Physiological Support Systems
advertisement

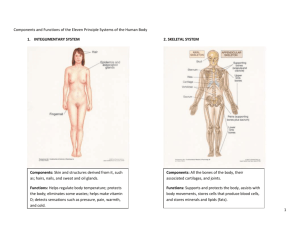
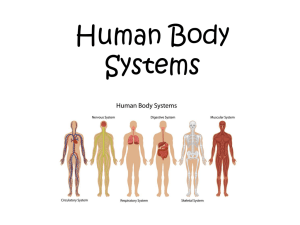
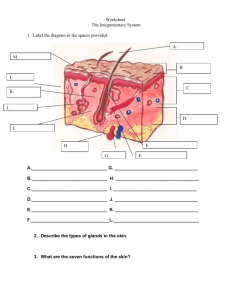
Physiological Support Systems Integumentary System Components • Skin and structures derived from it. • Hairs, nails, sweat and oil glands Functions • Eliminates some wastes (salts) • Waterproofs, cushions, protects deeper tissue • Detects sensations such as touch, pressure, pain warmth, & cold. • Regulates body temp • Helps make vitamin D Skeletal System Components • Bones, cartilages, ligaments, joints Functions • Support & protect the body • Provides a specific area for muscle attachments • Stores cells that produce blood cells • Stores minerals & lipids. • Framework for muscles & movement Muscular System Components • Specifically refers to skeletal muscle tissue • Which is muscle usually attached to bones • Other muscle includes smooth & cardiac Functions • Participates in bring about movements (locomotion) • Maintains posture • Produces heat Nervous System Components • Brain, spinal cord, nerves & sense organs such as the eyes & ears. Functions • Fast-acting central control system • Responds to external/internal stimuli via nerve impulses • Regulates body activities through nerve impulses by detecting changes in the environment • Interpreting the changes & responding to the changes by bring about muscle contractions or glandular secretions. Endocrine system Components • All glands and tissues that produce chemical regulators of body functions (hormones) • Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, thymus, pancreas, ovaries, testes…... Functions • Slow-acting control system • Glands produce hormones that regulate growth, reproduction, metabolism….. • Regulate body activities through hormones transported by the blood to various target organs. Cardiovascular System Components • Blood, heart & blood vessels Functions • Heart pumps blood through blood vessels • Blood carries O2 & nutrients to cells & CO2 & wastes away from cells • Helps regulate acidity, temperature, & water content of body fluids • Blood components help defend against disease & mend damaged blood vessels Lymphatic System Components • Lymphatic fluid & vessels; spleen; thymus, lymph nodes & tonsils • Cells that carry out immune response Functions • Complements circulatory system by returning leaked fluids & proteins back to blood vessels • Carries lipids from gastrointestinal tract to blood • Cleanses the blood • Involved in immunity Respiratory System Components • Lungs & air passages: pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea and bronchial tubes Functions • Transfers O2 from inhaled air to blood & CO2 from blood to exhaled air • Helps regulate acidity of body fluids • Air flowing out of lungs through vocal cords produces sounds Digestive System Components • Organs of gastrointestinal tract [mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines & large intestines, rectum & anus] • Accessory digestive organs: salivary glands, liver, gallbladder & pancreas. Functions • Achieves physical and chemical breakdown of food; • Absorbs nutrients & eliminates solid waste. Urinary System Components • Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, & urethra Functions • Produces, stores and eliminates nitrogenous waste from the body (urea & uric acid) • Regulates volume & chemical composition of blood • Helps regulate acidity of body’s fluids • Maintains body’s electrolyte & mineral balance • Helps regulate red blood cell production Reproductive systems Components • Male – Seminal vesicles, prostate, penis, vas deferens, testis, scrotum • Female – Ovaries, mammary glands, uterus, vagina, uterine tube Functions • Primary function for both sexes is to produce offspring • Male – testes produce sperm & male sex hormones • Female – ovaries produce eggs & female sex hormones • Mammary glands produce milk.