EOC Study PowerPoint 2
advertisement

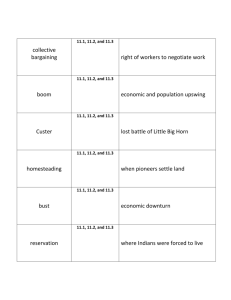
INDUSTRIALIZATION & THE GILDED AGE RISE OF AMERICAN INDUSTRY FREE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM -Individuals are free to produce and sell what they wish -People go into business to make a profit -Prices are set by supply and demand -Inefficient companies are unable to compete CONTRIBUTION OF GOVERNMENT -Protection of property and contracts -Passing of protective tariffs -System of patents leading to new inventions EMERGENCE OF MODERN INDUSTRIAL ECONOMY EXPANSION OF RAILROADS Transcontinental Railroad and other new railroad lines improve travel/trade. GROWTH OF POPULATION DEVELOPMENT OF NATIONAL MARKET TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCES -BESSEMER PROCESS used in steel production -Electricity gives rise to new industries -Oil industry develops DEVELOPMENT OF CORPORATION AS BUSINESS ORGANIZATION GREAT ENTREPRENEURS (BUSINESS MEN) “ROBBER BARONS” OR “CAPTAINS OF INDUSTRY”? ROBBER BARONS: Businessmen sometimes used ruthless tactics to destroy competition and to keep workers wages low. ANDREW CARNEGIE -Fostered the Gospel of Wealth. -Steel production -Philanthropist who gave money to libraries and schools JOHN D. ROCKEFELLER -Standard Oil Company -Controlled the refining of oil -Forced to dissolve when his company developed monopoly of oil industry -Like Carnegie, Rockefeller was a great philanthropist RISE OF ORGANIZED LABOR PROBLEMS FACED BY WORKERS: -Long hours, low wages -Poor working conditions, repetitive tasks -Child labor -Lack of job security RISE OF LABOR UNIONS: -KNIGHTS OF LABOR (Terrence Powderly) -AMERICAN FEDERATION OF LABOR (Samuel Gompers) GOVERNMENT ATTITUDE TOWARD UNIONS: -Anti-union bias -Saw unions as driving up cost of goods -Haymarket Affair of 1886 (association with violence) URBANIZATION MOVEMENT OF PEOPLE FROM COUNTRYSIDE TO CITIES BRINGS MANY PROBLEMS: -Crowded tenements (one room apartments with little daylight/ inadequate plumbing) -Pollution, sewage contamination of water -Inability to provide essential public services Political corruption: -”political machines” run by “bosses” that helped immigrants but took advantage of them IMMIGRATION WHY THEY CAME… -PUSH FACTORS: oppression, poverty, wars, ethnic persecution -PULL FACTORS: belief in American freedom, economic opportunity and cultural ties NEW IMMIGRANTS -From Southern and Eastern Europe, mostly Catholic and Jewish -Less educated, spoke no English PROCESS OF AMERICANIZATION: -Immigrants learned to speak, act and behave like Americans; often the children of the immigrants did this, not the adults… SETTLEMENT OF THE FAR WEST DISCOVERY OF GOLD AND SILVER -KLONDIKE GOLD RUSH: Gold found in Yukon, near Alaska (1896) TRANSCONTINENTAL RAILROAD (1869) -made travel and trade with West Coast easier HOMESTEAD ACT (1862) -made federal land available to settlers RANCHERS -Cattle drives took cattle across the open range FARMS -Dug water wells, made sod houses, used barbed wire and steel plows NATIVE AMERICAN POLICY INDIAN WARS -Federal troops defeated Sioux and other tribes on the Great Plains and forced them onto RESERVATIONS DAWES ACT (1887) -Sought to “Americanize” Native Americans. -Abolished tribes and allotted tribal lands to individuals AMERICAN INDIAN CITIZENSHIP ACT (1924) -Granted U.S. citizenship to all Native Americans born in the U.S. AGRARIAN MOVEMENT PROBLEMS OF FARMERS:1870-1900 -Increased farm production led to more crops per acre, but falling food prices -Farmers had to ship goods to market and were at the mercy of the railroad rates -Farmers were constantly in debt GRANGE MOVEMENT (1876) -Original goal was to reduce rural isolation -Turned into a group demanding economic and political reforms -Helped get Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 passed which regulated railroad rates POPULIST PARTY: 1891-1896 NATIONAL THIRD PARTY REPRESENTING LABORERS, FARMERS AND INDUSTRIAL WORKERS (ALSO KNOWN AS THE PEOPLE’S PARTY) POPULIST PLATFORM (1892) -Supported William Jennings Bryan for President -What they wanted: Unlimited coinage of silver (free silver) Direct election of Senators Term limits for President/Secret Ballots Immigration Restriction Graduated income Tax THIRD PARTIES IN AMERICAN POLITICS -Help educate voters on special issues -Provide an outlet for minority grievances -Pressure major parties to adopt their ideas