Compact bone
advertisement

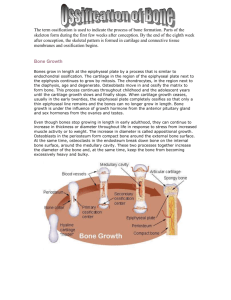
Bone cells › › › › Osteoblasts Osteocytes Osteoclasts Stem cells or osteochondral progenitor cells Woven bone: collagen fibers randomly oriented Lamellar bone: mature bone in sheets Cancellous bone: trabeculae Compact bone: dense 6-2 Bones are composed of connective tissue, chemicals, and fats Solid outer layer compact bone › Composed of osteons An inner layer of spongy bone › a honeycomb of flat, needle-like projections called trabeculae. Above: Note the relationship btwn the compact and spongy bone. Below: Close up of spongy bone. Haversian canals › allow the passage of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers. › Surrounded by layers of bone called a lamella. osteon Volkmann’s canals › Perpendicular to the haversian canals. › Connect the blood and nerve supply in the periosteum to those in the haversian canals and the medullary cavity. Osteoblasts › Bone building cells › Synthesize and secrete osteoblasts collogen fibers and other organic components of the bone matrix › Initiate calcification › Found in the periosteum and the endosteum Ossification › Formation of bone by Bone matrix osteoblasts. › Cells surround themselves by matrix. Osteocytes. › Mature bone cells. › Osteoblasts that have become trapped by the secretion of matrix. › Responsible for maintaining the bone tissue Lacunae › spaces occupied by osteocyte cell body Canaliculi › canals that allow for nutrient filled liquid to fill the lacunae 6-7 Osteoclasts Cells that ecretes digestive enzymes to digest bone matrix bone resorption Concentrated in the endosteum. On the side of the cell that faces the bone surface, ruffled border. Pumps out hydrogen ions Create an acid environment that eats away at the matrix. Why is there a depression underneath the osteoclast? What advantage might a ruffled border confer? What is the name of the third cell type shown here? What do you think the tan material represents? www.academic.pgcc.edu/~aimholtz/AandP/LectureNotes/ANP1_Lec/Skeletal/ BoneTissue.ppt Diaphysis - Shaft › Compact bone Epiphysis - End of the bone › Cancellous bone Epiphyseal plate - growth plate › Hyaline cartilage; present until growth stops Epiphyseal line: bone stops growing in length Medullary cavity: contains marrow › In children medullary cavity is red marrow, › In adults marrow is yellow in limb bones and skull (except for epiphyses of long bones). • Red marrow is found in in the cavities of the spongy bone of flat bones Periosteum › › › Outer is fibrous Inner is single layer of bone cells including osteoblasts, osteoclasts and osteochondral progenitor cells connected to bone matrix via Sharpey’s fibers Endosteum. › › Similar to inner layer of periosteum. Lines all internal spaces •Osteocytes •Lamellae •Haversian canals •Osteon •Volkmann’s canals •Lacunae •Diaphysis •Periosteum •Sharpy’s fibers •Epiphyses •Epiphyseal plate •Epiphyseal line •Yellow marrow •Medullary cavity •Sharpy’s fibers Consists of organic and inorganic components. › Organic component are secreted by the osteoblasts: Collagen fibers Elastin › Inorganic component Calcium phosphate Calcium hydroxide magnesium, fluoride, & sodium. What if the Calcium phosphate, Calcium hydroxide and the other minerals were removed from this bone? What if the collagen and elastin were removed from this bone. Figure 5.2 Prenatal: cartilage model Fetus: some conversion to bone Childhood: primary and secondary ossification sites formed Adolescence: cartilage growth plate elongates Changes in shape, size, strength: › Dependent on diet, exercise, age Bone cells regulated by hormones: › Parathyroid hormone (PTH): removes calcium from bone › Calcitonin: adds calcium to bone Repair: hematoma and callus formation Protection: encases most internal organs Support: allows body positions Permit movement: muscle attachments for movement Mineral reservoir: calcium, phosphorus Classified by degree of movement: › Fibrous joint: immovable (e.g., fontanels) › Cartilagenous joint: slightly movable, cartilage connection (e.g., backbone) › Synovial joint: freely movable Figure 5.12a Joint capsule: synovial membrane + hyaline cartilage Synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid as lubricant Hyaline cartilage cushions Sprains: stretched or torn ligaments Bursitis and tendinitis: inflammations Arthritis: inflammation of joints