9/30 Neuron Foldable & Nervous System Anatomy
advertisement
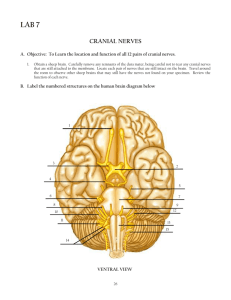
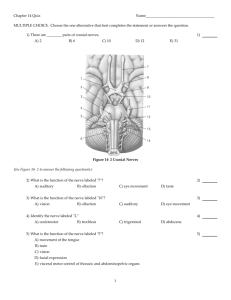
Science Starter 1. List the 5 senses 2. What is the difference between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system? 3. What do anterior and posterior mean? Today’s Agenda • Science Starter • Neuron Foldable (30 minutes) • Nervous System Anatomy • Cranial Nerves Practice • Exit Quiz Neuron Review FOLDABLE! 1. Label 2. Describe the structures and their functions in the boxes 3. Color the foldable 4. Place it in your binder with your Unit 3 notes! **Use your notes, internet, and book (ch.7) to complete today during class** Neuron Review Unit 3: The Nervous System Objective 3.4: Nervous System Anatomy Peripheral Nervous System The spinal nerves comes out of the spine, and the cranial nerves come out of the brain directly. A. The 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves Figure 14.8 I. OLFACTORY Sense of smell II. OPTIC NERVE Transmits information from the eye’s retina. VISION III. Oculomotor Nerve Controls most of the muscles of the eye that move the eyeball. IV. Trochlear Nerve Innervates an extrinsic eye muscle, eyelid V. Trigeminal Nerve This is the main sensory nerve of the face. It has a large branch that passes through the foramen of the skull. It has three parts. VI: Abducens Controls one of the eye muscles (lateral rectus). VII. Facial Nerve ●Innervates the muscles of facial expression. ●BELL’S PALSY is damage of the facial nerve causing paralysis on one side. VIII. VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR Hearing and balance. (also called Auditory nerve) IX: GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL ●pharynx, tongue ●swallowing, speech, saliva X. Vagus Nerve ●(vagrant = “wanders”) - the only cranial nerve that travels into the abdomen. ●This is the most important cranial nerve because it innervates all of the organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities XI. ACCESSORY NERVE ●Enters the skull through foramen magnum ●It just supplies the shoulder muscles. XII. HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE ●Supplies the tongue. ●Damage causes impairment of speech. I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Occulomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducens sense of smell sight move eyelids move eyes face, jaw, chewing eyes VII. Facial facial expressions VIII. Vestibulocochlear sense of equilibrium, (Auditory) hearing IX. Glossopharyngeal X. Vagus XI. Accessory XII. Hypoglossal pharynx, tongue major organs, viscera shoulders tongue Need to know all of the cranial nerves ? On Old Olympus Towering Top A Fin And German Viewed A Hop B. Spinal Nerves I. Cervical nerves- neck, shoulder, arms II. Thoracic nerves- chest, trunk, abdominal III. Lumbar nerves- butt, thigh, leg movement IV. Sacral nerves- lower body sensation V. Coccygeal nerves- tail bone ROOTS Each nerve emerges from the spinal cord at points called ROOTS Dorsal Root Ganglion Ventral root ganglion C. Spinal Nerve Roots • Afferent Nerve (AT): Towards the central nervous system, sensory information, dorsal (back) • Efferent Nerve (EXIT): Away from the central nervous system, motor information, ventral (front) Cranial Nerves Worksheet • Color code the front of the worksheet using any colors you choose • Answer the questions on the back by matching the nerve with its description! Exit Quiz 1. How many cranial nerves are there? 2. How many of the cranial nerves are associated with the eyes? 3. You lose feeling in your legs, which of the 5 spinal nerves could be effected? 4. Describe how a sensation results in movement using the terms: afferent/efferent, spinal cord, skin, muscle