if you have: •A discharge from your penis. You may also feel pain inside your penis. •Pain or burning when you pass urine. •Itching, soreness, bleeding, or rectal discharge, if you have receptive anal intercourse. •A partner that has gonorrhea or symptoms that might be gonorrhea. •Another STD, such as chlamydia. Gonorrhea can be treated and cured with antibiotics but if you don’t test your partner as well, often times you will just get re-infected. Both partners need to be tested and treated before any sexual contact is initiated again. What happens if I don't get treated? Gonorrhea stays in your body if it is not treated. You may have a higher risk of getting HIV infection if you have unprotected sex with a partner living with HIV. Gonorrhea can also spread to the blood or joints. This condition can be very serious. IF YOU ARE A WOMEN •Gonorrhea can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a serious infection that happens when gonorrhea spreads to the reproductive organs. •PID can also cause damage that makes you unable to get pregnant. •Untreated gonorrhea may cause chronic pain in your pelvic area. •If you have untreated gonorrhea, you could pass the infection to your baby when giving birth. Gonorrhea can cause serious health problems for babies. IF YOU ARE A MAN •You may develop a painful condition in the testicles. In rare cases, this may prevent you from fathering children Genital herpes (STD) •Genital herpes is common in both men and women in the U.S. •Most people who have genital herpes don’t know it. There are often no symptoms. •You can pass genital herpes to others without knowing it and oral and genital can be passed to each other as well. •There is no cure for genital herpes, but there are treatments for the symptoms. •Genital herpes does not usually cause serious health problems. What are the symptoms of genital herpes? Genital herpes often doesn’t cause any symptoms. If you do have symptoms, you might notice: •Painful blisters or sores on or around the genitals or anus. These sores typically heal within two to four weeks. •Feeling like you have the flu when the sores are present. •Sores that come back several times within a year. The presence of the sores is called an outbreak. There are two types of genital herpes virus - HSV1 and HSV2. Both types can cause sores or blisters on or around the genitals. HSV1 can also cause sores on the mouth or lips, which are called fever blisters or are commonly known as cold sores. How does someone get genital herpes? •You can get genital herpes by having sex with someone who has it. “Having sex” means having anal, oral, or vaginal sex. •You can also get genital herpes if your genitals touch the infected skin or secretions (like saliva through oral sex) of someone who has it. Sexual touch using the mouth is also another common way of contracting this virus. •You can get genital herpes even if your partner shows no signs of the infection. This is a virus and has no cure! There are treatments for its symptoms. •Some medicines can prevent the blisters or make them go away faster. •If you have several outbreaks in a year, a treatment called daily suppressive therapy can reduce your chance of passing the infection to your sex partners. What can I expect to happen if I have genital herpes? MEN AND WOMEN You can expect to have several outbreaks (usually four or five) a year. Over time you can expect to have fewer outbreaks. You have a higher chance of getting an HIV infection if you have unprotected sex with a partner living with HIV. Knowing that you have genital herpes may make you feel worried or sad. Talk with a doctor about your concerns. PREGNANT WOMEN In rare cases, you could pass the infection to your baby. If you have active genital herpes when you go into labor, the doctor may do a cesarean delivery (“C-section”) so that the baby does not pass through this virus and get the infection to their body. Be sure to tell your doctor if you or your partner has genital herpes. Pictures of Herpes Passed through oral sex On the base of the penis In a women’s pubic hair region Genital human papillomavirus (/pap pil LO ma VY rus/)(HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States. STD At least 50% of sexually active people will have genital HPV at some time in their lives. Most people who have genital HPV don’t know they have it. There are often no symptoms, and it goes away on its own—without causing any serious health problems. HPV is passed on through genital contact (such as vaginal and anal sex). You can pass HPV to others without knowing it. There is no cure for HPV, but there are treatments for the health problems that some types of HPV can cause, like genital warts and cervical cancer. HOW CAN I LOWER MY RISK FOR HPV? The surest way to prevent HPV is not to have sex.If you decide to be sexually active, limit the number of partners you have. The fewer sex partners you have, the less likely you will be to get HPV. Condoms may lower chances of getting HPV, genital warts, or cervical cancer if used the right way every time you have sex. However, HPV can infect areas that are not covered by a condom— so you should not expect condoms to fully protect against HPV. Washing the genitals, urinating, or douching after sex will not prevent any sexually transmitted disease. Females and males