ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System
advertisement
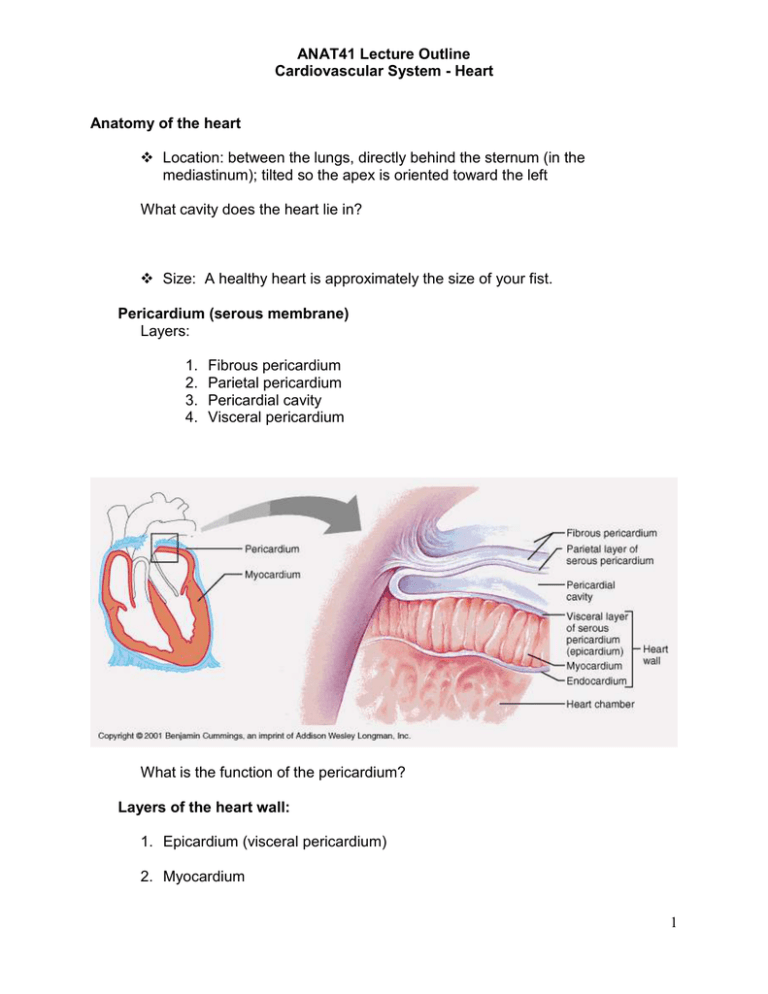
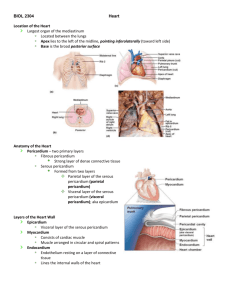
ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart Anatomy of the heart Location: between the lungs, directly behind the sternum (in the mediastinum); tilted so the apex is oriented toward the left What cavity does the heart lie in? Size: A healthy heart is approximately the size of your fist. Pericardium (serous membrane) Layers: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fibrous pericardium Parietal pericardium Pericardial cavity Visceral pericardium What is the function of the pericardium? Layers of the heart wall: 1. Epicardium (visceral pericardium) 2. Myocardium 1 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart 3. Endocardium Which layer is a biopsy taken from? Microscopic anatomy review: Branched Centrally located nuclei Striated Intercalated discs Chambers of the heart A. Atria (singular, atrium) Auricles Interatrial septum B. Ventricles Features: Papillary muscles 2 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart Chordae tendineae Trabeculae Interventricular septum Grooves of the heart A. Coronary sulcus (AV groove): B. Anterior longitudinal (interventricular) sulcus: Valves: What is the purpose of the valves? They prevent backflow. AV valves (atrioventricular valves): (lie between the atria and ventricles) Bicuspid or mitral valve (lies on the left side) Tricuspid valve (lies on the right side) 3 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart What determines when the valves are open and closed? Semilunar valves: (lie between the ventricles and the large vessels that leave those chambers) 4 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart Flow of blood through heart chambers. A. Right atrium 1. Receives blood from: 2. Sends blood to: B. Right ventricle 1. Pumps blood into: C. Left atrium 1. Receives blood from: 2. Sends blood to: D. Left Ventricle 1. Pumps blood into: Heart Sounds –the sounds are created by the closing of the heart valves Which valves produce each sound below? “Lub” “Dup” Summary of circulation through the heart: Inferior Vena Cava, Superior Vena Cava or coronary sinus Right Atrium through tricuspid valve Right Ventricle through pulmonary valve pulmonary artery pulmonary capillaries pulmonary veins Left Atrium through bicuspid valve Left Ventricle through aortic valve aorta systemic arteries systemic capillaries systemic veins 5 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart 6 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart Intrinsic Conduction system of the heart: Neural Automaticity of cardiac muscle Functions of the conduction system 1. Initiate beat of the heart 2. Conduct messages around the heart 3. Coordinate beating of atria and ventricles Components 1. Sinoatrial node (SA node): "pacemaker" 2. Atrioventricular node (AV node) 3. AV bundle (Bundle of His) 4. Right and Left Bundle Branches 5. Purkinje fibers 7 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart The electrical activity of the heart is recorded on an EKG (electrocardiogram). EKG = A. P wave B. QRS complex C. T wave Extrinsic Control of the Heart: Where is the cardiac control center located in the brain? It is controlled by our autonomic nervous system. Do you remember the two subdivisions of this system? 8 ANAT41 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular System - Heart How does each control the activity of the heart? Calculation of cardiac output - The amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle during a minute CO= SV x HR B. Heart rate = C. Stroke volume = D. Cardiac output = Factors that can effect cardiac output: 9