Notes Sheet
advertisement
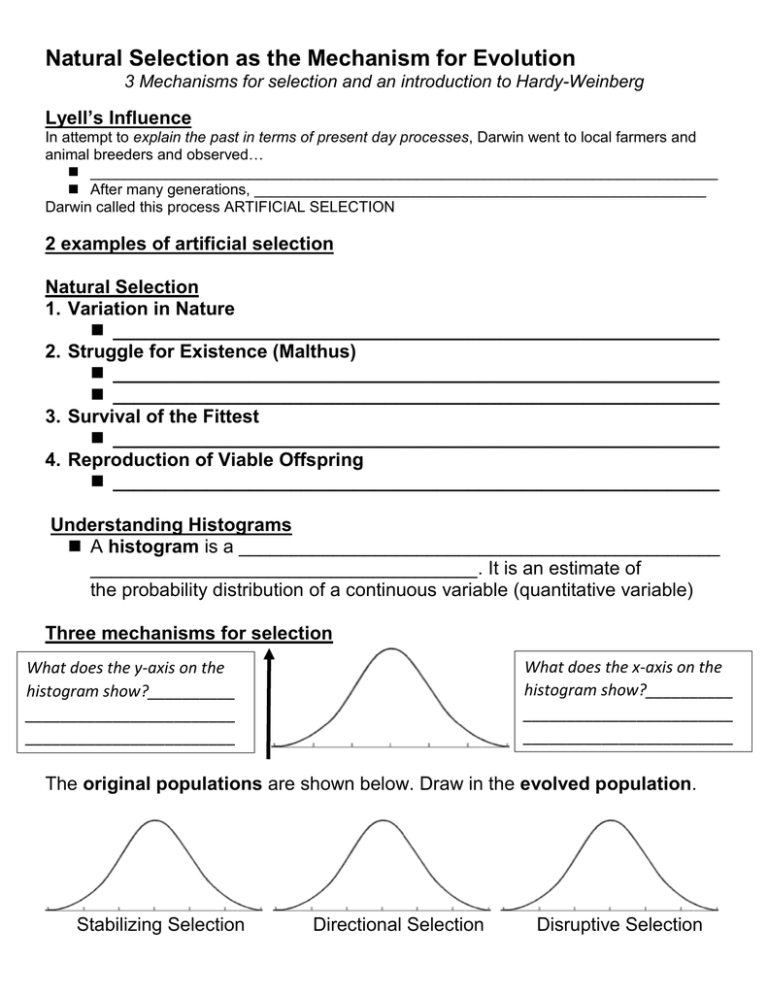
Natural Selection as the Mechanism for Evolution 3 Mechanisms for selection and an introduction to Hardy-Weinberg Lyell’s Influence In attempt to explain the past in terms of present day processes, Darwin went to local farmers and animal breeders and observed… ___________________________________________________________________________ After many generations, ______________________________________________________ Darwin called this process ARTIFICIAL SELECTION 2 examples of artificial selection Natural Selection 1. Variation in Nature __________________________________________________________ 2. Struggle for Existence (Malthus) __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 3. Survival of the Fittest __________________________________________________________ 4. Reproduction of Viable Offspring __________________________________________________________ Understanding Histograms A histogram is a ______________________________________________ _____________________________________. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable (quantitative variable) Three mechanisms for selection What does the x-axis on the histogram show?__________ ________________________ ________________________ _ What does the y-axis on the histogram show?__________ ________________________ ________________________ _ original populations The original populations are shown below. Draw in the evolved population. Stabilizing Selection Directional Selection Disruptive Selection Stabilizing Selection Examples? What happens to the variation with a population when it encounters stabilizing selection? Directional Selection Examples? What happens to the variation with a population when it encounters stabilizing selection? Disruptive Selection Examples? What happens to the variation with a population when it encounters stabilizing selection? Microevolution: A Population’s Gene Pool A gene pool is all the ____________________________________________ Microevolution_________________________________________________ Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium It is a condition in which ______________________________________ The equation used to ________________________________________ Example 1: In one hypothetical Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) population, most of the individuals have dark, zebra-striped shells (below left). However, solid light-colored shells (below right, caused by a homozygous recessive gene, aa) occur in 1 of every 10,000 individuals. Example 2: The Coquina Clam (Donax variabilis) is highly polychromic: (Polymorphism expressed as existing in several different colors. (adj. polychromic)) (with shells of many different colors.) In a population of 2,000 clams, 1,920 are solid colored, whereas the remainder has radiating color bands. Solid color occurs in homozygous dominant (BB) and heterozygotes (Bb); color banding only occurs in homozygous recessive individuals (bb). Problem: Calculate gene frequencies and numbers of BB and Bb.