Classroom_Instruction_that_Works_Session_1 - Oak-Grove-Tech
advertisement

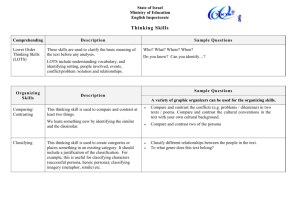
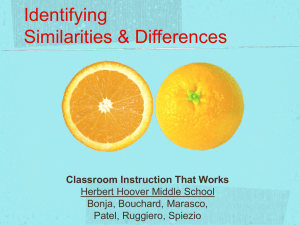
Using Technology with “Classroom Instruction that Works”: Effective Instructional Strategies Three Elements of Effective Pedagogy Instructional Strategies Management Techniques Effective Pedagogy Curriculum Design Instructional Strategies • Classroom Instruction that Works by Robert Marzano • Nine instructional strategies that have been identified as having the greatest impact on student performance Percent vs. percentile • Percent - One part in a hundred – e.g. John correctly answered 90% of the items on the test. • Percentile – The percent of ranked scores falling below a specific score – e.g. John placed in the 90th percentile on a nationally normed exam; he scored higher than 90% of the tested students, and lower than 10% of the students 23-point percentile gain All students’ scores Average student at ineffective school Average student at effective school Effect size and percentile gain Mean -3 2.1% -2 13.6% -1 +1 34.1% 34.1% +2 13.6% +3 2.1% 2 s.d. = effect size 2.0 An effect size of 2.0 translates into a 47.7 point percentile gain (pg 160) Basic research and meta-analysis Study 1 Study 2 Study 3 Study 2 Effect size 0.2 Effect size 1.1 Effect size -0.7 Effect size 0.6 Synthesis study Average effect size 0.4 Categories of Instructional Strategies that Affect Student Achievement Category Avg. Effect size Percentile gain Identifying similarities & differences 1.61 45 Summarizing and note taking 1.00 34 Reinforcing effort & providing recognition .80 29 Homework and Practice .77 28 Nonlinguistic representations .75 27 Cooperative learning .73 27 Setting objectives and providing feedback .61 23 Generating & testing hypothesis .61 23 Questions, cues, and advance organizers .59 22 Using Technology Four Planning Questions and Corresponding Instructional Strategies Planning Questions Instructional Strategies What will students learn? Setting Objectives What strategies will provide evidence of student learning? •Providing feedback •Providing recognition Which strategies will help students acquire and integrate learning? •Cues, questions, and advance organizers •Nonlinguistic representation •Summarizing and note taking •Cooperative learning •Reinforcing effort Which strategies will help students practice, review, and apply learning? •Identifying similarities and differences •Homework and Practice •Generating and testing hypotheses Setting Objectives • Setting objectives = goal setting • “You got to be careful if you don't know where you're going, because you might not get there.” –Yogi Berra • General student population – Goals narrow student focus – Not too specific – Students should personalize the teacher’s goals • English Language Learner population – Clearly defined goals – Combine content and language objectives Goal Setting in the Classroom • Set a core goal for a unit, and then encourage students to personalize that goal by identifying areas of interest to them. Sentence starters like "I want to know" and "I want to know more about . . ." get students thinking about their interests and actively involved in the goal-setting process. • Use contracts to outline the specific goals that students must attain and the grade they will receive if they meet those goals. Surveys/Forms Student goal form created in Google Documents. Source:339 Web (http://339web.blogspot.com/2008/04/google-forms-for-student-goals.html) KWHL Setting Objectives Word processing software Word Openoffice tables X Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming X http://www.mywebspiration.com/launch.php Data Collection tools http://surveymonkey.com Multimedia Web Resources http://rubistar.4teachers.org/index.php Communication Software http://room613talk05.edublogs.org/2006/01/10/room-613-student-blogs/ X X X Providing “Dollops” of Feedback • Should be “corrective” in nature – Explanation of why an answer is correct or incorrect • Should be timely – Immediate feedback is the most effective • Should be specific to a criterion – Addresses a specific knowledge and skill • Students can effectively provide some of their own feedback – Rubrics, learning logs, blogs, wikis, kwhl+ charts, etc. Rubrics Creative writing rubric created using Rubistar (http://rubistar.4te achers.org) Feedback in the Classroom Class blog Teacher comment Feedback in the Classroom Objective Identify causes of the Great Depression 4—Very Competent 3—Somewhat Competent 2-Some Key Questions Remain X Evaluate governmental responses to the Depression X Describe longterm effects of the Depression still felt today. X Student Self-Assessment Rubric 1—Very Uncomfortable Feedback in the Classroom Classroom Performance System Don’t We Do This Already? • Although common practice in most K-12 classrooms, setting objectives and providing feedback are frequently underused in terms of their flexibility and power. -Robert Marzano X Providing Feedback Word processing software word inserted comments readability Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools SRS-Grading software Multimedia Web Resources http://www.coolmath-games.com/0-coffeeshop/index.html Communication Software http://teacherweb.com/TX/NorthsideEarlyChildhoodCenter/MrsHoelscher/index.html X X X X Providing Recognition • Rewards do