File
advertisement

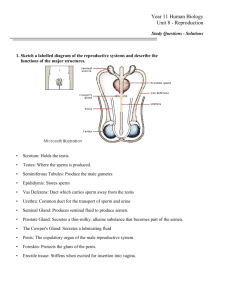
Reproductive System Combining Forms Amni/o: amniotic sac Andr/o: male Balan/o: glans penis Cervic/o: neck, cervix Colp/o, vagin/o: vagina Cry/o: cold Crypt/o: hidden Galact/o: milk Spermat/o, sperm/i, sperm/o: sperm cells Orch/o, orchi/o, orchid/o, test/o: testes Combining Forms Gonad/o: gonads, sex glands Lapar/o: abdominal wall Mamm/o: breast Men/o: menses, menstruation Nat/o: birth Pen/o: penis Perine/o: perineum Phim/o: muzzle Combining Forms Prostat/o: prostate gland Obstetr/o: midwife Salping/o: fallopian tube Semin/o: semen Vulv/o, episi/o: vulva Vesicul/o: seminal vesicle Vas/o: vas deferens, duct Vener/o: sexual contact Oophor/o, ovari/o: ovary Hyster/o, uter/o, metr/o: uterus, womb Suffixes -arch: beginning -blast: early form -cidal, -cide: killing -cyesis: pregnancy -genesis: beginning -gravida: pregnant woman -para: bearing offspring -plasia: formation -salpinx: fallopian tube -tocia: childbirth, labor -version: turning Prefixes Ecto-: outside Neo-: new Nulli-: none Pseudo-: false o/o: egg Female Reproductive System • Gynecologist: a medical doctor specializing in female reproductive disorders • Obstetrics: the branch of medicine concerned with pregnancy and menopause • Neonatology: the study of newborns Overview • Female reproductive organs: • Internal: ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and vagina • External: labia, clitoris, mons pubis and Bartholin glands • Female Function: to produce and transport ova(eggs) • to Nourish and provide a place for the developing fetus to grow Diseases and Conditions: female • Candidiasis: vaginal fungal infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans “yeast infection” • Symptoms: cheese-like discharge and extreme itching • Cervicitis: inflammation of the cervix because of an infection or STI (STD) • Ectopic pregnancy: implantation of the fertilized ovum (egg) anywhere outside of the uterine cavity “tubal pregnancy” • Endometriosis: the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterus Diseases and Conditions: female • Fibroid: a benign tumor in the uterus composed of fibrous tissue • Fistula: an abnormal tunnel connecting 2 body cavities • Vesicovaginal fistula: a tunnel between the bladder and the vagina • Gestational hypertension: high blood pressure during pregnancy • Symptoms: edema and proteuria • Preeclampsia: a form of gestational hypertension that may progress to eclampsia • Eclampsia: a life-threatening form of gestational hypertension to both mother and baby Diagnostic Procedures: female • Colposcopy: examination of the vagina and cervix with a magnifying instrument • Hysterosalpingography: radiography of the uterus and oviducts after injection of a tracer • Laparoscopy: visual examination of the abdominal cavity with a laparoscope through an incision made at the umbilicus • Mammography: radiography of the breasts used to diagnose tumors Papanicolaou test: (Pap) a microscopic analysis of a small tissue sample obtained from the cervix and vagina using a swab to detect carcinoma Medical and Surgical Procedures: female • Amniocentesis: a surgical puncture of the amniotic sac to retrieve fetal cells • Cerclage: an obstetric procedure in which a suture is used to close the uterus in order to prevent spontaneous abortions • Dilation and curettage: dilation of the cervix so that the endometrium can be scraped to stop heavy uterine bleeding or to obtain a biopsy specimen • Hysterosalpingooophorectomy: surgical removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries Medical and Surgical Procedures: female • Lumpectomy: excision of a small breast tumor and some of the tissue around it • Mastectomy: complete or partial excision of one or both breasts • Modified radical: mastectomy of the entire breast and lymph nodes under the arm • Radical: mastectomy of the entire breast, lymph nodes and chest muscles • Total: mastectomy of the entire breast, nipple, areola and the overlying skin Medical and Surgical Procedures: female • Reconstructive breast surgery: reconstruction of the breast that has been removed because of a tumor • Usually done immediately following the mastectomy • Tissue expansion: uses a balloon expander just beneath the skin and saline solution is injected to create a natural looking breast • Transverse rectus