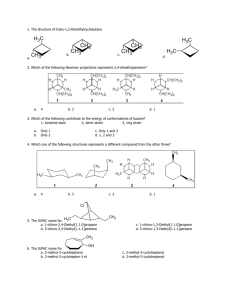
2-butanol
advertisement
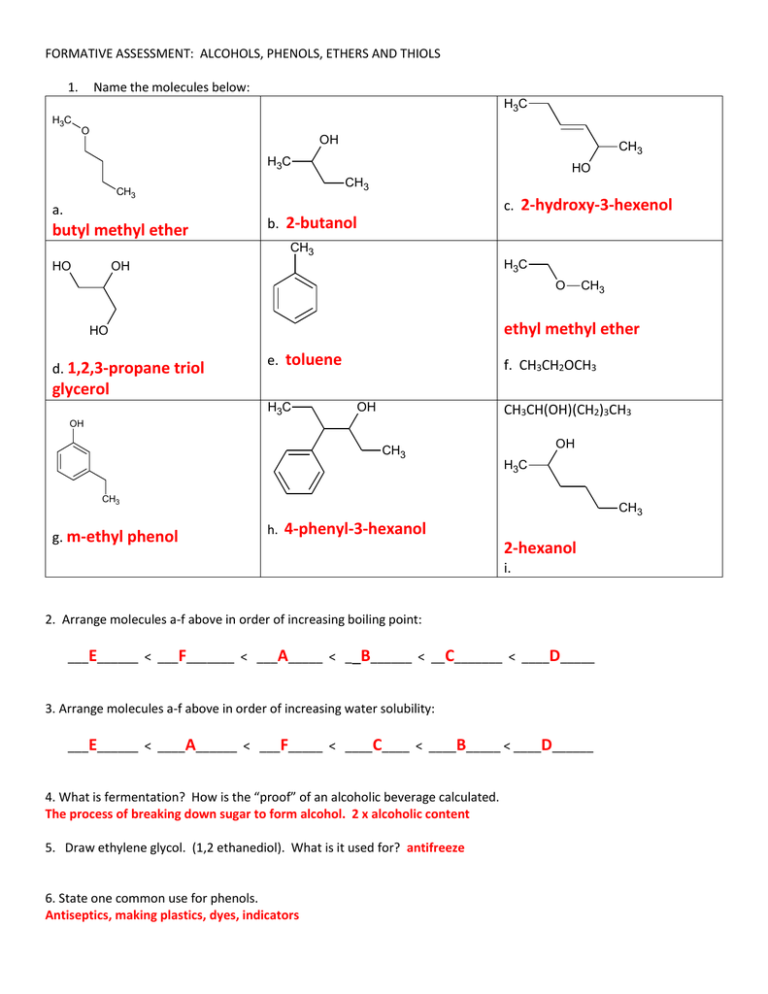
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT: ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS, ETHERS AND THIOLS 1. Name the molecules below: H3C H3C O OH CH3 H3C CH3 a. butyl methyl ether HO CH3 c. 2-hydroxy-3-hexenol b. 2-butanol CH3 HO H3C OH O ethyl methyl ether HO d. 1,2,3-propane triol CH3 e. toluene f. CH3CH2OCH3 glycerol H3C OH CH3CH(OH)(CH2)3CH3 OH OH CH3 H3C CH3 g. m-ethyl phenol CH3 h. 4-phenyl-3-hexanol 2-hexanol i. 2. Arrange molecules a-f above in order of increasing boiling point: ___E______ < ___F_______ < ___A_____ < __B______ < __C_______ < ____D_____ 3. Arrange molecules a-f above in order of increasing water solubility: ___E______ < ____A______ < ___F_____ < ____C____ < ____B_____ < ____D______ 4. What is fermentation? How is the “proof” of an alcoholic beverage calculated. The process of breaking down sugar to form alcohol. 2 x alcoholic content 5. Draw ethylene glycol. (1,2 ethanediol). What is it used for? antifreeze 6. State one common use for phenols. Antiseptics, making plastics, dyes, indicators 7. What was diethyl ether originally used for? Why is it no longer in use? anesthesia, harmful side effects 8. How do alcohols act as acids? How do they act as bases? O R Acids: lose H+ to form: - 1 R 2 + H+ H O R Bases: gain H+ to form: + 1 R 2 H + HO - 9. Write out each reaction below. Include structural diagrams for the products and reactants: a) Isopropyl alcohol (strong acid, above 180◦) acid OH H3C + H3C 180°C CH3 H2O CH2 b) 2- butanol + chloroethane (Na catalyst) + OH CH3 Cl H3C CH3 HCl H3C CH3 c) + O Na CH3 1 propanol (strong acid, 140°C) + H3C acid HO 140 °C CH3 OH + H3C H2O O CH3 d) 1-propanol (oxidation) 2 products (O) H3C OH (O) H3C H3C O O HO e). 2-butanol (oxidation) O OH H3C H3C CH3 f) 2-methyl-2-pentanol (oxidation) CH3 NO REACTION 10. Write out the complete reaction mechanism for one of the reactions above.