not necessarily have a negative effect on intrinsic motivation. • Reward is most effective when it is contingent on the attainment of some standard of performance. • Abstract symbolic recognition is more effective than tangible rewards. • Personalize recognition • Use Pause Prompt and Praise strategy • Use concrete symbols of recognition Providing Recognition Word processing software Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools use of SRS group &individual bonus coupon Multimedia personlized certificate Web Resources Web showcases Communication Software Audioemail http://kidbibs.com/awards/card.htm X X X X Cues and Questions • Cues and questions should focus on what is important as opposed to what is unusual. • "Higher level" questions produce deeper learning than lower level questions. • "Waiting" briefly before accepting responses from students increases the depth of student answers. • Questions are effective learning tools even when asked before a learning experience. Advance Organizers • Advance Organizers should focus on what is important as opposed to what is unusual. • "Higher level" advance organizers produce deeper learning than the "lower level" advance organizers. • Advance Organizers are most useful with information that is not well organized. • Different types of advanced organizers produce different results. Cues, Questions, and Advance Organizers Word processing software Expository, Narrative,Graphic advanced Spreadsheet software rubric excel Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools Multimedia videos (http://ww.teachertube.org http://www.schooltube.com Web Resources Communication Software X X X X Nonlinguistic Representations • A variety of activities produce nonlinguistic representations. • • • • Creating graphic representations. Generating mental pictures. Drawing pictures and pictographs. Engaging in kinesthetic activity. • Nonlinguistic representations should elaborate on knowledge. Nonlinguistic Representation Word processing software (vocabulary clipart) X Spreadsheet software (plotting information earthquakes) Organizing and Brainstorming inspiration X ispiredata..\..\..\..\Program Files\Kidspiration 3\New Word.kid Data Collection tools digital probes video camera Multimedia student creation of ppt or movies give most engaged learning animation Web Resources http://www.dvolver.com/live/movies-293119 Mulitmedia simulations Communication Software X X X X Summarizing • To effectively summarize, students must delete some information, substitute some information and keep some information. • To effectively delete, substitute, and keep information, students must analyze the information at a fairly deep level. • Being aware of the explicit structure of information is an aid to summarizing information. Rule based Summarizing 1. Take out the material that is not important to understanding 2. Take our words that repeat information 3. Replace a list of things with a word that describes the things in the list 4. Find a topic sentence Delete trivial material that is unnecessary to understanding Delete redundant material Substitute super ordinate terms for more specific terms Select a topic sentence or invent one if it is missing Note Taking • Verbatim is the least effective way to take notes. • Notes should be considered a work in progress. • Notes should be use as study guides for tests. • The more notes that are taken, the better. Summarizing and Note Taking Word processing software track changes in word auto summarize Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming inspiration kidspiration Data Collection tools Multimedia combination notes Web Resources google docs cornell notes X X X http://notestar.4teachers.org/teacher/home.jsp X Communication Software wikis blogs X Cooperative Learning • Organizing groups based on ability should be done sparingly. • Cooperative groups should be kept small in size. • Cooperative learning should be applied consistently and systematically, but not overused. • Five Defining Elements – – – – – Positive interdependence Face-to-face interaction Individual and group accountability Interpersonal and small group skills Group processing Cooperative Learning Word processing software Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools Multimedia creating video PPT Web Resources http://webquest.sdsu.edu/webquestwebquest.html X X shared bookmarking http://delicious.com/jmccarthy Communication Software wiki skype X Reinforcing Effort • People generally attribute success at any given task to one of four causes: ability, effort, other people and luck. • Not all students realize the importance of believing in effort. • Students can learn to change their beliefs to an emphasis on effort. – Explicitly teach students about importance of effort – Have students keep track of their effort and achievement Reinforcing Effort Word processing software Spreadsheet software excel effort rubrics EffortRubricExamples.doc Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools survey Multimedia Web Resources Communication Software X X Four Effective Forms of Using Similarities and Differences • Marzano's research indicates there are four processes that identify how items, events, processes, or concepts are similar and different: Comparing Classifying Creating Metaphors Creating Analogies Similarities and Differences • Teach students