File
advertisement

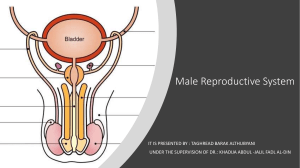
Anatomy Practical [PHL 212] Reproductive System Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Reproductive System Producing offspring The male and female gonads (testes and ovaries) produce Sex cells (ova and sperm) and The hormones necessary for the proper development, maintenance, and functioning of the organs of reproduction and other organs and tissues. Testis The testes produce testosterone, which is responsible for sperm production and the development of male secondary sex characteristics Ovary The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen is required for the development of secondary sex characteristics and for the development of eggs. Progesterone prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg. Testes Duct system Epididymis Vas Deferens Urethra Accessory organs Seminal Vesicle Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland (Cowper’s glands) External genitalia Penis Scrotum Glans Penis Prepuce Testes Paired oval glands measuring 2 X 1in. Produce Sperm Surrounded by dense white capsule Septa form 200 - 300 compartments called lobules Each is filled with 2 or 3 seminiferous tubules where sperm are formed Mature male produces 300-500 million/ejaculation Seminiferous tubule Seminiferous tubules contain Sperm forming cells Interstitial (leydig) cells in between tubules secrete testosterone Scrotum Sac/Location of testes Epididymis Over 20 feet long, Located in scrotum Receives sperm from the seminiferous tubules Allows sperm to mature & stored until released Vas deferens is the dilated continuation of the epididymis joins with a seminal vesicle to form an ejaculatory duct Duct transports sperm from epididymis to urethra Penis: Delivers semen to the vagina Urethra: Tube that delivers urine & semen out of body Glans penis: Swollen head of the penis Prepuce (foreskin): In a circumcision procedure, the prepuce is removed. Seminal Vesicles ◦ Paired glands, secrete 60% of clear, alkaline seminal fluid, with fructose sugar, ATP and prostaglandins for normal sperm nutrition & function Prostate ◦ Single, lies under the urinary bladder ◦ Secretes 30% of milky seminal fluid with an antibiotic to kill bacteria ◦ Its secretions also help to neutralize vaginal acidity and make sperm motile. Cowper’s Glands ◦ Two tiny glands below the prostate, secrete clear, alkaline mucus to lubricate urethra Ovary Two ovaries, Location of egg production Located in the pelvic part of the abdomen on either side of the uterus Fallopian Tubes (Uterine Tubes or oviducts) Paired tubes that connects ovaries to uterus & transports eggs Transport is by peristalsis & beating cilia Uterus Hollow, thick-walled muscular chamber located in the pelvis anterior to the rectum and posterosuperior to the bladder Contains environment to allow for the development of a fertilized egg & provides nutrition to embryo Expands 500 x’s its normal size during a full term pregnancy Cervix Neck of the uterus Vagina Thin-walled muscular tube lying between the bladder and the rectum, extending from the cervix to the exterior of the body, Provides a passageway from uterus to outside for birth, menstrual flow, and is the organ of copulation External genitalia (Vulva) Includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, and clitoris.