Medulla Cortex
advertisement

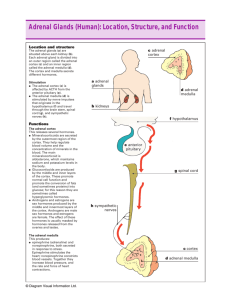
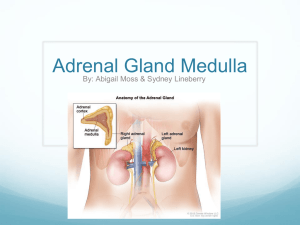
By: Victor Kasianov & Connor Slaunwhite Location • The adrenal glands are situate atop the kidneys Adrenal Cortex • The adrenal cortex is the outer layer of the adrenal gland, it produces three main types of hormones: 1. Glucocorticoids (steroid) – associated with blood glucose levels Mineralcorticoids (steroid) – second major group of hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. Small amounts of sex hormones The adrenal cortex also produces other steroid hormons. 2. 3. 4. Glucocorticoids • One of the most important glucocorticoids is cortical. Cortical increases the amount of amino acids in the blood in an attempt to help the body recover from stress. Mineralcorticoids • The most important mineralcorticoid is Aldosterone. The secretion of aldosterone increases sodium rotation & water reabsorption by the kidneys. Thereby helping to maintain homeostasis. Regulation • Both hormones are regulated by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland that secretes ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone). This ACTH is carried through the blood cells to the adrenal cortex. The Adrenal Medulla • The adrenal medulla is enclosed in the adrenal cortex. • The medulla is promaraly composed of cells called chromaffin cells. • The medulla is considered to be an extention of the sympathetic nervous system. • The medulla produces two similar hormones called epinephrine and norepinephrine. Epinephrine/Norepinephrine • Epinepherine and norepinephrine are water soluble hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla. • Their primary function is to increase the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. • When the hormones are secreted into the bloodstream it activates the glycogen, a carbohydrate storage compound in muscle and liver cells and releases ready to use glucose. The elevated presence of blood sugar increases the amount of usable energy. • This increases the heart rate, breathing rate and cell metabolism. It also causes dilation of blood vessels, and dilation of the iris, increasing the size of pupil allows more visual information to be received. Regulation • The secretion of hormones from the medulla is activated by the sympathetic nervous system. In a stressful situation, when the fight-or-flight reflex is initiated the adrenal medulla secretes its hormones into the blood stream. Possible Problems • Hypersecretion of corticosteroids: – Changes in carbohydrate and protein metabolism resulting in a puffy appearance. In extreme cases, "buffalo hump" and "moon face" occur. • Hypersecretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine: – Hypertension, hyperglycemia, nervousness, sweating, and complete exhaustion occur. • Hyposecretion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids: – Hypoglycemia, sodium and potassium imbalance, dehydration, hypotension, and rapid weight loss. If treatment is not pursued, death will occur. Interesting Facts • The adrenal medulla can be surgically removed without any bad side effects. But if the adrenal cortex were removed, death would be the resulting factor. The cortex and medulla are found as 2 separate glands in some species like amphibians. Some speculate that they were once separated in out body as well because they work independently of each other. ~Quiz~ • 1. Where is the adrenal gland located? • 2. Name a hormone produced by each part of the adrenal gland. • 3.Can you die by removing the adrenal cortex? Adrenal Wrapz • • • • • • • • • Yea yea check it out, this is wud it’z all about, hoez all up in here, settin up the adrenal gear. We got da cortex n’ medulla, beefin er up, Spittin up so many hormonez its fillin up a cup. We be feelin fine,(unless my sympathetic system kicks in then I’m a little stressed out but no worries the adrenal gland will secrete the hormones so I will be ready to perform my fight-or-flight reflex) • • • • • All we do rhyme Cause that’s how we roll, We pass in dem projeks on tyem. Our time is up, time for the next presenter So we leave you with our last slide, it’s a bro’n’out good ender. Bonus marks please Beef up