to use comparing, classifying , metaphors and analogies • Give students a model for the process • Use a familiar context to teach these steps • Give students graphic organizers as a visual clue • Guide students in this process. Gradually give less structure and less guidance Identifying Similarities and Differences • Comparing- identifying similarities and differences between or among things • Classifying- process of grouping based on characteristics • Creating metaphors- process of identifying a general pattern in a specific topic and then finding another, seemingly different topic, with the same general pattern • Creating analogies- identifying relationships between relationships How To…Compare • The Venn Diagram-A fantastic tool for comparing using similarities and differences… • Learning Experience: Citrus A Great Web Site http://gets.gc.k12.va.us/VSTE/2008/1simdiff. htm • This site gives examples of different programs and websites that provides samples of graphic organizers for identifying similarities and differences. • It shows how graphic organizers look in different programs and how to download options for classroom use. • The first sample is from Kidspiration (software program) • Second and third samples are from http://www.readwritethink.or g/materials/venn/ this site allows you to put in the topics and print the diagram Comparing with Comparison Matrix • The first sample is from EXCEL but could also be created in WORD • The second sample is from Inspiration (software program) • The third sample is from: http://www.readwritethink.org /materials/compcontrast/map / The websites listed below all give examples of using the Frayer Model for comparing http://www.justreadnow.com/strategies/frayer.htm http://www.longwood.edu/staff/jonescd/projects/educ5 30/aboxley/graphicorg/fraym.htm http://www.tantasqua.org/superintendent/Profdevelop ment/etfrayermodel.html Classifying: Semantic Feature Analysis Sample: Bonds Bonds Issued by corporations Bearer Bond X Convertible Bond X Corporate Bond X Government Bond Fixed Interest Rate X Zero Coupon Bond X Local Taxing Authority More likely to default Equal to a number of shares of stock X X X X Junk Bond U.S. Treasury X X X X X X X Classifying • A column format can be created in Word and EXCEL Samples of Classifying using Technology • Classifying with word or picture sorting can be done with Kidspiration software • Classifying with a Webbing format can be done in Kidspiration or Insipiration software Classifying: Concept Attainment • • • • Examine the factual information Identify similarities; sort into general categories Name each category Write a topic sentence for each category which generalizes the similarity ___________________________________ • Select five pieces of factual information which best support the topic • Evaluate them by rank ordering them in descending order of importance in supporting the topic sentence Creating Metaphors and Analogies • Metaphors and Analogies are complicated due to the “relationships between relationships.” having students identify these relationships is the focus of instruction • Creating metaphors is the process of identifying a general or basic pattern in a specific topic and then finding another topic that appears to be quite different but that has the same general pattern • Creating analogies is the process of identifying relationships between pairs of concepts - in other words, identifying relationships between relationships. Analogy Graphic Organizer is to Relationship: is to as Interactive Web Sites for Analogies • These are interactive sites for analogies that are free: • http://www.sadlieroxford.com/phonics/analogies/analogiesx. htm • http://www.funtrivia.com/flashquiz/index.cf m?qid=159519 • This website has a free 30 day trial: http://www.quia.com/cb/7146.html Identifying Similarities and Differences Word processing software X Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools Multimedia Web Resources Communication Software X X X Homework • Less homework should be assigned to younger students than to older students. Parent involvement in homework should be kept to a minimum. The purpose of homework should be identified and articulated. If homework is assigned, it should be commented on. Practice • Mastering a skill requires a fair amount of focused practice. While practicing, students should adapt and shape what they have learned. Homework and Practice Word processing software X Spreadsheet software Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools Multimedia Web Resources Communication Software X X X X Generating and Testing Hypotheses • Deductive thinking requires students to apply current knowledge to make a prediction about a future action or event. • Inductive thinking involves students in a process of drawing new conclusions based on information they know or have presented to them. • Teachers should ask students to clearly explain their hypotheses and their conclusions. Research has shown the power of asking students to explain, in a variety of communication modes, their predictions and results Generating and Testing Hypotheses Word processing software Spreadsheet software ex Organizing and Brainstorming Data Collection tools Multimedia Web Resources http://web.wm.edu/hsi/cases/frankfort/frankfort_student.html http://fantasticcontraption.com/ Communication Software X X X