Adaptations & Natural Selection
advertisement

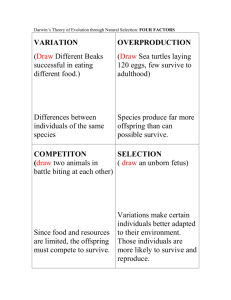
Adaptations & Natural Selection NICHE • A habitat supplying factors necessary for existence of an organism and its ecological role in regard to food consumption. Polar Bear-fur • Lives: – Cold environment • Why? – Blend in for hunting and protection • Job: – Keep population of seals down Woodpecker-long narrow beak • Lives: – In a tree • Why? – Safe from predators • Job: – Control insect population that harms trees ADAPTATION • A characteristic that helps an organism survive and reproduce. –Survive means: eat, blend, hunt, protect self, find food, etc. DESERT FOX • Hot environment • Big ears • Little to no fur short hair ARCTIC FOX • Cold environment • Small ears • Heavy thick fur DESERT RABBIT • Hot environment • Big ears • Little short haired ARCTIC HARE • Cold environment • Small ears • Heavy thick fur BIG IDEA Heat escapes through the ears Fur traps heat Adaptations • Bioluminescence – Light that is given off by a creature • Lightening bugs • Angler fish • Mushrooms in Brazil Adaptations • Echolocation – An animal’s (or human’s) ability to tell where an object is by detecting the sound bouncing off of it – Bat, dolphins Adaptations • Flippers – Legs that are specialized for swimming • Sea turtles • Ducks • Walrus Adaptations • Claws – Used for gripping, digging and tearing things apart • Bears • Moles • Cats Adaptations • Teeth – Used for tearing, chewing, ripping food for consumption – Sharp • Lion • Eating Meat – Flat • Horse • Grass/Grains – Baleen (filter-like) • Blue Whale • Krill – Mixed • Humans • Meat and plants Adaptations • Smell – Ability to detect scent to find food, a mate, or avoid danger • Vultures • Turkey • Dogs Another Adaptation • Asexual reproduction – A form of reproduction without a mother and a father; genetically identical to its parent (like a clone) – Strawberries plants will make runners, vines that will root and make a new plant – A potato will sprout and produce new potato plants Fungi make spores that will explode off of themselves and make new fungi. Black bread mold grows on bread Black bread mold produces spores Black bread mold spores spread over surface of bread and continue to grow more Natural Selection • Process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than other members of the species – Therefore, they pass on the more desired traits for survival Natural Selection • Its theorized that giraffes adapted to the climate change in Africa when it went from being a lush jungle to a drier savannah over two million years ago. • Normal food sources died out. Trees became the main food source, with leaves high up. • Offspring that were born with shorter necks could not reach the food and did not survive. • Only the giraffes with the longer necks were able to survive and reproduce, so the giraffe population passed on the long neck gene to its offspring. Basic Concepts of Natural Selection • Individual living things are different from each other. This is called variation. • Variation is important because without it, populations cannot evolve over time. • Living things produce more offspring than can survive, and many that survive do not reproduce. • Living things compete for limited resources, such as food and shelter. Natural Selection • Factors that affect the process: – Overproduction – Variation – Competition – Selection – Environmental Change – Genes and Natural Selection Variation • An inherited trait that makes an individual different from other members of its species; an adaptation is a variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment. • Causes of variations: • 1. Environmental factors can cause changes in source of genes. • 2. Geographic isolation can make two populations so different they become different species. • http://www.pbs.org/wnet/nature/lessons/the-birds-and-the-beaks/video-segments-extraordinary-birds/1481/ Variety Competition • Whenever two niches overlap, competition ensues between organisms. • If two organisms have the same requirements - for food, water, nesting sites, whatever (resources) - there will not be enough of that thing to go around http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/animals/mammals-animals/bears-andpandas/bear_grizzly_wolves/ Overproduction • Most species produce far more offspring than can possibly survive. Why? • Environmental Conditions • Predators • Diseases • Preservation of the Species Environmental Change: • A change in the species environment can affect on the organism’s ability to survive leading to natural selection. • Ex. Monkey flowers do not normally grow in soil high in copper concentration; because of genetic variation some varieties have been found growing near copper mines. Genes and Natural Selection: • Will have to add on the notes I left this off • Variations result from the shuffling of the genes when the egg and