ADRENAL KORTEX AND ADRENAL MEDULLA HORMONES
advertisement

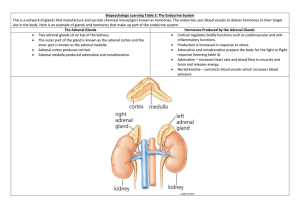
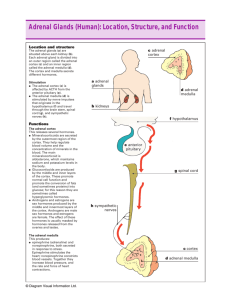
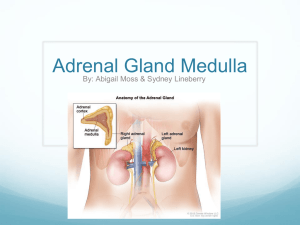
Adrenal glands are two pyramid-shaped structures that sit on top of the kidneys, one gland each kidney. Adrenal glands release hormones that help the body prepare for and deal with stress. An adrenal gland has an outer part called the adrenal cortex and inner part called the adrenal medulla. ADRENAL CORTEX About 80 % percent of adrenal cortex produces more than two dozen steroid hormones called corticosteroids. ALDOSTERONE CORTISOL Aldosteron Aldosteron regulates the reabsorption of sodium ions and excretion of potassium ions by kidneys. Cortisol Helps control rate of metabolism of carbonhydrates, fats and proteins. Helps people cope with stress. Adrenal Cortex Disorders Addison disease Cushing syndrome Addison Disease Weight loss Low blood pressure General weakness Cushing Syndrome Obesity Increased blood sugar levels High blood pressure Weakening of the bones ADRENAL MEDULLA Adrenal medulla is a specialized part of the sympathetic nervous system. For this reason, the adrenaline and noradrenaline it secretes are called neurohormones. Adrenaline is sometimes known epinephrine. The words adrenaline and epinephrine are derived from Latin and Greek words, and mean “near the kidneys”. Adrenal medulla produces the “fight or flight” response to stress. This response is the feeling, you are excited or frightened. ADRENAL MEDULLA HORMONES Adrenaline Noradrenaline Adrenaline causes the heart rate to increase, respiration rate to increase, smooth muscle in air ways to relax, muscles in the arteries to contract and glucose levels to increase. Noradrenaline Noradrenaline or norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter released by the nerve cells. Its chemical structure as well as function is similar to adrenaline. It increases blood pressure by constricting the blood vessels. This action normalizes heartbeat due to which breathing becomes more deep and normal. The main purpose of Noradrenaline is to normalize life threatening low blood pressure (acute hypotension). Noradrenaline deficiency can lead to tiredness, fatique, lethargy and sullenness.