Anatomy of the Heart
advertisement

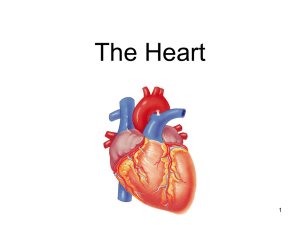
Anatomy of the Heart STD 3251.4.2: Explore the anatomy of the heart and the pathway of blood through this organ. Heart Function • Generates the pressure that propels blood thru blood vessels • Keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate • Helps regulates the body’s blood supply. Human Heart • Weighs less than a pound –About the size of a fist • Hollow, cone shaped organ • Within the mediastinum – the medial cavity of the thorax Landmarks • Apex – Rests on the diaphragm – Points toward the left hip • Base – Points towards the right shoulder • The heart is – Medial to the lungs – Anterior to the esophagus and vertebrae – Posterior to the sternum. Heart Coverings • Enclosed by the double layered pericardium – Fibrous pericardium • outermost layer, protects and anchors – Serous pericardium • 2 layered serous membrane. – Parietal pericardium outer – Visceral pericardium, a.k.a. the epicardium Heart Wall • 3 Layers – Epicardium (visceral pericardium) • Outer layer - Simple squamous epithelium – Myocardium • Middle layer • Fibrous skeleton & Cardiac muscle – Endocardium • Thin, inner layer - simple squamous epithelium • Lines chambers, continues into blood vessels Heart Coverings and Wall Heart Chambers • 4 hollow chambers – 2 Atria • Receiving chambers • Low pressure – 2 Ventricles • Thick walled • Pumps of heart Pulmonary circulation • Runs between the heart and the lungs RIGHT SIDE of heart 1. 2. 3. 4. Right ventricle Deoxygenated blood from veins enter venae cavae Pumps through pulmonary trunk Splits into pulmonary arteries (to lungs) Pulmonary veins carry blood back to left side of heart Pulmonary trunk Pulmonary arteries Pulmonary capillaries Pulmonary veins Left atrium Systemic circulation • Runs between the heart and body tissues LEFT SIDE of heart 1. 2. 3. 4. Left ventricle Blood from left atria enters left ventricle Blood leaves heart by aorta Aorta branches into systemic arteries Blood returns to heart by systemic veins Aorta Systemic arteries Systemic capillaries Systemic veins Venae cavae Right atrium Circulation Heart Valves (4) • One direction flow – Atria to ventricles (AV valves) • Left AV valve (mitral) –Bicuspid (2 flaps) • Right AV valve –Tricuspid (3 flaps) – Semilunar valves • Separates ventricles from their great vessels –Pulmonary semilunar valve –Aoritc semilunar valve Heart Valves AV Valves •Closed during contraction •Open during relaxation Semilunar Valves •Open during contraction •Closed during relaxation Cardiac Circulation • Blood pumping through heart doesn’t directly nourish heart! •Coronary arteries •Base of aorta •Supply oxygen •Cardiac veins •Drain myocardium •Empties into right atrium