sperm join (fertilization) • Only traits that are inherited may be passed down to the offspring and can be acted upon by natural selection. Evolution •Change in inherited characteristics of a species over time. Theories • Scientific theory: well-tested concept or explanation not proven – Jean Baptiste de Lamarck – Charles Darwin Lamarck Lamarck's Theory of Evolution: Darwin was not the first person to propose a theory of evolution. In the early 1800s, a wellknown French naturalist named Jean-Baptiste Lamarck also developed a theory of evolution. •He introduced the idea that the environment caused changes in animals and these changes were inherited by the animals' offspring. •changes in an organism during its lifetime could be passed on to its offspring. •if an organism that used certain organs more than others, then the organ used the most would evolve. • For example, Lamarck thought that giraffes could stretch their necks to feed on the leaves of tall trees. These giraffes would have offspring with long necks. • He called this the hypothesis of use and disuse. • This idea is often called "the inheritance of acquired characteristics," or "soft inheritance," and it is now known to be incorrect. • Changes in an organism cannot be passed onto its offspring unless they are controlled by genes. Charles Darwin http://www.sciencechannel.com/videotopics/earth-science/galapagos-beyonddarwin-charles-darwin.htm H.M.S. Beagle Darwin • Darwin observed that species of finches on islands off the coast of South America looked similar to a mainland species of finches • He hypothesized that plants and animals on the islands originally came from South America http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/explore-galapagos.html • Darwin reasoned that members of a population best able to survive and reproduce will pass their traits to the next generation; over time • Resulting in a different (separate) species • Darwin saw similarities but could not explain WHY they existed. Darwin • His hypothesis became known as a theory of evolution by natural selectionorganisms with traits suited for the environment will more likely survive and reproduce http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/darwin-never-knew.html http://videos.howstuffworks.com/science/evolution-of-life-videosplaylist.htm#video-29147 • Fossils- the preserved remains of an organism that had died long ago. • Darwin saw the fossil bones of organisms that had died and was puzzled by some of them, such as the fossil bones that resembled living sloths. These were much larger than those that were still living. He wandered what had happened to the giant creatures of the past. Fossils • Fossil records show extinct organisms • Showed similarities to living organisms • Hypothesized current organism descended (came from) from the fossilized organism http://videos.howstuffworks.com/discovery-health/4911-100-greatest-discoveries-evolution-video.htm Species • A group of • They also have organisms that to be able to share traits reproduce (characteristics) • Way to survive that may be similar. • Adaptation: A change in an organism over time that helps it to survive and reproduce in its environment. • Biodiversity: The variety and complexity of life on Earth. • Camouflage: Appearance that is designed for hiding in the environment. • Competition: Living things striving for food, living space, mates, and other resources. • Evolution: The process whereby new species arise from earlier species by accumulated changes. Often referred to as “change over time.” • Fitness: The ability of a living thing to survive and reproduce in its environment. • Natural Selection: The process by which individuals in a population inherit genes that allow them to survive and be reproductively successful. • Variation: Differences in individual living things from each other. • Scientific theory: well-tested concept or explanation not proven • Fossils- preserved remains of animals that died long ago • Genetic Diversity- Vocabulary – Difference in the genes among a species • If every human was exactly the same and an infectious, deadly disease came around, what would happen??? • Variations– Any difference between individuals of the same species • Resilient– Able to overcome a tough situation • Continuous– Never ending; cycle • Water cycle, carbon cycle, changes • Migration– Movement of a species during certain times of the year • Birds, sea turtles, monarchs • Competition– Interaction among organisms by which they compete for survival, for biotic and abiotic factors, reproduction, and hierarchal position. Speed of Evolution • Two models that explain the speed of evolution –Gradualism –Punctuated equilibrium Speed of evolution • Gradualism – Slow, ongoing process – Change may take place through a slow but continuous process • Punctuated equilibrium – Gene mutation can result in a new species in a short period of time