What is the bond angle?
advertisement

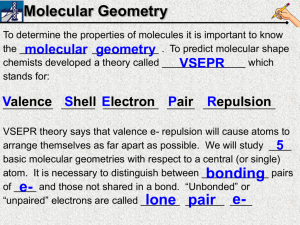
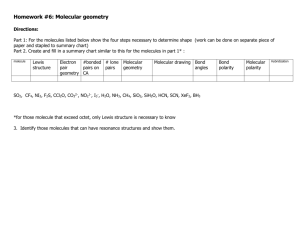
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2/5 Molecular Geometry ***If you didn’t watch last night’s VSEPR video, do that now. If you did watch it, do the Do Now question below Use your notes from last night’s video. Draw the lewis dot structure of OF2. What is the molecular geometry (shape)? What is the bond angle? Molecular Geometry To determine the properties of molecules it is important to know the ____________ molecular ____________ geometry . To predict molecular shape chemists developed a theory called _______________ which VSEPR stands for: Valence Shell Electron Pair _____________ Repulsion _________ ______ __________ _____ VSEPR theory says that valence e- repulsion will cause atoms to arrange themselves as far apart as possible. We will study ____ 5 basic molecular geometries with respect to a central (or single) atom. It is necessary to distinguish between ____________ bonding pairs of ____ e- and those not shared in a bond. “Unbonded” or “unpaired” electrons are called _______ elone _______ pair ____ # of egroups 1 or 2 3 4 4 4 # of lone pairs of e- 0 0 0 1 2 Angle between atoms 180° 120° 109.5° ~107° ~105° Trigonal Pyramid Bent Geometry Trigonal Tetrahedral Linear Planar Linear Trigonal Planar Tetrahedral Trigonal Pyramidal Bent Stability e- These valence shells OR All atoms are surrounded by _____. clouds OR _____________ orbitals full of electrons surrounding each atom _________ repel each other because electron clouds are ____________ charged and like charges repel. Therefore, atoms negatively in a ______________will molecule arrange themselves as ____________ far apart minimize the repulsion as possible from one another to _____________ and make the molecule stable. Symmetry Once the molecular geometry of a compound has been symmetry can be determined. A determined, the _______________ molecule can have ________ many or _______ no lines of symmetry. Generally, lines of symmetry are found by cutting through the _________ bond between two atoms. Seeing symmetry will take practice! 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2/5 Molecular Geometry Which of the following molecules has only 1 lone pair of e- on its central atom? Draw each e- dot structure in your notebook and describe the molecular geometry (shape and angle) of each molecule. A) H2S B) CH2Cl2 C) PF3 D) HBr 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2/5 Molecular Geometry Which of the following molecules has only 1 lone pair of e- on its central atom? Draw each e- dot structure in your notebook and describe the molecular geometry of each molecule (name and angle).. A) H2S B) CH2Cl2 C) PF3 D) HBr 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2/6 Symmetry Which of the following molecules is unsymmetrical? In your notebook, draw e- dot structures and label the molecular geometry with bond angles as evidence of your answer. A) BeCl2 B) H2CO C) C2H2 D) OF2