CITW Similarities and Differences
advertisement

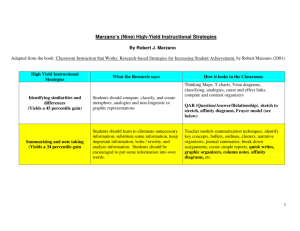
Identifying Similarities & Differences Classroom Instruction That Works Herbert Hoover Middle School Bonja, Bouchard, Marasco, Patel, Ruggiero, Spiezio The Numbers Setting Objectives & Providing Feedback 90.5% Cues/Questions & Advanced Organizers 36% Reinforcing Effort and Providing Recognition 28% Nonlinguistic Representation 19.8% Identifying Similarities and Differences 6% Homework & Practice 7% The Numbers (continued) Generating and Testing Hypothesis 3% Co-operative Learning 5% Summarizing & Note Taking 8% WALT Today’s Objectives: • Understand the purpose and importance of identifying similarities and differences • Determine ways to implement identifying similarities and differences in the classroom • Review examples of identifying similarities and differences activities Categories of Instructional Strategies that Affect Student Achievement Standard Ave. Effect Size Percentile (ES) Gain 1.61 45 31 .31 1.00 34 179 .50 .80 29 21 .35 Homework and practice .77 28 134 .36 Nonlinguistic representations .75 27 246 .40 Cooperative learning .73 27 122 .40 .61 23 408 .28 .61 23 63 .79 .59 22 1,251 .26 Category Identifying similarities and differences Summarizing and note taking Reinforcing effort and providing recognition Setting objectives and providing feedback Generating and testing hypotheses Questions, cues, and advance “Classroom Instruction that Works”, Marzano, Pickering and Pollock organizers No. of ESs Deviation (SD) Create the Environment for Learning Setting Objectives & Providing Feedback Reinforcing Effort & Providing Recognition Cooperative Learning Develop Understanding Cues, Questions, Advanced Organizers Nonlinguistic Representation Summarizing & Note Taking Homework & Practice Extend & Apply Knowledge Identifying Similarities & Differences Generating & Testing Hypotheses How can we use this strategy to improve student achievement? • Give students a model for the process • Use familiar content to teach the steps • Give students graphic organizers • Both teacher directed guidance & student centered opportunities The Big Picture: • The brain works by building connections and associations • The brain remembers more easily things that are unusual Four Thinking Process Tasks … of how items, events, processes, words, things or concepts are similar and different. Higher Level Thinking… Bridging Comparing Known Classifying New Creating Creating Metaphors Analogies ...is identifying a …is identifying and articulating S & D between or among items or ideas. …is identifying characteristics and grouping like items. pattern in one topic, then finding a different topic that has the same pattern. …is identifying and analyzing relationships between ideas. For example, Comparing Recognize and compare the following The identification of important plane and solid characteristics is the key to effective geometric comparison. figures: square, It is these characteristics that are then rectangle, used as the basis to identify similarities triangle, . . . and differences. SD Standard: 3.G.1.1 (Comprehension) -Marzano,2001 Steps to Comparing 1. Select the items you want to compare. 2. Identify the characteristics of the items on which you want to base your comparison. 3. Explain how the items are similar and different with respect to the characteristics you identified. ** Model the process, provide corrective feedback, set the stage for students to provide their own feedback. Graphic Organizers for Comparing Characteristics Items to be compared #1 #2 #3 Similarities Differences Similarities Differences Similarities Differences Similarities Differences Comparison Matrix -more useful to provide a greater number of details -most useful when comparing only two items Science Math & Tech World Language Unconventional Venns Cooperative Learning When there is nothing in common... For example, Invertebrates animals without a backbone or spinal column Vertebrates Classifying The process of grouping things that are alike into categories on the basis of their characteristics. -Marzano,2001 animals with a backbone or spinal column Graphic Organizers for Classification Place Categories in column headings -most useful when all categories are equal in generality -more useful when all categories are not equal in generality Comparison Matrix Author Study: Comparing Texts Affinity Diagrams Identifying Similarities & Differences Classifying Activity • • With your group, classify the geographical features listed on the accompanying sheet into four categories Work together to determine category names Creating Metaphors For example, Love is a rose. The two items in a metaphor are connected by an abstract or non-literal relationship. -Marzano,2001 Steps for Creating Metaphors 1. Identify important or basic elements. 2. Write basic information as a general pattern by • Replacing works for specific things with words for more general things • Summarizing info when possible. 3. Find new information/situation to which the general pattern applies. Graphic Organizer for Metaphors Element 1 Literal Pattern 1 Abstract Literal Pattern 2 It depicts that two elements have somewhat different literal patterns, but they share a common abstract pattern. Element 2 Metaphor Activity • We’ll read you a scenario... tell us how to solve the problem! Carpenter is to hammer as painter is to brush. Hot is to cold as night is to day. Creating Analogies Analogies help us to see how Oxygen is to seemingly dissimilar things are humans as similar. carbon dioxide is They increase our understanding of to plants. new information (most complex). Core is to earth as nucleus is to atom. -Marzano,2001 Steps for Creating Analogies 1. Identify how the 2 elements in the first pair are related. 2. State the relationship in a general way. 3. Identify another pair of elements that share a similar relationship. Graphic Organizers for Analogies Is to Relationship Is to Creating Analogies Coming Up... • January 29th: Whole Group Session: PLC Guidelines Moving Forward • February 26th: PLC Breakout Sessions For Fun...