marginal cost.
advertisement

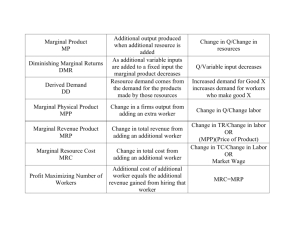
Chapter 11 Output and Costs 1) An example of a variable resource in the short run is A) a building. B) capital equipment. C) an employee. D) land. 2) The short run is a period of time in which A) the quantity used of at least one resource is fixed. B) the quantities used of all resource are fixed. C) output prices are fixed. D) resource prices are fixed. 3) An example of a fixed factor of production is A) capital equipment. B) labor. C) electricity. D) postage for mailing. 4) A cost that has already been made and cannot be recovered is called a A) variable cost. B) fixed cost. C) sunk cost. D) marginal cost. 5) The long run is a time frame in which A) the quantities of some resources are fixed and the quantities of other resources can be varied. B) the quantities of all resources can be varied. C) the quantities of all resources are fixed. D) all costs are sunk costs. 6) Points below a firm's total product curve are A) both attainable and technologically efficient. B) neither attainable nor technologically efficient. C) attainable but not technologically efficient. D) technologically efficient but not attainable. 7) The marginal product of labor is equal to the A) total product divided by the total number of workers hired. B) increase in the total product that results from hiring one more worker. C) slope of the marginal product of labor curve. D) None of the above answers are correct. 8) The total output produced with any quantity of labor is equal to the sum of the A) marginal products of each of the workers hired. B) average products of each of the workers hired. C) total wages the firm pays its workers. D) Both answers A and B are correct. 9) Average product equals the A) increase in output that results from a one-unit increase in the quantity of labor employed with all other inputs remaining the same. B) total amount of output produced. C) total amount of output produced divided by the quantity of labor employed. D) total amount of output produced divided by price of the output. Pizza Hut Total product Labor (pizzas produced (workers) per hour) 0 0 1 5 2 9 3 12 4 14 5 15 10) Using the data in the above table, what is the marginal product of the second worker? A) 4.5 pizzas per hour B) 4 pizzas per hour C) 5 pizzas per hour D) The marginal product is undefined. 11) Using the data in the above table, what is the average product of three employees? A) 2 pizzas per hour B) 3 pizzas per hour C) 4 pizzas per hour D) 12 pizzas per hour 12) In the figure above, the marginal product of the second worker is A) 10 units. B) 5 units. C) 2 units. D) 1 units. 13) At point d in the above figure, the average product of labor equals A) 15. B) 4. C) 3.75. D) approximately 1. 14) In the figure above, A) d is an efficient point. B) f is an efficient point. C) g is an efficient point. D) there are no efficient points. 15) In the above figure, an inefficient point is A) a. B) e. C) g. D) f. 16) Increasing marginal returns to labor might occur at low levels of labor input because of A) increasing average costs. B) differing factor proportions. C) increasing specialization of tasks. D) decreasing use of machinery and increasing use of technology. 17) "Diminishing marginal returns" refer to a situation in which the A) marginal cost of the last worker hired is less than the marginal cost of the previous worker hired. B) average cost of the last worker hired is less than the average cost of the previous worker hired. C) marginal product of the last worker hired is less than the marginal product of the previous worker hired. D) average product of the last worker hired is less than the average product of the previous worker hired. 18) Diminishing marginal returns to labor occur because A) after awhile it is hard to find a good worker. B) the capital resources used by the firm are fixed in the short run. C) workers become more efficient over time. D) larger companies are less efficient. 19) The law of diminishing returns states that as a firm increases A) all the inputs is uses, the marginal product of each of these inputs always decreases. B) a variable input, with a given quantity of fixed inputs, the firm's marginal cost eventually decreases. C) a variable input, with a given quantity of fixed inputs, the marginal product of the variable input eventually decreases. D) a variable input, given the quantity of fixed inputs, the firm's average total cost will eventually decrease. 