Corporations: Organization and Capital Stock
advertisement

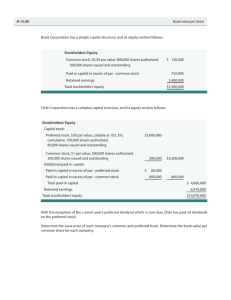
Corporations: Organization and Capital Stock Chapter 19 19- 1 Learning Objective 1 Defining a corporation; establishing a corporation; listing the advantages and disadvantages of a corporation. 19- 2 Learning Unit 19-1 1 2 3 4 What are the steps in forming a corporation? Incorporators write up and submit articles of incorporation to the state. The Secretary of State issues a charter. Stockholders are the owners. A board of directors is elected by stockholders at the first meeting. 19- 3 Learning Unit 19-1 – – – – – What are some advantages of the corporate form of organization? limited liability/separate legal entity unlimited life ease of transferring ownership no mutual agency ease of raising capital 19- 4 Learning Unit 19-1 What are some disadvantages? – difficulties in forming a corporation – corporate taxation (double taxation) 19- 5 Learning Objective 2 Journalizing entries for issuing par-value stock, no-par stock, and no-par with stated value stock. 19- 6 Learning Unit 19-2 Stockholders’ equity must be separated into two categories. Paid-in Capital Retained Earnings 19- 7 Learning Unit 19-2 Capital stock is the amount paid to the business. Par value is the legal capital assigned to each share. Usually it is the amount paid to the corporation for the initial issuances of stock. Retained earnings is net income less net loss less dividends. 19- 8 Learning Unit 19-2 – – – – What are some characteristics of common stock? voting rights profit sharing selling the stock preemptive right (right to maintain ownership ratio) 19- 9 Learning Unit 19-2 – – What are some characteristics of preferred stock? first claim to dividend distribution usually have no voting rights 19- 10 Learning Unit 19-2 – – Dividends are paid to stockholders as their share of the corporation’s profit. common dividends preferred dividends 19- 11 Learning Unit 19-2 Cumulative preferred stockholders have a right to receive a dividend each year. Amounts not declared and paid accumulate each year. These are paid before any current year dividends (dividends in arrears). 19- 12 Learning Unit 19-3 R.C. sells 200 shares of a $10 par value common stock at par. Accounts Affected Category Cash Asset Dr. 2,000 SE Cr. 2,000 Common Stock Rules 19- 13 Learning Unit 19-3 Assume R.C. sells 100 shares of $5 par value common stock at $20. 100 shares × $5.00 par value = $500 100 shares × $20.00 market value = $2,000 What is the journal entry? 19- 14 Learning Unit 19-3 Cash 2,000 Common Stock Paid-in-Cap in Excess of Par Value – Common Issued par value common stock 500 1,500 19- 15 Learning Unit 19-3 R.C. sells 300 shares of a no-par, common stock for $20 per share. Accounts Affected Category Cash Asset Dr. 6,000 SE Cr. 6,000 Common Stock Rules 19- 16 Learning Objective 3 Calculating dividends on preferred and common stock. 19- 17 Learning Unit 19-3 A $150,000 dividend was declared. preferred stock 6%, 1,000 shares, $200 par, and fully participative common stock, 6,000 shares, $100 par 19- 18 Learning Unit 19-3 Preferred dividend: 6% × $200 × 1,000 = $12,000 Common dividend: 6% × $100 × 6,000 = $36,000 How do we allocate the remaining $102,000? 19- 19 Learning Unit 19-3 Preferred stock $200,000 ÷ $800,000 × $102.000 = $25,500 Common stock $600,000 ÷ $800,000 × $102.000 = $76,500 19- 20 Learning Objective 4 Recording capital stock transactions under a stock subscription plan. 19- 21 Learning Unit 19-4 Subscriptions Receivable—Common Stock is an asset account. It is debited when the contract is signed. A temporary stockholder equity account, called Common Stock Subscribed, is credited for the the par value of the stock. Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value—Common is credited for any amounts above par value. 19- 22 Learning Unit 19-4 When stock is fully paid it is issued, and then the par value is transferred to common stock. Assume that R.C. received subscriptions for 1,000 shares of $100 par value common stock at $160 per share. What is the entry? 19- 23 Learning Unit 19-4 Subscription Receivable 160,000 Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value Received stock subscriptions 100,000 60,000 19- 24 Learning Unit 19-4 1 – – – 2 The balance sheet must show stockholders’ equity with two divisions. Paid-in capital common stock (par value) common stock subscribed (if any not fully paid) paid-in capital in excess of par Retained earnings 19- 25 End of Chapter 19 19- 26