can get vaccinated to protect against the types of HPV that most commonly cause health problems. These vaccines are given in 3 doses over 6 months. The vaccines are most effective when all doses are received before a person has sexual contact with his or her first partner. Get the HPV Vaccination before you begin any sexual activity and this is available for both females and males at your doctors office. Discuss this option with your parents. How does someone get HPV? Anyone who has ever had genital contact with another person can have genital HPV. Both men and women can get it - and pass it on - without even realizing it. What are the health effects of HPV? Genital HPV does not cause health problems for most people. There are many types of HPV. All HPV infections are either low-risk or high-risk. Low-risk HPV infections can cause genital warts. The warts are usually painless and not a serious problem. They can be flat or raised, single or in groups, and small or large. Without treatment, the warts may grow in size and number, or they may go away on their own. Women with HPV might have warts on the vagina, vulva, or cervix. Men with HPV might have warts on the penis, scrotum, or groin. Both men and women can have genital warts on the anus or thigh. High-risk HPV infections can sometimes develop into cancer of the cervix (the opening of the womb). These infections may also lead to other cancers, such as anal cancer. In some people, high-risk HPV infections can persist and cause cell changes. If these cell changes are not treated, they may lead to cancer over time. It is only persistent HPV infections (the kind that don’t go away for years) that put people at risk for cancer. The types of HPV that can cause cancer are not the same as the types that can cause genital warts. Most types of HPV do not cause cancer bur regular yearly pap test screenings in women are necessary to screen these types out. IF YOU ARE A WOMAN It’s important to know about the link between HPV and cervical cancer and about the steps you can take to prevent this disease. Getting 3 doses of an HPV vaccine and getting regular screening can prevent cervical cancer. One HPV vaccine brand (Gardasil) can also prevent most genital warts. It’s important to know about the link between genital HPV and cervical cancer and about the steps you can take to prevent this disease. Cervical cancer can be prevented with regular Pap tests and follow-up. Pap tests can find problems in the cervix that are caused by HPV. IF YOU ARE A MAN It’s important to know that you can have genital HPV—and pass it to your partner—even if you have no symptoms. Some types of HPV can lead to cancer of the anus and penis, but these cancers are rare in men with healthy immune systems. There is one vaccine brand (Gardasil) to prevent the most common problem caused by HPV in men, genital warts. This vaccine is available for 9-to-26 year-old males. Can HPV be treated? •There is no treatment for genital HPV itself. Most of the time, though, your body fights off the virus on its own and you can get the HPV Vaccination to lower your risk of 6 of the most common types of HPV that cause cervical cancer. •There are treatments for the health problems that genital HPV can cause, like genital warts, cervical changes, and cervical cancer. •Even after genital warts are treated, the virus may remain in the body. This means that you may still pass HPV to your sex partners. What about a vaccine? •The FDA has approved a vaccine that protects against four types of HPV. Together, these four types of HPV cause 7 out of 10 cases of cervical cancer and 9 out of 10 cases of genital warts. •Experts on vaccines have recommended that all girls and boys should get the vaccine when they are 11 or 12 years old. Men and women between 13 and 26 years old can also benefit from the vaccine. Different Types of Warts Different types of Warts Syphilis - STI Bacterial Infection Spread from direct contact with infection 4 Stage infection Primary Stage – Single Sore (Chancre) appears & lasts 3-6 weeks Secondary Stage – Skin Rash & Lesions. Starts on the hands and feet – red rash Late & Latent Stage – rash is gone and no symptoms appear but spreads throughout the body and enters the nervous system. If you go without treatment, disease spreads to internal organs, liver, bones, vessels, brain, & heart. Syphilis Rash & Cancre THE FACTS Both men and women can get trichomoniasis. Easy to treat & cure with an antibiotic You can pass trichomoniasis to others without knowing it. Many people who have trichomoniasis don’t know it. The infection often has no symptoms. Women are more likely than men to get symptoms. HOW CAN I LOWER MY RISK FOR TRICHOMONIASIS? The surest way to prevent trichomoniasis is not to have sex or to have sex only with someone who’s not infected and who has sex only with you. Stop having sex and see a doctor right away if: • You notice any unusual discharge. • You feel burning when you pass urine. Condoms can reduce your risk of getting trichomoniasis if used the right way every single time you have sex. Washing the genitals, urinating, or douching after sex will not prevent any STD. How does someone get trichomoniasis? You can get trichomoniasis by having vaginal sex with someone who has it. Women usually get the infection in the vagina. Men