20) When marginal product of labor is a maximum, average product of labor is ________. A) a maximum B) increasing C) decreasing D) equal to marginal product 21) When the marginal and average products of labor are equal to each other, the A) average product must be at its maximum value. B) marginal product must be at its maximum value. C) total product must be at its maximum value. D) None of the above answers is correct 22) With a technological change that increases productivity, the average product curve ________ and the marginal product curve ________. A) shifts upward; is unchanged B) is unchanged; is unchanged C) is unchanged; shifts upward D) shifts upward; shifts upward 23) Total cost is the sum of fixed costs and A) accounting costs. B) explicit costs. C) implicit costs. D) variable costs. Answer: D 24) Total fixed cost A) increases as output increases. B) does not change as output changes. C) decreases as output increases. D) initially decreases and then increases as output increases. 25) Total variable cost is the sum of all A) costs of the firm's fixed inputs. B) costs associated with the production of goods. C) costs that rise as output increases. D) implicit costs. 26) Ernie's Earmuffs produces 200 earmuffs per year at a total cost of $2,000 and $400 of this cost is fixed. What is Ernie's average total cost? A) $12 B) $10 C) $8 D) $2 27) As output increases, average fixed cost A) always decreases. B) increases, then decreases. C) decreases, then increases. D) remains constant. 28) The average total cost curve A) is U-shaped. B) diminishes initially because average fixed costs diminish. C) increases eventually because of diminishing returns. D) All of the above answers are correct. Output (pies) 0 100 200 300 400 Total variable Total cost cost (dollars) (dollars) 0 300 400 1,000 1,800 2,800 29) The above table gives some of the costs of the Delicious Pie Company. What is the total fixed cost of producing 100 pies? A) $300 B) $400 C) $700 D) More information is needed to calculate the total fixed cost. 30) The above table gives some of the costs of the Delicious Pie Company. The marginal cost of increasing pie output from 200 to 300 pies equals ________ per pie. A) $1.800 B) $1,000 C) $8 D) $6 31) The above table gives some of the costs of the Delicious Pie Company. What is the average variable cost of producing 300 pies? A) $1,800 B) $6 C) $5 D) More information is needed to calculate the average variable cost. 32) The vertical distance between a firm's total cost (TC) and its total variable cost (TVC) curves A) decreases as output decreases. B) is equal to the average variable cost, AVC. C) is equal to the total fixed cost, TFC. D) is equal to the marginal cost, MC. 33) In the above figure, the total fixed cost curve is curve A) A. B) B. C) C. D) none of the curves in the figure 34) In the figure above, curve C is the ________ curve. A) average fixed cost B) average variable cost C) average total cost D) marginal cost 35) In the figure above, curve A is the ________ curve. A) average fixed cost B) average variable cost C) average total cost D) marginal cost 36) In the figure above, curve B is the ________ curve. A) average fixed cost B) average variable cost C) average total cost D) marginal cost 37) In the figure above, when 20 units are produced the marginal cost is A) less than $8. B) $8. C) more than $8 and less than $16. D) None of the above answers is correct. 38) In the figure above, when 40 units are produced the average fixed cost is A) $4 B) $8 C) $12 D) $20 39) Average variable cost is at a minimum at the same amount of output at which A) average product is at a maximum. B) marginal product is at a maximum. C) average product is at a minimum. D) marginal product is at a minimum. 40) A technological change that increases productivity ________ marginal product and ________ marginal cost. A) increases; increases B) increases; decreases C) decreases; increases D) decreases; decreases 41) Which curve intersects the AVC curve at its minimum point? A) the MC curve B) the ATC curve C) the AFC curve D) the MP curve Essay Questions 1) What is the difference between the short run and the long run? Answer: The short run is a time period so short that the firm cannot change the quantity of at least one factor, say plant size for a manufacturer or land for a farmer. The only way to increase output, therefore, is by combining more units of the variable factors with the fixed factor. The long run is a time period sufficiently long that a firm can change the quantity of all factors. Nothing is fixed so output can be produced with whatever combination of factors the firm chooses. 2) What does the average product of labor equal? Answer: The average product of labor equals the total product (the total output) divided by the quantity of labor. 3) How do we calculate average fixed cost and why does average fixed cost fall as output increases? Answer: Average fixed cost is calculated by dividing total fixed cost by the quantity of output. Because total fixed cost stays the same for all levels of output, as the quantity produced increases, the average fixed cost decreases. 4) "Marginal cost is the increase in total cost that results from a one-unit increase in a variable input." True or false? Explain. Answer: False. Marginal cost is the increase in total cost that results from a one-unit increase in output, not a one unit increase in an input.