FAT - Hatboro-Horsham School District

Nutrients
Nutrients are compounds in food that your body needs to function properly for survival, growth, and energy.
Six Essential Nutrients
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are sugars and starches that the body uses for ENERGY
45% to 65% of your calories should come from carbohydrates
Two types of Carbohydrates: Simple and
Complex
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple Carbohydrates are quickly digested and provide a boost of energy for the body
Found in foods with lots of sugar
They do not usually supply other nutrients and fiber
Simple Carbohydrates
Examples
Table sugar
Brown sugar
Honey
Maple Syrup
Corn Syrup
Fruit
Dairy products
Jams/Jellies
Juices
Soda
Candy
Many Packaged
Cereals
Complex Carbohydrates
Complex Carbohydrates provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than simple carbohydrates
Found in many vegetables and whole grains
Scenario: Eating cereal such as oatmeal will fill you up and give you longer lasting energy than a bowl of sugary cereal due to the way the body processes and uses the carbohydrates.
FAT
Although consuming too much fat is unhealthy, the truth is that fat is necessary for many reasons
Fat is a source of energy for the body
Fat helps protect and cushion vital organs as well as joints
Fat insulates the body
Used for vitamin storage
Three Types of FATS
There are three types of FATS:
Unsaturated Fat
Saturated Fat
Trans Fat
Three Types of FATS
EAT MORE:
Unsaturated Fat
Vegetable oils, nuts, and seafood
*Needed for energy storage*
EAT LESS:
Saturated Fat (worst fat)
Beef, pork, egg yolks, dairy products
Trans Fat
Fried food, processes foods, or baked goods- long shelf life.
*Can cause heart disease*
Cholesterol
A fat liked substance already made by the body and found in foods of animal origin
HDL= Good Cholesterol * LDL = Bad Cholesterol
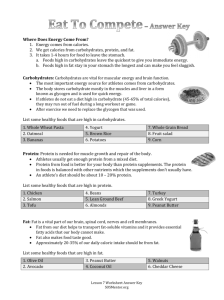
Protein
Protein provides the building materials our body needs to grow and repair itself
Protein is needed for energy
Our body uses protein to build: skin, nails, organs, hair, muscles
When you eat foods that contain protein, our body breaks protein down and reassembles amino acids from protein to create structures it wants to make
Foods That Contain
Protein
Lean Meats
Eggs
Nuts
Seafood
Beans and Seeds
Poultry
Calorie Calculations
A calorie is a measurement of the amount of energy a food contains
Carbohydrates 1g = 4 Calories
Protein 1g = 4 Calories
Fat 1g = 9 Calories
1 pound = 3500 calories
More calories than calories burned = FAT
Sample Calculation
Get out a piece of paper and see if you can do the calculations…..
A slice of bread has 9g of carbohydrates, 2g of protein, and
1g of fat.
Vitamins
Vitamins are compounds that help regulate many vital body processes, including the digestion, absorption, and metabolism of other nutrients
Vitamins boost the immune system, support normal growth and development, and help cells and organs do their jobs. Example: Carrots (Vitamin K = Good
Eyes) Vitamin Chart
Vitamins fall into two categories: fat soluble and water soluble
Two Types
Water –Soluble Vitamins
Vitamins C and B
Vitamins that dissolve in water and are not stored in your body for future use.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamins A, D, E, and K
Vitamins that dissolve into and are transported by fat
They can be stored in fat tissue, the liver, and the kidneys
Minerals
Minerals are inorganic substances that are required by your body in order to develop and grow properly
Some Important Minerals:
Calcium- helps build strong bones and teeth
Iron- helps red blood cells carry oxygen to all parts of the body
Potassium- helps the body maintain the balance of water in the blood and body tissues
Magnesium- helps muscles and nerves function, steadies the heart rhythm, and keeps bones strong
Mineral Chart
Water
Most important nutrient!
