SG-Systems_Sessions 1 and 2
advertisement

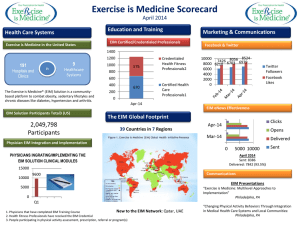
“SG-Systems” (Smart Grid – Operational Applications Integration) “Boot Camp” Overview Brent Hodges, Chair, SG-Systems Greg Robinson, Co-Chair, SG-Systems Session 1 Agenda Welcome & introductions Agenda review & update Results/comments/concerns from boot camp “Inquiring minds want to know…” IEC 61968-1 Interface Reference Model Update Overview (Shawn) SG-Systems Roadmap review and update – identify member needs not currently addressed (Greg) NIST, IEC, SEP 2.0, SAE, Unite, USB, EISA, etc. Additional thoughts (not covered during plenary) by task force leads General discussion, questions and answers SG-Systems WG Process Overview Use Cases From SCE and others HomePlug & ZigBee SE 2.0 IEC TC57 WG14, OASIS, IEEE Other SDOs NIST EPRI, MultiSpeak Task Forces System Requirements (SRS) Team Use Case Team SG-Security WG Service Definitions Team Recommendations to IEC TC57 WG14: •Proposed CIM Extensions •Message Schemas Updates •Requirements Updates Recommendations to other SDOs SG-Conformity Working Group Business-Oriented, Common Format Use Cases Based on SRS Reference Model •Integration Requirements •Patterns •Sequence Diagram •Services •WSDL Organizational Structure SG-Systems WG Chair: Brent Hodges Co Chair: Greg Robinson AMI-Ent TF OpenADE TF OpenADR TF OpenHAN TF Chair: Mark Ortiz Co-Chair: Greg Robinson Chair: Dave Mollerstuen Co-Chair: Steve Van Ausdall Chair: Albert Chiu Co-Chair: Ed Koch Chair: Erich Gunther Co-Chair: Mary Zientara Use Case Team Chair: Kay Stefferud SRS Team About to Vote Chair: Joe Zhou Service Definitions Team Chair: Jerry Gray Co-Chair: Shawn Hu EIM Chair: Greg Robinson Co-Chair: SG Security WG SG Conformity WG Collaboration With NAESB, IEC & OASIS Collaboration With NAESB, IEC & OASIS Collaboration With SEP 2.0 & IEC Session 2 Agenda New EIM Task Force Organizational Meeting Overview of EIM Roundtable to hear about experiences and expectations of members Form strategy that will help members to mitigate risk and lower costs for their companies Establish key points for charter Develop milestones Subsequent meeting(s) possible on Wednesday if members are available 8:00 - 10:00am Smart Grid Challenges… Requires Integration – LOTS of integration Onslaught of new applications and technologies AMI, MDMS, HAN, DR, ADE, etc. In a complex IT environment A plethora of changing technologies with disparate methodologies/philosophies over many years Many custom systems, legacy technologies Departmental objectives tend to encourage “silos” Project funding gives priority to project-focused implementations Without fitting into an enterprise context Aging / outsourced systems and IT workforce Historically, extremely low R&D expenditures It’s More Than Just Technical Matters Driving Forces Restraining Forces Consistent enterprise-wide data 1. Lack of stable industry standard definitions 2. One version of the truth 2. Vendor’s way = lower project costs 3. Access to data regardless of source 3. Vendors pushing for ‘proprietary lock-in’ 4. Business transformation agility 4. Consultants pushing to be ‘thought leaders’ 5. Reduced project implementation costs 5. Hours-sold revenue driving System Integrators 6. Reduced maintenance costs 6. Internal system experts want to remain experts 7. Reduced IT risks 7. Project managers striving for control 8. Availability of external services 8. Inertia – why change? 9. Scalable business process automation 9. Our situation’s unique – standards hinder us Status Quo 1. 10. Scalable business activity monitoring 11. Accurate reporting – regulatory, KPIs 12. Mergers and acquisitions For further information, please refer to the article on page 56 of the January issue of Utility T&D Automation & Engineering: http://www.uae-digital.com/uae/200801/ Defining EIM (Gartner) Enterprise Information Management (EIM) is: An organizational commitment to structure, secure and improve the accuracy and integrity of information assets, to solve semantic inconsistencies across all boundaries, and support the technical, operational and business objectives within the organization's enterprise architecture strategy. A commitment to EIM is recognition that information in the enterprise is as important as process (application development) and infrastructure (technology) Overall EIM Framework Enterprise Vision & Strategy Enterprise Architecture Enterprise Business & IT Core Processes Enterprise Business & IT Organizations Enterprise Infrastructure EIM Vision & Strategy EIM Governance EIM Core Processes EIM Organization EIM Infrastructure Data Quality Vision Sponsorship CSFs & KPIs Data Integrity Mission Stewardship Data Security & Protection Data Lifecycle Management Strategy Goals & Objectives Value Propositions Policies, Principles & Tenets Data Movement Alignment Database Management Roles & Responsibilities Semantics Management Master Data Management Structure Structure (Virtual, Hybrid……) Information Services Services & Support Functional Services Business Value and Relationship Management Information Architecture Blueprint Management Technologies (DBMS, Content Mgmt, ETL, EAI, EII, Data Modeling, BI/DW, Collaboration…..) Knowledgebase and Repositories Standards & Best Practices EIM Vision & Strategy This is a statement of what EIM is and what value it shall bring to the enterprise. Vision Mission This is a statement of why and how EIM program will bring value to the enterprise and help achieve the EIM vision. The strategy to be executed to achieve the EIM vision and mission. Strategy Goals & Objectives Value Propositions Specific goals and objectives that the EIM strategy and program would like to achieve in accordance with the vision and mission. Specific business and technology value (tangible and intangible, strategy and tactical) that the EIM strategy and program would provide, as well as specific