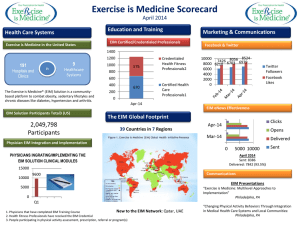
Electrical impedance myography - University of Rochester Medical
advertisement

Electrical impedance myography (and a little MUNE) Seward B. Rutkove, MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures 1. Consultant and equity in Convergence Medical Devices, Inc. 2. Consulting for Neuralstem, Inc., 3. Two patent applications in electrical impedance 4. Grant funding from NIH, ALSA Association, the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Foundation, and NASA. Electrical impedance testing? • The assessment of characteristics of a material by measuring changes to an applied electrical current • Used in forestry, metallurgy, geology But also in humans… • Whole body bioimpedance analysis – Total body water/fat • Electrical impedance tomography – Imaging • Electrical impedance mammography (also EIM) – Breast cancer detection • Electrical impedance dermography Electrical impedance myography The broad hypothesis: Alterations in composition and structure of muscle with disease will impact the electrical impedance of muscle in unique and reproducible ways. Different disorders, different pathologies Normal Myopathy/Dystrophy Neurogenic Disuse Atrophy Electrical impedance in healthy muscle Current Generator Voltmeter Applied electrical current Measured voltage amplitude is proportional to muscle resistance (R) Tissue reactance (X), related to capacitance, causes shift in timing Measured voltage Electrical impedance in diseased muscle Current Generator Voltmeter Applied electrical current Increased tissue Resistance (R) causes higher amplitude voltage From neuromuscular.wustl.edu Reduced tissue Reactance (X) causes reduced shift in timing Measured voltage Phase will decrease Phase = arctan(X/R) Off-the-shelf bioimpedance devices Useful, but limited • Single Frequency • Multifrequency Instrumentation: Past and Present 2001 2005 2009 On the animal front Phase (degrees) Resistance (ohms) Reactance (ohms) What we measure Raw muscle data • Gives us the capability of relating surface data to intrinsic muscle data and vice versa • Measure muscle conductivity and permittivity Conductivity and permittivity plots Ahad et al, 2009 Repeatability Adhesive electrodes-humans ICC = 0.98 15 Retest Healthy 10 5 ALS 0 0 5 10 15 Test CMD system-humans Rats Mice Current Data? – ALS – SMA – DMD – Sarcopenia – Nerve injury (radiculopathy, crush models) – AMN Follow-up ALSA-funded study • Patient visits approximately 3 months apart (a total of 5 visits over 1 year) • 8 Sites involved, 60 patients • EIM measurements performed on • Biceps, wrist extensors, abductor pollicis brevis, quadriceps, and tibialis anterior • Intra-session repeatability on biceps • Also performed handheld dynamometry, ALSFRS, MUNE • Major EIM outcome measure: – Rate of decline in 50 kHz phase Results: In patient terms for 6 month trial Outcome measure Patients needed per study arm EIM steepest 95 EIM mean 182 HHD 266 ALSFRS-R 220* Assuming 6 month, placebo-controlled trial, 3 measurements, 20% treatment effect, p < 0.05, one-sided Neuralstem study Glass et al, 2012, Stem Cells ALS Rat Data: Measuring Disease Progression 16 animals followed from pre-symptomatic to death Advanced Early Early Early Advanced Advanced Wang et al, 2011 SOD1 g93a ALS rat data Wang et al, 2011 As a biomarker in spinal muscular atrophy • Natural history study of EIM in SMA, funded by SMA Foundation – Collaborative effort with Children’s Hospital Boston, Dr. Basil Darras – 28 SMA children mean age 9.6 years, followed for mean of 16 months – 20 Normal children enrolled, mean age 9.8 years, followed for mean of 17 months – Mainly Type 2 and Type 3 children SMA Multifrequency Data SMA cross-sectional data Type 2 Type 3 healthy SMA in older kids: no active motor neuron loss, but no muscle growth either Healthy Healthy kids SMA P = 0.018 From Rutkove et al, 2012 Primary muscle disease Tarulli et al, 2006 Preliminary DMD data: Quantitative Ultrasound and EIM in DMD (QED) • Funded by NIH/NIAMS fall 2011 • Basil Darras, MD: Co-PI • Enrolling 35 healthy kids and 35 with DMD and follow over 2 years • Frequent measurements early on; less frequent later • Started recruiting in March; about 17 DMD boys and 15 healthy boys already recruited Sarcopenia Quadriceps Tibialis anterior From Aaron et al, 2006 EIM in 4 healthy older subjects over a several year period Two subjects overlap Quadriceps From Aaron et al, 2006 And sensitive to improvement too… • Improvement in EIM data upon returning to normal activity after recovery from ankle fracture Mean Value Closed circles, upon partial or full recovery Open circles, immediately after injury Lower limit of normal From Tarulli et al, 2009 Hind Limb Suspension studies in rats and mice: A model for assessing sarcopenia and disuse EIM phase declines and recovers with hind limb suspension N = 45 Relationship between phase and muscle fiber size What does it mean? • Is correlation sufficient? • How do we an answer the question? – Animal models? – Tissue culture studies? – Single cell studies? Thanks • Physicists and Engineers • • • • Carl Shiffman, PhD Ronald Aaron, PhD Joel Dawson, PhD Jacob White, PhD • Physician researchers • • • • • • • • • • • Andrew Tarulli, MD Basil Darras, MD Pushpa Narayanaswami, MD Jeremy Shefner, MD, PhD Ted Burns, MD (also for wine) Mary Bouxsein, PhD Jonathan Bean, MD Jonathan Glass, MD Eva Feldman, MD, PhD Jim Caress, MD Michael Benatar, MD • Research Staff • • • • • • • • • Mohammad Ahad, PhD Jia Li, PhD Lucy Wang Phil Mongiovi Minhee Sung Mina Jafarpoor Lindsay Garmirian Anne Chin Andrew Spieker • Convergence Medical Devices • • • • Jose Bohorquez, PhD Mike Rinehart, PhD Neil Lupton, PhD Laura Freeman, RN Funding R01 NS055099; R01 AR060850; K24 NS060951