60% to 80% of the human body is made up of water
Water assists with the transport of materials in the body by making up most of the liquid part of blood, helping to regulate body temperature, and breaking down food in the digestive system
Female Teens~ 10- 8 oz glasses of water
Male Teens~ 14- 8 oz glasses of water
What is MyPlate?
MyPlate is a tool designed to remind Americans to eat healthy
MyPlate illustrates the five food groups using a familiar meal time visual and a plate setting
MyPlate Guidelines Video
Fruits Group
Choose fresh, canned, frozen, or dried fruits.
Any fruit or 100% fruit juice counts as part of the
Fruit Group.
Make half your plate fruit and vegetables
Healthy Fruit Video
Boys 9-13 1 ½ c. daily
Boys 14-18 2 C. daily
Girls 9-18 1 ½ C. daily
apples
avocados
bananas
blueberries
cherries
lemons
grapes
watermelon
Fruits
oranges
nectarines
peaches
limes
plums
pineapple
Vegetables Group
Choose any vegetable or
100% vegetable juice.
Eat red, dark green, and starchy vegetables.
Make half your plate fruits and vegetables.
Healthy Vegetables Video
Boys 9-13
Boys 14-18
Girls 9-13
Girls 14-18
2 ½ c. daily
3 c. daily
2 c. daily
2 ½ c. daily
Broccoli
spinach
collard greens
squash
sweet potatoes
corn
Artichokes
Vegetables
asparagus
beets
cauliflower
eggplant
cucumbers
bell peppers
potatoes
onions
Protein Group
Select a variety of protein foods to improve nutrient intake and health benefits
In place of meat and poultry, choose 8oz of seafood per week
Keep meat and poultry portions small and lean
Boys 9-13
Boys 14-18
Girls 9-18
5 oz. daily
6 ½ oz. daily
5 oz. daily
lean cuts of beef
lean cuts of pork
chicken
turkey
eggs
almonds
peanuts
lentils
Protein
lean ground beef
lean ground pork
salmon
halibut
tuna
swordfish
shrimp
scallops
crab
Grains Group
Grains can be whole or refined
At least half of all the grains eaten should be whole grains
The Benefits of whole grains
Boys 9-13
Boys 14-18
Girls 9-13
Girls 14-18
Grains
6 oz. daily
8 oz. daily
5 oz. daily
6 oz. daily
Whole Grain
3 oz. daily
4 oz. daily
2.5 oz. daily
3 oz. daily
brown rice
oatmeal
popcorn
tortillas
grits
Grains
pasta
pita bread
whole wheat bread
pretzels
Dairy Group
Foods made from milk that retain their calcium content are part of this group
Choose fat-free or low-fat foods
Boys 9-18
Girls 9-18
3 c. daily
3 c. daily
milk
flavored milk
puddings
ice cream
frozen yogurt
yogurt
ricotta cheese
Dairy
cottage cheese
processed cheese
cheddar cheese
mozzarella cheese
parmesan cheese
swiss cheese
soy milk
The Dietary Guidelines for
Americans
The Dietary Guidelines provide information about how to make smart food choices, balance food intake with physical activity, get the most nutrition out of the calories you consume, and handle food safely
Making smart food choices
Eat a wide variety of foods
Include whole-grains, vegetables and fruits which are rich in complex carbohydrates and fiber
Choose low-fat & fat-free milk products which provide calcium, which is needed to prevent bone loss; and help keep cholesterol down and reduce your risk for heart disease
Get the Most Nutrition Out of
Your Calories
Choose foods that are nutrient dense
Nutrient-dense foods contain lots of vitamins and minerals relative to the number of calories
Nutrient-dense foods are low in saturated fat, trans fat, added sugar, and salt
Examples: lean meats, fish, poultry, & corn
Using the Food Guidelines:
Meals
Breakfast: Don’t skip breakfast; choose whole-grain cereals, low fat milk or yogurt. Limit pastries, eggs, and bacon
Lunch: focus on whole grains, fruit, and vegetables.
Use mustard or ketchup instead of mayo. Try low-fat cheese on pizza
Dinner: Trim excess fat from meats. Instead of fried meats or fish, try them grilled. Choose low-fat dressing, and limit butter.
