mode of action heroin
advertisement

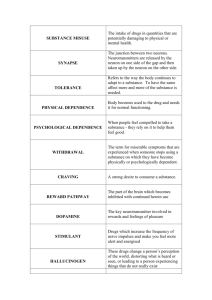
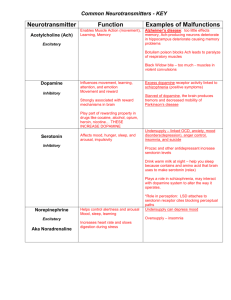
ADDICTION Heroin According to the Specification you need to be able to : Describe, with reference to 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. heroin and nicotine Substance misuse Mode of action Effects Tolerance Physical / psychological dependencies withdrawal What is Addiction? Doctors call a drug addictive if it makes you dependent on the drug. Unpleasant withdrawal symptoms appear unless you take the drug. Addictive drugs also make you crave them - you have an overwhelming urge to continue taking the drug, even after withdrawal symptoms have disappeared. Tolerance More of the drug is needed to obtain the feelings that were produced at first. A stage may be reached where no amount of the drug will achieve the resulting high. Simply take the drug to delay withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal Unpleasant symptoms occur when the drug is not taken, such as sickness and depression. Can get rid of the withdrawal symptoms by taking the drug again. This leads to a cycle of drug taking where users may try to stop but then have to take it again to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Some startling statistics… • Heroin overdoses have caused more deaths than traffic accidents in the past several years • The use of Heroin has quadrupled in the last 15 years • 1.2 million people in the UK use Heroin • 300,000 children live with parents who have serious heroin addiction What is the difference between biological addiction and psychological addiction? Biological Addiction • The body becomes dependant on the drug. • Without it, severe withdrawal symptoms occur such as pain or sickness. • Body becomes used to the drug and causes a physical reaction if they don’t receive it. • Body develops a tolerance to the drug – require more of it to have an effect. Psychological Addiction • Conscious desire to obtain drug out of a perceived need for its affect. • User might say it makes them “feel good” or “calm down”. • May use drug to escape from real-life. • Think it is the only way they can cope. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v6uBkJSbQO0 Addiction • What is the difference between drug abuse and drug addiction? • When does drug abuse become addiction? Addiction • Drug abuse is initially a voluntary behaviour • There is a Continuum of drug abuse and drug addiction • You can reach addiction at different points depending on the individual No use Drug Abuse Drug Addiction Abuse is voluntary; addiction is the continued compulsive drug use despite adverse health or social consequences. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-hLVl7Asp3k Heroin • Tolerance - The reward circuit becomes highly activated - Over-production of dopamine - The body has to adapt to the heroin – try and achieve homeostasis (balance) - Reduces the amount of dopamine produced - More enzymes are produced to break it down - Stifles the brain's reward circuit through inhibitionthe same dose of drug is less rewarding Heroin • Tolerance - Heroin rapidly develops tolerance - Users very quickly need increasing amounts of it to get the “high” - Eventually just users take heroin to delay unpleasant withdrawal symptoms Heroin • Physical Dependence - Linked to tolerance – need increasing amounts to reach high so become physically dependent. - Body is used to functioning with heroin – so needs it for normal functioning. - E.g. Brain of heroin users produce less endorphins so addicts will rely on heroin for pleasure and reduction of pain. Heroin Psychological Dependence - Heroin becomes a great importance in their life. - Important for person’s mental state. - Often taken by people with living difficulties, no self-esteem and employment problems - Heroin gives users a feeling of pleasure and dulls the senses – don’t despair as much. Heroin Withdrawal - Usually start within 12 hours of last fix. - Severity of withdrawal is dependent on the level of addiction - Starts with agitation and restlessness Heroin Withdrawal - After a day, become more agitated and restless - Then “skin crawl” – itchy blood - Cramps and vomiting - Diarrhoea and sweating - Twitching and shaking - Muscle ache and pain Heroin • Withdrawal - Symptoms usually go after about a week. - Sudden withdrawal after sustained use can cause death. Morphine Withdrawal : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7hw4HvuHnQ8&NR=1 Diary of Heroin Addiction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7thZbHTvZIQ To learn more about Heroin addiction watch this film You can think of a brain pathway as a power line that connects two brain regions. Brain pathways are made up of interconnected neurons along which signals are transmitted from one brain region to another. Dopamine is the neurotransmitter used by the reward pathway. But there are other important pathways in the brain that utilize dopamine. Generally, drugs that affect dopamine levels in the brain affect all of these dopamine pathways. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tl8-C9ZuLTA Dopamine and another neurotransmitter called Serotonin are released by a small number of neurons in the brain. Nigrostriatal pathway Substantia Nigra to Striatum . Motor control . Death of neurons in this pathway can result in Parkinson's Disease Mesolimbic and Mesocortical pathways Ventral Tegmental Area to Nucleus Accumbens, Amygdala & Hippocampus, and Prefrontal Cortex . Memory . Motivation and emotional response . Reward and desire . Addiction . Can cause hallucinations and schizophrenia if not functioning properly There are 3 main pathways that use Dopamine Tuberoinfundibular pathway Hypothalamus to Pituitary gland . Hormonal regulation . Maternal behavior (nurturing) . Pregnancy . Sensory processes http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/rewardbehavior/ Mode of Action: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/c ontent/addiction/crossingdivide/ Glutamate and GABA A system in Balance • Glutamate and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) are the brain's major "workhorse" neurotransmitters. • Over half of all brain synapses release glutamate, and 30-40% of all brain synapses release GABA. • Since GABA is inhibitory and glutamate is excitatory, both neurotransmitters work together to control many processes, including the brain's overall level of excitation. • Many of the drugs of abuse affect either glutamate or GABA or both to exert tranquilizing or stimulating effects on the brain. As an antagonist of the GABA receptor, Heroin blocks GABA. This in turn elevates the quantity of Dopamine produced in this pathway. This causes an increase in the concentration of dopamine at the synapse throughout the reward pathway. Heroin blocks the inhibitor Gaba (traffic cop) –controls the dopamine activity in the synapse Heroin stops it from working by locking it up Mode of Action: Can you describe it? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. In groups….. • Use this system to explain how tolerance may occur… • Why may the first ‘high’ never be achieved? • Describe how this leads to physiological dependence? • Describe how this leads to psychological dependence? • Why is withdrawal so bad? Pete has been admitted to rehab clinics on a regular basis over the past 3 years. He has had drug dependency and addiction issues for around 5-6 years which has seriously jeopardized his health. Pete abuses heroin on a regular basis, mainly injecting the substance. However, he has failed to fully comply with any of his doctor’s orders. This includes complete detoxification (controlled withdrawal from drugs) which also involves counseling sessions. In your groups List all of the Bio-psycho-social factors that may be preventing Pete from choosing a healthy lifestyle. HW Read and make notes on Heroin in textbook Look at the Talk to Frank website http://www.talktofrank.com/ The Home Office’s advertising campaign to encourage young people to 'talk to FRANK' for accurate and impartial information about drugs Do anti drugs adverts work? http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/magazine-21242664 Task Describe and evaluate one campaign that has encouraged people to use recreational drugs.