application program
advertisement

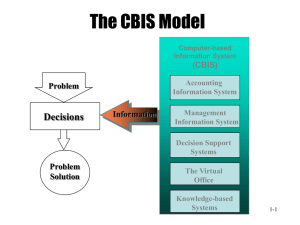
CHAPTER 1&2 Information Systems: Concepts and Management 1.1 Information Systems: Concepts and Definitions Data Item Information Knowledge Information Systems: Concepts and Definitions Information Technology Architecture Information Technology Infrastructure Example: IS (IT Architecture of Online Travel Agency) 2.1 Types of Information Systems Computer-based information systems (CBIS) use computer technology to perform some or all of their tasks and are composed of: Hardware Software A Database A Network Procedures People Information Systems Inside Your Organization Information Technology Outside Your Organization Application Programs An application program is a computer program designed to support a specific task, a business process or another application program. Breadth of Support of Information Systems Functional area information systems Enterprise resource planning systems Transaction processing systems Interorganizational information systems Information Systems Support for Organization Employees Office automation systems Functional area information systems Business intelligence systems Expert Systems Dashboards 2.2 Competitive Advantage and Strategic Information Systems Competitive Advantage Strategic Information Systems (SIS) Strategies for Competitive Advantage Cost Leadership Differentiation Innovation Operational Effectiveness Customer-orientation 2.3 Why are Information Systems Important to Organizations & Society IT will reduce the number of middle managers. IT will change the manager’s job. IT impacts employees at work. IT provides quality-of-life improvements. Managing Information Resources Which IT Resources are Managed and By Whom? The Role of the IS Department Traditional Major IS Functions Managing systems development and systems project management Managing computer operations Staffing, training, developing IS skills Providing technical services Infrastructure planning, development, control New (Consultative) IS Functions Initiating and designing strategic information systems Incorporating the Internet and e-commerce into the business Managing system integration Educating non-IS managers about IT Educating IS staff about the business Supporting end-user computing Partnering with executives Managing outsourcing Innovate Ally with vendors and IS departments in other organizations Supporting End Users One form of end-user support is the help desk, where IS staffers help users troubleshoot problems with their systems. This video shows the first help desk.