Chapter 14 Notes
advertisement

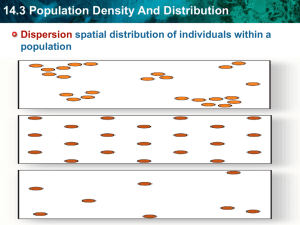
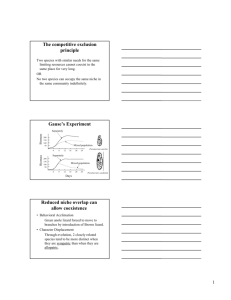
14.1 Every Organism has a Habitat & a Niche Objectives • Differentiate between a habitat and a niche • Differentiate between competitive exclusion and ecological equivalents Vocabulary • Habitat • Niche • Competitive exclusion • Ecological equivalent A habitat differs from a niche. • • A __________________________________ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives. – ___________________________________________ – ___________________________________________ An ecological niche includes all of the factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce. – ____________________________________________ – ____________________________________________ – ____________________________________________ Resource availability gives structure to a community. • ___________________________ can share ________________________ and _________________________. • Competition occurs when two _____________________ use ___________________________ in the same way. • __________________________________________ keeps two species from occupying the same __________. Competitive exclusion has different outcomes. • – . – . – . ____________________________________________ are species that occupy similar niches but live in different geographical regions. 1. What are the 3 parts of an organisms ecological niche? 2. What does the principle Competitive Exclusion say will happen when 2 species compete for the same resource? 3. If a group of mantella frogs were transported to the ecosystem of the poison dart frogs, what might happen to the 2 species populations? 4. Considering the competitive exclusion principle, why may it be harmful to transport a species such as a rabbit, to another habitat where it currently does not exist? 14.2 Community Interactions Objectives • Compare & Contrast interspecfic and intraspecific competition • Describe the 3 types of symbiosis Vocabulary • Competition • Predation • Symbiosis • Mutualism • Commensalism • Parasitism • Parasite • Host • Predator • Prey _________________________________ and ___________________________________ are two important ways in which organisms interact. Competition occurs when two organisms fight for the same limited resource. – Intraspecific competition – Interspecific competition • Predation occurs when one organism captures and eats another. • There are three major types of ___________________________________________ relationships. – _________________________________: ____________________________________________ – _________________________________:_____________________________________________ – _________________________________:_____________________________________________ Identify & Describe 3 examples of symbiosis – Parasites meet their needs as ______________________ (such as leeches) and ___________________ (such as hookworms) 1. During the fall spawning of salmon, grizzly bears fight over space on the banks of a river. What type of competition is this? 2. Describe and give an example of the 3 types of symbiosis 3. How are predation & parasitism similar? How do they differ? 4. After a lion has made a kill birds will sometimes arrive to pick at the carcass. The birds would be considered __________________________ while the lions would be considered ______________________________ 14.3 Population Density & Distribution Objectives • Consider density and geographic dispersal as characteristics of populations • Describe 3 basic types of survivorship curves in relation to reproductive strategies. Vocabulary • Population density • Population dispersion • Survivorship curve • Clumped dispersion • Uniform dispersion • Random dispersion Population density is the ____________________________________________________ that live in a defined area. Scientists can calculate population density. Geographic dispersion of a population shows how individuals in a population are spaced. • Population _____________________________________ refers to how a population is spread in an area. clumped uniform random Survivorship curves help to describe the _______________________________________________________ of a species. A ________________________________________________ is a diagram showing the number of surviving members over time from a measured set of births. • Survivorship curves can be type I, II or III. 1. An Organism has 10 offspring. Two of these offspring die each year over a 5 year period. Is this organism more likely to be a bird or insect? Explain. 14.4 Population Growth Patterns Objectives • Describe 4 characteristics that affect population size • Compare exponential and logistic population growth • Identify factors that limit population growth Vocabulary • Population growth • Immigration • Emigration • Exponential growth • Logistic growth • Limiting factor • Density-dependent limiting factor • Density-independent limiting factor • Carrying capacity Changes in a population’s size are determined by immigration, births, emigration, and deaths. The size of a population is always changing. • Four factors affect the size of a population. – . – . – . – . Population growth is based on available _______________________________. • __________________________________________________________ is a rapid population increase due to an abundance of resources. • • __________________________________________________ is due to a population facing limited resources. • _______________________________________________ is the maximum number of individuals in a population that the environment can support. Ecological factors limit population growth. • A ____________________________________________ is something that keeps the size of a population down. • _______________________________limiting factors are affected by the number of individuals in a given area. • ________________________________limiting factors limit a population’s growth regardless of the density. 1. What 4 factors determine the growth rate of a population? 2. How does carrying capacity affect the size of a population? 3. What is the main difference between a density-dependant limiting factor and a density-independent limiting factor? Give an example of each. 4. What might cause exponential growth to occur only for a short period when a new species is introduced to a resource filled environment. 5. Give an example of how a symbiotic relationship could cause a population to crash. 14.5 Ecological succession is a process of change in the species that make up a community. Objectives • Describe the process of primary succession • Explain the difference between primary and secondary succession Vocabulary • Succession • Primary succession • Secondary succession • Pioneer species • Climax community • Lichen: _____________________________________________________________________________ Succession occurs following a ____________________________________________ in an ecosystem. • • ________________________________________ regenerates or creates a community after a disturbance. – a sequence of ___________________________ changes – damaged _______________________________ are regenerated – new communities arise in previously ______________________________________ There are two types of succession. – Primary succession: _____________________________________________________________ Draw it – Secondary Succession: ___________________________________________________________ 1. How is primary succession different from secondary succession? 2. Why are pioneer species so important for primary succession? 3. Does the process of primary succession take longer in the tropical or arctic areas? Explain. 4. Which reaches a climax community 1st, an area undergoing primary or secondary succession? Explain 5. During succession, what might be the limiting factor for sun-loving mosses as taller plants begin to grow? 6. At what point during primary succession does an ecosystem provide the fewest habitats for an organism? Explain.