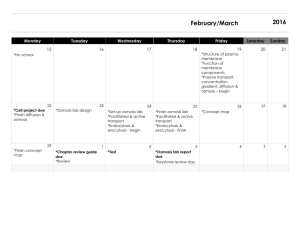
File
advertisement

Warm Up • Last week, we compared the cell to a complex factory. • Why is it important for factories to get deliveries? • How do you think the cell gets “deliveries”? Cell Membrane • Gatekeeper • Regulates what comes in and out of the cell • Main components: proteins and phospholipids • The cell membrane is selectively permeable • Allows some things through without energy, but not everything Cell Wall • Found only in plant cells and bacteria cells • Main function is support Diffusion • The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Molecules tend to “spread out” • Requires no energy Equilibrium • When molecules are evenly spread throughout a space Osmosis • The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane. • Water will travel to where there is a lower concentration • If you add something like salt to the solution… Rule for Osmosis: Water will get sucked to wherever there is a higher concentration of salt. The following slides illustrate what direction water travels if a cell is placed in different solutions. Why is Osmosis Important? •Osmosis is important to cell functions. •Red blood cells use osmosis to carry nutrients from plasma in the cell and wastes out of the cell. Effect on living cells Hypertonic Cells There is a higher concentration of salt outside of the cell so water moves out of the cell Why is it dangerous to drink sea water? Cells In Different Solutions Isotonic cells= There is an equal amount of salt inside and outside of the cell, so water stays in balance and cell is at equilibrium. Hypotonic = less There is a higher concentration of salt inside of the cell so water rushes into the cell. Warm Up • What will happen to a houseplant if you water it with salt water (a hypertonic solution)? • True or False: Diffusion happens naturally when particles go from a lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. (Think about food coloring in water) Passive Transport • The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell. Used for transporting small particles • Examples Diffusion & Osmosis Active Transport • Cell uses energy to move things in and out. Example: food molecules • Cell membrane actually opens and closes. Active Transport Video Check for understanding • The prefix exo- means “out of” and the prefix endo- means “taking in”. How do these meanings relate to the meaning of exocytosis and endocytosis? Exocytosis & Endocytosis Exocytosis: large molecules “exit” the cell. Ex: Waste products Endocytosis larger substances “enter” the cell. Ex: Food molecules Two Types of Endocytosis • Pinocytosis: the cell takes in liquid substances • Phagocytosis- the cell takes in food particles “phood” (food) Check for understanding #2 Endocytosis/Exocytosis • Taking “in” or letting “out” large molecules by the cell • Phagocytosis = “phood”, taking in food particles • Pinocytosis = liquid substances • Organelles and functions • Difference between animal and plant cells • What organelles look like Exit Slip • Create three scenarios in which osmosis would make water • 1.Come into the cell • 2. Leave the cell • 3. Stay isotonic and balanced • Draw a sketch of what the resulting cell would look like