Revising River Landforms
advertisement

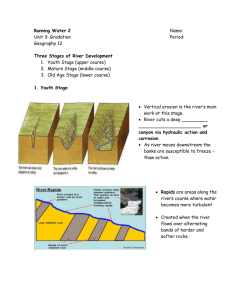
Revising River Landforms You need to know about these river landforms; Erosion Landforms 1. Waterfalls and gorges 2. V shaped valleys (to show you understand vertical erosion) Erosional and Depositional Landforms 1. Meanders and Ox Bow Lakes Depositional Landforms 1. Levees 2. floodplains Most commonly in the exam you will get a 4 mark question on how one of these features is formed such as “explain the formation of an oxbow lake.” (2011) The mark scheme for this question was: Level 1 Basic (1-2 marks) Simple points. Order not correct – jumps about. Sequence may be incomplete. CMI annotation • L1 Simple points, incomplete sequence Level 2 Clear (3-4 marks) Complete, clear, statements. Statements are developed and linked. Sequence and formation of ox bow lakes is complete and clear. So the way to get better and full marks is to: 1. 2. 3. 4. Have the sequence (order) correct Explain as well as describe the way the landform is made Use key words Try to give an example (even if you aren’t asked for one) To help you gain top marks in such questions we have designed these revision aids for each of the landforms you need to know about. Simply arrange these statements into the correct order. When you go in to the exam you should be confident that you know how to explain how any of these has been formed. Waterfalls and Gorges 1/ As the step gets more and more eroded it becomes a waterfall 3/ As the waterfall retreats further upstream this creates a gorge 5/ The softer rock erodes more quickly than the harder rock causing a ‘step’. These can turn into rapids. 7/ Apart from the abrasion what other erosion is happening? 2/ Water flows over hard rock and then soft rock 4/ The collapsed material causes abrasion of the soft rock which creates a plunge pool 6/ The hard rock is undercut by erosion. It collapses and the waterfall retreats up stream Example: High force on the River Tees on NE England V shaped Valleys 1/ Steeper land means more vertical erosion than lateral erosion 3/ In the upper course of the river basin land is steeper 2/ This creates V- shaped valleys 4/ Example: High force on the River Tees on NE England Meanders 1/ So more deposition happens 2/ As it is shallower there, water here and slip off slopes are goes slower on the inside bend created 3/ As it is deeper there, water 4/ So more erosion happens on goes faster on the outside of a the outside bend and river cliffs bend are formed 5/ Always remember its both erosion and deposition that forms a meander. Which happens where? And what types? (on the River Amazon) Ox Bow Lakes (as meanders grow they can turn into oxbow lakes) 1/ After the flood deposition will cut off the old meander creating an ox bow lake 3/ As a river erodes the outside of the bends more these can get closer together 5/ Link erosion and deposition to the energy of the river. What type of each happens when in this process? 2/ As meanders get close together they leave only a small piece of land called a neck. 4/ When water levels are high in a flood the river can break through the neck. (on the River Amazon) Flood Plains (the flat area of land either side of the river in its lower course) 1/ By spreading out the water slows right down as the land is flatter and there is more friction to slow it down 3/ The deposition on the inside of meanders also helps add to a floodplain 5/ Meanders migrate across the flood plain and so can make it wider 2/ When it slows down on the land it will therefore deposit material creating a flood plain 4/ When the river overflows its banks the water spreads out quickly over the land 6/ this is all about deposition. Make sure you know why it happens. The bit about meanders is a real A/A* part to an answer An example is the land in Laverstock the other side of the road from school. The river is called the River Bourne Levees 1/ Over many floods this process is repeated and the mini wall becomes a levee 3/ This heavy material forms a mini wall by the edge of the river 2/ By spreading out the water slows right down as the land is flatter and there is more friction to slow it down 4/ When the river overflows its banks the water spreads out quickly over the land 6/ By slowing down it will lose energy and so deposit material 5/ The heaviest and biggest material will be deposited first right on the river banks 7/ When the river is high it has 8/ The key to all this is knowing lots of energy so it is transporting when a river deposits and when it lots of material transports or erodes material You know from your Bangladesh flooding video that there are natural levees there (which people have built up as a defence)