Plant Systems Notes plantsystems12
advertisement

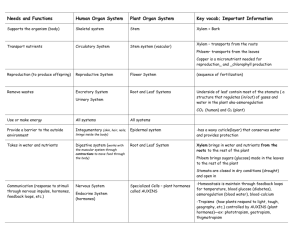
7th Grade Science LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the basic structure and function (job) of the tissues, organs, and organ systems of plants Consider the similarities between animal systems and plant systems Plant CELLS (review) Have all the same basic parts as animals EXCEPT also have a CELL WALL and CHLOROPLASTS Larger vacuoles for storing water Usually have a more square shape Plant TISSUES Tissues = cells that are working in a team to do the same job (function) Are the “circulatory system” of the plant Both are TUBES used for transport Xylem (pronounced zi-lem) tissue is made of tubes that carry WATER and MINERALS (*usually upward from the roots to the rest of the plant) Usually xylem tubes are larger (in diameter) Phloem (pronounced floem) tissue is made of tubes that carry FOOD (or SUGARS) (*usually downward from the leaves to the rest of the plant) Phloem Tube Form the “veins” in leaves Also called “vascular” tissue Each line = a vein (made of xylem & phloem tissue) Xylem Tissue Phloem Tissue Plant ORGANS Organs = 2 or more tissues working together to do the same job (function) Jobs of a Root: Absorb water & minerals from the soil. Transport water & minerals up to stem & leaves. Anchor the plant in soil. Store food (ex. carrot, radish, & turnip) Jobs of a Stem: To support leaves and flowers To transport water, minerals, and food To store and sometimes make food Jobs of Leaves Take in sunlight to make food (photosynthesis) Chloroplasts are the organelle that make this possible in plant cells Chlorophyll is the molecule in green parts of plants that uses the energy in sunlight to turn water (H2O) and carbon dioxide gas (CO2) into sugar (glucose— C6H12O6) and oxygen gas (O2). This process is called photosynthesis. Leaves come in many sizes and shapes; they are often used to help identify plants. Plant spines (like cactus spines) are actually modified leaves Label your diagram as we go! (Add the numbers and arrows!) leaf is made of many layers that are sandwiched between two layers of tough skin cells (called the epidermis). Label as #1 2 A 1 The epidermis also secretes a waxy substance called the cuticle (2). These layers protect the leaf from insects, bacteria, and other pests. 1 Among the epidermal cells are pairs of sausageshaped guard cells (3). Each pair of guard cells forms a pore (called stoma; the plural is stomata-4). Gases enter and exit the leaf through the stomata. 4 3 3 Most food production takes place in mesophyll cells. Gas exchange occurs in the air spaces between the oddly shaped cells of the spongy mesophyll (5). 5 Veins (6) support the leaf and are filled with vessels that transport food, water, and minerals to the plant through branches. 6 Photosynthesis by Brainpop Autumn Leaves by Brainpop Leaves Video Clip-Discovery Channel Jobs of Flowers reproductive system of seed plants PETALS Parts of the flower include: opetals Parts of the flower include: sepals SEPALS Parts of the flower include: opistil (the female reproductive organs) Parts of the flower include: o stamens (the male reproductive organs). Can you identify the male and female parts of this flower? Flowers produce fruits, which grow seeds that can mature into new plants GERMINATION = when a seed starts growing SEEDS Can you see the new baby plant at the bottom of the peanut? FRUITS come from FLOWERS! *Anything that has SEEDS on the inside is a FRUIT!!! Pollination by Brainpop Plant Growth by Brainpop Flower Parts by Discovery Channel Extreme Plant Adaptations—Discovery Channel Sources