usually get the infection in the urethra (urine canal). Women can get the disease from infected men or women. Men usually get it only from infected women. IF YOU ARE A WOMAN You might notice these symptoms: •An unusual discharge, with a strong smell, from your vagina. •Discomfort when you urinate and when you have sex. •Irritation or itching around your genitals. IF YOU ARE A MAN Most men who have trichomoniasis don’t have any symptoms, but you might notice: •An irritation or burning feeling inside your penis. A discharge from your penis. •Can cause infections in the urethra or prostate gland Many people show no symptoms and don’t find out they have this parasite until they get an STD test. Harder to diagnose in men than women. Pubic "Crab" Lice •Adult pubic lice are 1.1-1.8 mm in length. Pubic lice typically are found attached to hair in the pubic area but sometimes are found on coarse hair elsewhere on the body (for example, eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, mustache, chest, armpits, etc.). •Pubic lice infestations are usually spread through sexual contact. •Both over-the-counter and prescription medications are available for treatment of pubic lice infestations. Make sure the over the counter medicine is safe for genital use. •Lice can not jump or fly, but only crawl slowly so you can not get pubic lice from a public toilet seat unless you sit directly onto the lice itself. •Lice can live outside of the human body for 48 hours. •Lice can be spread from clothing, bedding, towels if the infected person was in direct contact with them – the best way to disinfect lice is in the dryer on high heat for 20 minutes. Water will not destroy lice. Pubic Lice & Eggs Hep A ViralHepHepatitis B Liver Disease Hep C Feces & contaminated Food Sex, Blood or Sharing Needles Who is at risk? Who is at risk? Who is at risk? • Children & young adults •Anyone can be infected, but adults have the most risk, IV drug users, anal sex and anyone having unprotected sex. >300,000 cases each year in the US 1 million chronically infected. •Before 1990, the risk came in blood transfusions, now the sharing of needles and inadequate sterilization of needles in tattoo or body piercing as well Symptoms •Drug IV users account for 50% of the infections today • Eat food by a person who has Hep A or someone who didn’t wash their hands after using the restroom & handled food • Drink water or eat shellfish contaminated by sewage Symptoms •Lack of energy, diarrhea, fever, nausea, stomach pain, and yellowing of eyes or skin. •Symptoms last 1-6 weeks •40-180 days after you get the virus, you will get flu like symptoms with fatigue, nausea and vomiting. Can also cause muscular pain, sore throat, headache and jaundice. •Spread through sexual contact and IV drug use. Piercing, tattoos, razors can also spread Hep B Blood or from infected body fluids •4 million Americans are infected Symptoms •Same as Hep B •Spread through blood, mainly sharing of needles, but sexual contact may play a role. •80% show no symptoms • Hep A & B are vaccine preventable • Hep C is the most common chronic blood borne infection in the US. – Approx 2.7 million are chronically infected. – They have therapy for HCV patients, but no vaccine will be available, due to the complexity of its mutation process. – Avoid, iv drug use, street tattoos, sharing of needles, razors, or tooth brushes of infected persons or accidental needle sticks in health settings Bacterial Curable w/ antibiotics Chlamydia Gonorrhea Syphilis Yeast Infection Viral Parasites No Cure Available Herpes Simplex Genital Warts Antibiotic Treatment Trichomonas Pubic Lice Viral Hepatitis HIV *Antibiotic treatment for symptoms may be available All statistics and facts were provided by the Centers for Disease Control 2011 facts. How do I prevent myself from contracting an STD? •Get an STD test after every relationship that involved sexual activity and ask to see the results – do not go by word of mouth •Consistent and correct use of latex condoms with nonoxial-9 spermicide will lower your risk however, many std’s are transmitted through sexual touch so condoms do not provide protection prior to intercourse •Be abstinent from sexual behaviors – sexual touch and intercourse •Involve yourself in monogamous relationships •Spend your time getting to know your partner without sexual activity and form honest and open communication between each other. •Know and set sexual goals for YOU prior to getting involved in a relationship. These are your goals and should not change no matter who your partner is. Communicate openly and honestly and hold your partners accountable to respect your goals. When should I get tested? Chlamydia testing every year for women (sexually active) Annual HIV Tests (sexually active and IV drugs) If you have unprotected sex If you have had sex with someone whose history of sex partners and or drug use is unknown to you or if you or your partner has had many sexual partners, then you have more of a chance of being infected with HIV. Both you and your new partner should be tested for HIV, and learn the results, before any sexually activity occurs. Where can I get tested for HIV/STD’s in Spokane? Local Doctors Office Planned Parenthood Clinics Spokane County Health District Personal Physicians Office Pregnancy Clinics Home Test Kits