Chapter 14 and 15 Review Sheet answers
advertisement

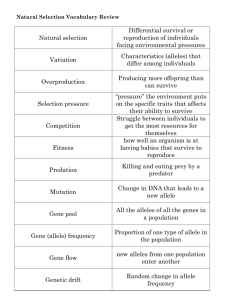
Chapter 14 and 15 Review Sheet Name__________________________ EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION: 1. Fossils - Where are fossils formed? - Formed in sedimentary rock - Examples of fossils: - Bones, imprints, shells, teeth 2. Homologous structures (give specific examples): - Same structures in different organisms showing common ancestry. - Forearm of a human, flipper of dolphin, wing of bat 3. Vestigial structures (give specific examples and 1 not in humans): - structure that still exists but is not needed anymore - Ex: wisdom teeth and appendix - Ex: hindlimbs of a whale 4. What can embryology tell us about evolution? - all embryos at some stage are similar (common ancestry) NATURAL SELECTION: 5. Definition: - Organisms that are best adapted to their environment, survive, reproduce, pass on their traits 6. Natural selection can be contrasted to _artificial______________ _____selection______________ when a farmer breeds his/her best livestock. 7. Charles Darwin traveled to the Galapagos Islands. What did he observe on the different islands? Be specific. - He observed species of finch that all had different beaks, specific for the envt they lived in 8. How did Charles Lyell influence Darwin? He determined that geologic forces change Earth 9. Fill in the blanks: Natural selection begins with a population. There are genetic differences within a population, known as ___variation________________________. Due to ____overproduction_____________________ more offspring are produced than can survive. Certain individuals leave more offspring than others. Their survival is due to: (write an explanation below) - adaptations that make them better fit to their environment 10. What is the raw material for natural selection? - Mutation MICROEVOLUTION: 11. What is the difference between microevolution and macroevolution? - Micro- Small scale evolution (within a few generations) - Macro- large scale evolution (takes time) 12. Define: allele frequency- how often a particular allele (gene) occurs 13. Genetic drift is a change in the gene pool (allele frequency) over time and can be due to: - The bottleneck effect: - Due to a change in the environment only a certain portion of the population survive - Founder effect: - the colonization of an area by a small group of individuals - Gene flow: - fertile individuals enter or leave a population - 2 IMPORTANT EXAMPLES: The peppered moths and Darwin’s finches 14. In a deer population, if the gene frequency for long legs changes from 10% to 80%, what can you say about the population? They are evolving SPECIATION 15. What is a population? A group of the same species 16. Speciation- the evolution of a new species, can result from: - Geographic isolation: - a population is separated geographically ( allopatric speciation) - Reproductive isolation: (name and explain a few barriers like temporal, behavioral, mechanical) Temporal: timing of mating Behavioral: different mating behaviors (songs) Mechanical: parts don’t fit 17. A species that has evolved into several different forms living in different ways has undergone ___adaptive radiation___________________________. 18. Timing of speciation - Long, stable periods with rapid change is called ____punctuated equilibrium_____________________. - Gradual changes over time is called _____gradualism_________________________. 19. Why would a geographic barrier like a river cause the formation of a new species of beetle but not a new species of bird? - birds can fly, their populations are never separated Questions to Ponder: 20. Do individuals evolve? - NO, only populations 21. Can an individual pass along acquired characteristics? - NO!!! CLASSIFICATION 22. What is the classification scheme beginning with Domain? Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 23. Look at the chart and answer the following question below Human Ostrich Dog Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordate Class Mammalia Aves Mammalia Order Primates Struthioniformes Carnivore Family Hominidae Struthionidae Canidae Genus Homo Struthio Canis Species Sapian camelus lupus Corn Plantae Anthophyta Monocotyledoes Commelinales Poaceae Zea Zea mays Which 2 organisms in the table are most closely related. Explain how you know. Human and Dog because they share 3 groups 24. Recall our discussion on heterozygote advantage. - What is so interesting about people who are heterozygous for the sickle cell trait? - resistant to Malaria - Why hasn’t the recessive allele been eliminated? - because those that are heterozygous survive Malaria - What areas of the world would have a high frequency of heterozygotes, why? – Coastal areas 25. You will have to analyze a phylogenetic tree (cladogram)- use the practice ones we did in class