Using the Food Guidelines:
Snacks
Choose foods with high nutrient density
Try satisfying your sweet tooth with fruit instead of cookies
Make a whole-grain bagel, not a donut, your after-school treat
When you go to the movies, choose unbuttered popcorn
Using the Food Guidelines:
Eating Out
Substitute low-fat milk, water, or fruit juice for shakes and soft drinks
Select the salad bar or broth-based soups in place of fries or onion rings. But go easy on the dressings, cheese, bacon bits, and croutons
Choose a items that are grilled, steamed or broiled; not fried
Ask your server to put half of your meal in a to-go container at the beginning of your meal
Fast Food Choices
Fast food consumption should be limited since it generally includes foods that are high in calories, fat, and sodium
Try to choose smaller portions since larger portion sizes greatly increase the calorie, fat, and sodium content of your meal
Some fast food choices are healthier than others so try to choose the healthier options.
Eating Disorders
Both men and women suffer from eating disorders each year. Eating disorders are a group of serious conditions in which you're so preoccupied with food and weight that you cannot focus on much else
Three main types of eating disorders:
Anorexia Nervosa
Bulimia Nervosa
Binge-eating disorder
Anorexia
Psychological disorder that involves a person starving themselves due to an unhealthy fear of becoming obese
Possible Causes
Low self-esteem or desire to please others
History of troubled relationships
Anorexia
Warning signs:
Eating extremely small amounts of food per day
False impression of their own body image
Obsessed with exercise
Harmful effects:
Damage to the heart
Excessive weight loss
Negatively affects the immune system
Starve to death
Anorexia~ Treatment
People with anorexia usually deny their problem and need encouragement to get help
Doctors, nurses and dietitians work together to stop weight loss and change the person’s eating habits
Mental health worker’s work to address underlying emotional problems
Bulimia
Psychological disorder that involves a person overeating (“binging”) followed by the use of laxatives or purging to keep from gaining weight
Possible causes: same as anorexia, plus
Purge because they feel better emotionally
Purge because they are concerned about weight gain
Bulimia
Possible signs of Bulimia
Unable to control eating binges
Eating too much food too quickly
Eating in private
Cycles of weight gain and loss
Bathroom visits right after eating
Hoarding or storing food
Bulimia
People who suffer from this disorder usually have a false sense of their body image, and they are constantly striving to obtain the “perfect body.”
Harmful effects:
Tooth decay (from excessive vomiting)
Damage to the kidneys
Dehydration
Death
Bulimia~ Treatment
Treatment
People with bulimia are aware of their problem, but are unable to control their behavior. Often ashamed to seek help.
Mental health professionals, nutritionist, dentists, and a team of doctors work together
Binge-Eating Disorder
A disorder characterized by compulsive eating, consuming huge amounts of food while feeling out of control and powerless to stop
Behavioral Symptoms:
Frequent episodes of uncontrolled eating
Feeling extremely distressed or upset after bingeing
No regular attempts to “make up” for bingeing
Binge Eating Disorder
Possible Causes:
Eat to avoid dealing with difficult emotions, such as anger, or with stressful situations
Use food to provide temporary relief
Binges can lead to depression and guilt
Health Risk:
Excess weight gain & unhealthy dieting
Greater risk for diabetes & high blood pressure
Fad Diets
Diets that promise quick weight loss and usually require you to eat specific types of food
The weight that you lose is usually water and/or lean muscle rather than body fat.
Some of these diets can be harmful to your health.
They sometimes do not include exercise which is important for healthy living.
Fad Diets
They limit your food choices and usually keep you from a balanced diet.
These diets do not offer long-term success, and you usually gain back all the weight you lose.
Common Fad Diets
Atkins
South Beach
NutriSystem
Slim Fast
Metabolife 356
Weight Watchers
Paleo
Raw Food
Jenny Craig
Hollywood Diet
Mediterranean Diet
Cabbage Soup