abdominis muscle flap: surgical creation of a skin flap shaped into a natural-looking breast • Tubal ligation: a sterilization procedure that involves blocking of both fallopian tubes by cutting them and burning the ends Pharmacology: Female • Antifungals: treat vaginal fungal infections • Estrogens: treat symptoms of menopause through hormone replacement • Hormone replacement therapy: used to correct a deficiency of estrogen, progesterone, or testosterone to relieve symptoms of menopause and prevent osteoporosis • Oral contraceptives: prevent ovulation to avoid pregnancy “birth control pills” Male Reproductive System • Urology: the study of the urinary tract of men and women and the male reproductive tract • Male reproductive organs: gonads (testicles), scrotum, penis, sperm, semen and transporting ducts • Male Functions: producing and delivering sperm to the woman’s reproductive tract Diseases and Conditions: Male • Anorchism: congenital absence of one or both testes “anorchia” • Balanitis: inflammation of the prepuce (the skin covering the glans penis) caused by irritation or infection • Benign prostatic hyperplasia: enlargement of the prostate gland that normally occurs in men over age 60 • Cryptorchidism: failure of one or both testicles to descend into the scrotum “hidden testicles” Diseases and Conditions: Male • Epispadias: a congenital defect in which the urethra opens on the upper side of the penis • Hypospadias: a congenital defect in which the male urethra opens on the under surface of the penis • Impotence: the inability to achieve or maintain an erection “erectile dysfunction” • Phimosis: stenosis of the prepuce so that it cannot be pushed over the glans penis Diagnostic Procedures: Male • Digital rectal examination: examination of the prostate gland by finger though the anal canal • Prostate-specific antigen test: a blood test used to screen for prostate cancer • Transrectal ultrasound and biopsy of prostate: an ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum to obtain an image of the prostate gland and to collect multiple biopsy specimens Medical and Surgical Procedures: male • Circumcision: surgical removal of the prepuce (foreskin) • Transurethral resection of the prostate: relieves obstructions caused by benign hyperplasia by insertion of a scope into the penis to chip away at and flush out excess tissue • Vasectomy: a sterilization procedure involving removal of part of the vas deferens to prevent sperm being mixed into semen Pharmacology: Male • Gonadotropins: hormonal treatment used to increase sperm count • Spermicides: method of birth control that destroys sperm Diseases and Conditions: Both • Sexually transmitted infections: any disease acquired through sexual intercourse “venereal disease” • Chlamydia: one of the most damaging STIs caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis • Symptoms: Cervicitis and urethritis • Genital warts: warts in the genital area caused by human papilloma virus • Gonorrhea: an extremely contagious STI caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae and affects the genitourinary tract and the rectum or pharynx Diseases and Conditions: Both • Herpes genitalis: an infection caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2 affecting the anorectal skin and genitalia • Can be passed through the placenta • Syphilis: an infectious STI characterized by skin lesions on the genitals, rectum or mouth • Can cause death if untreated • Trichomoniasis: an infection of the vagina, urethra or prostate caused by a protozoan • Most common STI in both men and women Abbreviations • • • • • • • • • • • CS, C-section: cesarean section D&C: dilation and curettage HRT: hormone replacement therapy IVF: in vitro fertilization LMP: last menstrual period OB-GYN: obstetrics and gynecology Pap: Papanicolaou test Para 1,2,3: number of viable births PID: pelvic inflammatory disease TAH total abdominal hysterectomy TRAM: transverse rectus abdominis muscle Abbreviation • • • • • • • • • • • TSS: toxic shock syndrome TVH: total vaginal hysterectomy BPH: benign prostatic hyperplasia DRE: digital rectal examination PSA: prostate-specific antigen TURP: transurethral resection of the prostate GC: gonorrhea HPV: human papillomavirus STD: sexually transmitted disease STI: sexually transmitted infection VD: venereal disease