NEW Measurement Notes
advertisement

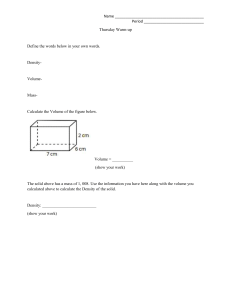
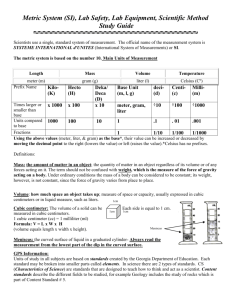
Measurement Notes Basic Units of Measure in the SI: 1. 2. Length- Meters (m) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mass- Kilograms (Kg) Volume- liters (L) for liquids and cubic centimeters (cm³) for solids Weight- Newtons (N) Time- seconds (s) Temperature- Kelvin, but we use Celsius (˚C) Density- g/mL, g/cm³, g/m³ Area- m²or cm² Length- distance from one point to another - Metric ruler is most common instrument for measure Volume- amount of space an object takes up - Three dimensional Three different methods used to figure out volume: 1. The common measurement tool for liquids is a graduated cylinder. - Must take in account for the meniscus 2. This formula is used to find volume for solids. - Volume = Length x Width x Height - Units are either cubic centimeter (cm³) or for larger volumes is it cubic meters (m³) - Sugar cube is about the size of 1 cm³ - One cubic centimeter is equal to one milliliter 3. Immersion is used to find the volume of irregular objects. Meniscus- the curve associated with the top surface of the water in a graduated cylinder - to determine the volume of water, you read the millimeter marking at the bottom of the curve Immersion- the method associated with finding the volume of irregular objects by placing it in water and determining how much the water level rises. Mass- a measure of the amount of matter an object contains - Triple beam balance is the common measurement tool - Never changes with location Triple- beam balance- works by comparing the mass of the object you are measuring to a known mass Weight- measure of the force of gravity acting on an object - Spring scale is the common measurement tool - Varies between locations in the universe Time- an interval between two events usually measured with a watch or clock Temperature- measure of average vibrations of the particles that make up a material (or amount of kinetic energy in a substance) - Measured in degrees with a thermometer Density- measure of the amount of matter that occupies a given space - formula used is Density = Mass/ Volume Area- the amount of surface included within a set of boundaries - Expressed in square units (m²) or (cm²) - formula used is Area = Length x Width - Tool for measuring- must be calculated