metrics including ROI associated with EIM. EIM Governance Sponsorship This establishes the business and IT executive sponsorships that are required to ensure proper support, buy-in, and success of EIM program. Includes steering committee with members from business and IT and specified decision making roles and responsibilities. Stewardship This establishes the data and information ownership (stewardship) structure, policies and procedures, and relationships to organization functional and process roles and responsibilities. Policies, Principles & Tenets Alignment Reference Model This provides the essential policies, principles and tenets for what EIM is and how EIM will be conducted and enforced with business/IT functions and programs. This provides the structure, relationship, and policies and procedures necessary to align EIM vision and strategy with business vision and strategy as well as enterprise architecture goals and objectives. Alignment with major programs is a critical part of this component. This provides the overall governance reference model of the EIM program, and includes the reference architecture model showing the key components of EIM capabilities and services, which provides the foundation for alignment analysis and recommendations. EIM Core Processes Data Quality Processes to identify, analyze, improve, and measure the data quality issues and improvement efforts. Data Integrity Processes to identify, analyze, improve, and measure the data integrity issues and improvement efforts. Data Security/ Protection Data Lifecycle Management Data Movement Processes to ensure corporate data and information is secure and protected, and managed according to the corporate policies and regulatory mandates. Processes to govern how to create, classify, update, use, distribute, and archive, and obsolete data and information, for new projects as well as ongoing maintenance. Processes to identify and guide how data should be managed when they are moved around the enterprise and Line of Business systems, applications, and data files. Semantic Management (Definitions, metadata, Models……) Processes to establish, manage, and use the business and IT semantics (that is business terms and definitions, metadata management, enterprise semantic models management, semantic integration etc. ) Database Management Processes to manage the physical corporate databases and data files. Master Data Management Processes to manage the creation, maintenance, distribution, and usage of corporate master and/or reference data entities to support business processes and business transactions with the objectives of improving data quality and integrity, improving data and information accuracy, and reducing process inefficiencies. Information Services Processes to establish, maintain, and use actual data and aggregation services in the form of reusable software components for business systems and processes to share and leverage data and information across both transactional and analytical needs. Services & Support Management Processes for the EIM program and/or organization to provide functional services and support to the rest of enterprise IT and business organizations and projects. EIM Organization CSFs & KPIs Critical Success Factors and Key Performance Indicators to be established for the EIM organization or program to be measured. Structure (Virtual, Hybrid……) The EIM organizational structure internally and externally, with focus on not only how it is organized internally but also how it interacts with external stakeholders and users of EIM services. Roles & Responsibilities Roles and responsibilities of every position within the organization. Functional Services A list of functional services and core competencies relative to the EIM core processes that this organization would provide internally and externally. Alignment and reference to other IT services will be defined as well. Business Value and Relationship Management How will the EIM organization manage the relationship with business and IT to ensure that business value is delivered and measured in accordance with the CSFs and KPIs established? EIM Infrastructure Information Architecture Blueprint Management Technologies (DBMS, Content Mgmt, ETL, EAI, EII, Data Modeling, BI/DW, Collaboration, ……) Knowledgebase and Repositories Standards & Best Practices This is to establish and maintain the enterprise information architecture blue print to ensure its viability and relevance to Enterprise Architecture and the rest of the IT core competencies. A portfolio of technologies required to provide the basic and advanced EIM services. A knowledgebase of EIM best practices, methodologies, architecture patterns, design models, implementation guidelines, IT lifecycle management related to data/information, etc. And repository of metadata and enterprise semantic models. Standards and best practices that EIM program adopts or develops to ensure efficient and effective services of EIM functions. Summary Points The Smart Grid is about Smart Data Too many moving parts & too much investment at risk - to go on doing “more of the same” IT practices Smart Data Requires: Planned Enterprise Information Management (EIM) Architecture for incremental deployment over many years Based on an architecture with strong interfaces Makes practical use of industry standards Decouples projects Master Plan implemented in phases Each increment must fit cohesively with previously installed components Getting help by leveraging effective user organizations Lowers costs and mitigates risks for nominal cost … and here we are! Session 2 Agenda New EIM Task Force Organizational Meeting Overview of EIM Roundtable to hear about experiences and expectations of members Form strategy that will help members to mitigate risk and lower costs for their companies Establish key points for charter Develop milestones