The Process of Evolution
advertisement

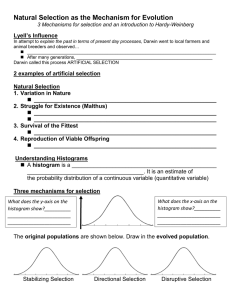
The Process of Evolution How it Works and How we See It Topic Outline Evolution in a Genetic Context - Microevolution Hardy-Weinberg Causes of Microevolution Natural Selection Types of Selection Maintenance of Variations Speciation Modes of Speciation Background Vocabulary Gene Allele Phenotype vs Genotype Homozygous Heterozygous Gene pool Microevolution Polygenic (Quantitative) vs Monogenic Traits The Hardy-Weinberg Model 2 p + 2pq + And p+q=1 2 q What Does it Mean? p=Frequency of Dominant allele q=Frequency of recessive allele p2=frequency of Homozygous dominant individuals q2=frequency of homozygous recessive indviduals 2pq=frequency of heterozygotes So What? The Hardy-Weinberg principle states an equilibrium of allele frequencies in a gene pool of a sexually reproducing population, p2 + 2pq + q2, won’t change as long as certain conditions are met. What are these conditions? Example: Industrial Melanism Causes of Microevolution Genetic Mutations Gene Flow Nonrandom Mating Genetic Drift Natural Selection MUTATIONS Gene mutations -- -- the only source of new alleles Chromosomal mutations -- -- alterations in the number, composition, or the arrangement of gene’s on a chromosome Chromosomal mutations Deletion Translocation Duplication Inversion Gene Flow Physical Movement of Alleles Nonrandom Mating Assortative mating Sexual selection Genetic Drift Bottleneck Founder Effect Effect Bottleneck Effect Founder Effect Founder Effect 2 Natural Selection Types of Selection Directional Selection Stabilizing Selection Disruptive Selection Directional Selection Stabilizing Selection Disruptive Selection Maintenance of Variations Are there any advantages to variation in a population? Sickle Cell Distribution Speciation Species Definition Morphological Biological Reproductive Isolation Phylogenetic Species A group of interbreeding populations that share a gene pool and are reproductively isolated from other species. Subpopulations can exchange genes. Different species can’t. Reproductive Isolating Mechanisms Prezygotic Isolating Mechanisms Postzygotic Isolating Mechanisms Modes of Speciation Allopatric Speciation-spatial separation Sympatric Speciation- no spatial separation SYMPATRIC SPECIATION --EX SPECIES A: 2N=14, N = 7 DUPLICATION SPECIES A’: 2N=28 N = 14 SPECIES A X SPECIES B 2N=21 N=? Adaptive Radiation Review Evolution in a Genetic Context - Microevolution Hardy-Weinberg Causes of Microevolution Natural Selection Types of Selection Maintenance of Variations Speciation Modes of Speciation